Preparing for the CFA Exam requires an understanding of “Option Strategies,” a crucial concept in derivatives and risk management. Option strategies involve using various combinations of calls and puts to achieve investment objectives, such as hedging, income generation, or speculative gains. Understanding these strategies helps candidates assess risk-reward profiles, evaluate potential payoffs, and adapt to changing market conditions effectively.
Learning Objectives
In studying “Option Strategies” for the CFA, you should aim to understand the fundamental concepts and applications of various option strategies in investment management, including how to utilize options to hedge risks, enhance portfolio returns, and speculate on market movements effectively. Analyzing different strategies such as covered calls, protective puts, and spreads is essential for assessing their impacts on overall portfolio performance, while understanding the mechanics of options pricing, including factors like volatility and time decay, is crucial for mastering this topic. Grasping these concepts enables you to implement options in diverse market conditions and asset classes, ultimately improving your ability to manage risks and capitalize on market opportunities.
What are Option Strategies?

Option strategies refer to various techniques and methods employed by traders and investors to utilize options contracts in the financial markets. These strategies are designed to achieve specific investment goals, such as maximizing profits, minimizing risks, or enhancing portfolio returns. Common option strategies include buying calls or puts, selling covered calls, and employing spreads or straddles. Each strategy has its own risk-reward profile and can be tailored to market conditions, investment objectives, and the trader’s risk tolerance. By carefully selecting and combining options, investors can create flexible approaches to manage their investments effectively.
Types of Option Strategies
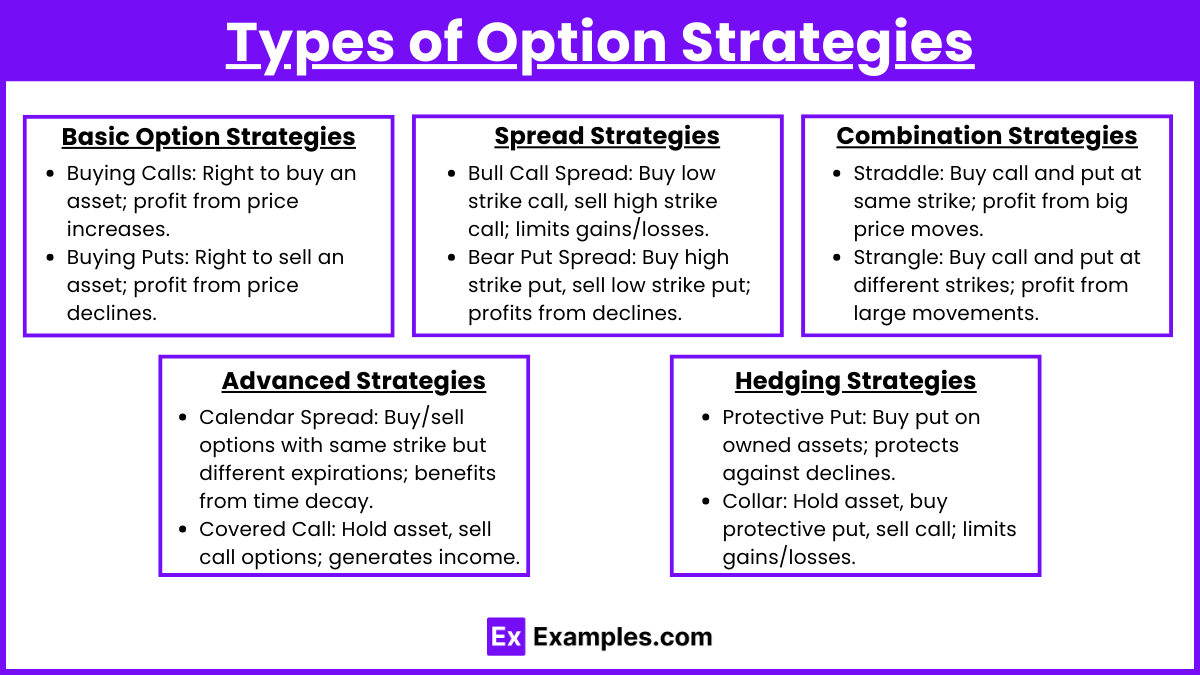
1. Basic Option Strategies
- Buying Calls: Investors purchase call options to gain the right to buy an asset at a certain price, benefiting from potential price increases.
- Buying Puts: Investors buy put options to have the right to sell an asset at a predetermined price, profiting from potential declines in the asset’s price.
2. Spread Strategies
- Bull Call Spread: This involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling another call option at a higher strike price. It limits both potential gains and losses.
- Bear Put Spread: This strategy entails buying a put option at a higher strike price while selling another put option at a lower strike price, aiming to profit from a decrease in the underlying asset’s price.
- Iron Condor: This strategy combines a bull put spread and a bear call spread, allowing traders to profit from low volatility in the underlying asset.
3. Combination Strategies
- Straddle: Involves buying a call and a put option at the same strike price and expiration date, allowing the investor to profit from significant price movements in either direction.
- Strangle: Similar to a straddle, but the call and put options have different strike prices. It also aims to benefit from large price movements.
4. Advanced Strategies
- Calendar Spread: Involves buying and selling options with the same strike price but different expiration dates, benefiting from time decay and volatility changes.
- Covered Call: This strategy entails holding a long position in an asset while selling call options on the same asset to generate income.
5. Hedging Strategies
- Protective Put: Investors buy put options on assets they own to protect against potential declines in the asset’s price, acting as an insurance policy.
- Collar: Involves holding an asset while buying a protective put and selling a call option, effectively limiting both potential gains and losses.
Applications of Option Strategies
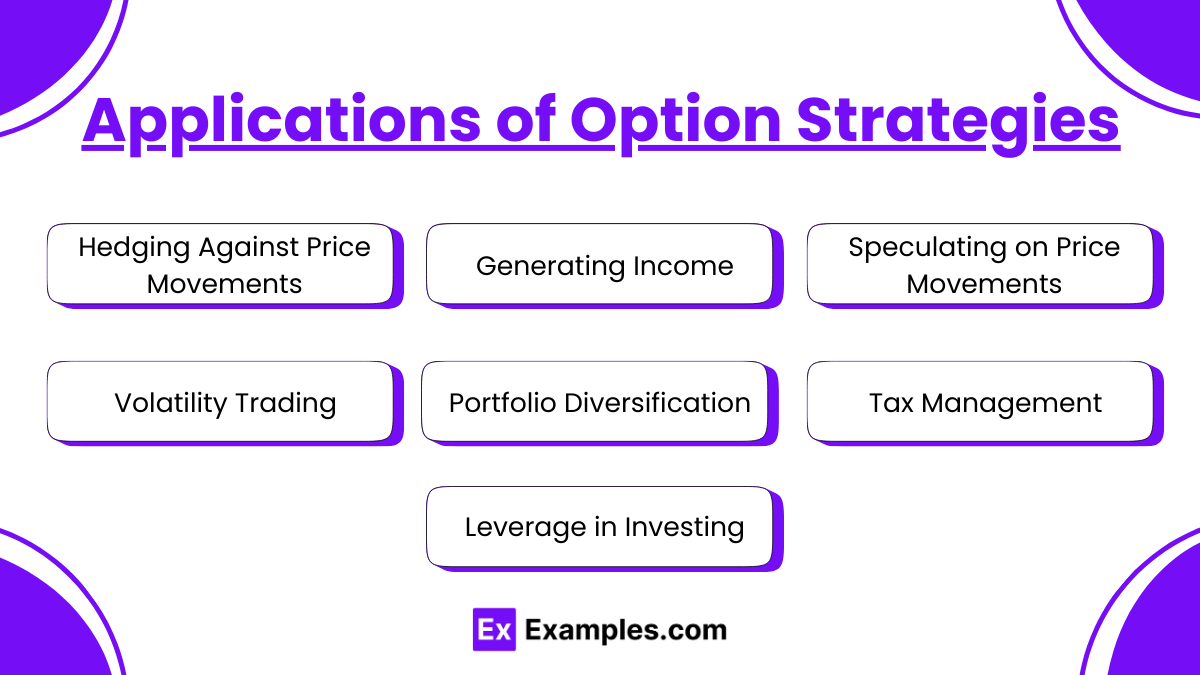
Option strategies are a vital part of financial trading, providing various applications to manage risk, enhance returns, and achieve specific investment goals. Here are some key applications:
- Hedging Against Price Movements
Options can be used to hedge against potential losses in an underlying asset. For instance, buying put options can protect against a decline in the stock price, while selling call options can generate income when holding a stock long term. - Generating Income
Investors can use covered call writing, where they sell call options against stocks they own. This strategy generates income through premiums collected while still holding the underlying asset. - Speculating on Price Movements
Traders can use options to speculate on the future price movements of an asset with limited risk. For example, buying call options allows an investor to leverage potential upside without committing to the full cost of the underlying asset. - Volatility Trading
Options can be used to capitalize on expected changes in volatility. Strategies like straddles and strangles involve buying both call and put options to benefit from large price movements, regardless of direction. - Portfolio Diversification
Options can enhance portfolio diversification by allowing investors to take positions in multiple assets without directly owning them. This can reduce overall portfolio risk and improve returns. - Tax Management
Options can be strategically used to manage tax liabilities. For example, investors might sell options to realize short-term losses or defer gains, optimizing their tax situation based on their income and capital gains. - Leverage in Investing
Options provide leverage, allowing investors to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify returns, though it also increases risk if the market moves against the position.
Examples
Example 1. Hedging Against Market Downturns
Investors often use put options as a hedge against potential declines in their stock portfolios. By purchasing put options, investors acquire the right to sell their underlying assets at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. This strategy can protect against significant losses during market downturns, as the value of the put option will increase when the stock price drops, effectively offsetting losses in the portfolio.
Example 2. Generating Income with Covered Calls
A popular strategy among investors seeking to generate additional income from their stock holdings is the covered call. In this strategy, investors sell call options on stocks they already own. By doing so, they collect the premium from the sale of the options while retaining ownership of the underlying shares. If the stock price does not exceed the strike price, the investor keeps the premium and can repeat the process, creating a steady income stream.
Example 3. Speculating on Price Movements
Options can also be used for speculative purposes, allowing traders to profit from expected price movements in a stock or asset. For instance, a trader might buy call options if they believe a stock will rise significantly within a certain timeframe. If the stock price increases above the strike price before expiration, the trader can exercise the option for a profit or sell the option for a premium.
Example 4. Utilizing Straddles for Volatility
Investors can use straddles to profit from significant price movements in either direction. A straddle involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is particularly effective in volatile markets, where the investor anticipates large price swings but is uncertain about the direction. If the stock moves substantially, either the call or put option will become profitable, potentially outweighing the costs of both options.
Example 5. Implementing Iron Condors for Limited Risk
The iron condor strategy combines two spreads to take advantage of low volatility in the market. By selling an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put while simultaneously buying further out-of-the-money options, investors can create a range of prices where they expect the underlying asset to stay. This strategy allows traders to collect premiums from selling options while limiting potential losses, making it an attractive choice for those looking to profit from stable price movements.
Practice Questions
Question 1
What is the primary purpose of a “protective put” strategy?
A) To generate income through premiums received from selling options.
B) To hedge against potential losses in a stock position.
C) To speculate on the future price movement of the underlying asset.
D) To create a synthetic long position in the underlying asset.
Correct Answer: B) To hedge against potential losses in a stock position.
Explanation:
A protective put involves purchasing a put option for a stock that an investor already owns. This strategy serves as a form of insurance against a decline in the stock’s price. If the stock price falls, the value of the put option increases, offsetting the losses on the stock position. Thus, the primary purpose of a protective put is to hedge against potential losses, making it a risk management tool rather than a speculative one.
Question 2
Which of the following strategies is best suited for a trader who expects a moderate increase in the price of the underlying asset?
A) Long call
B) Short call
C) Bull call spread
D) Long put
Correct Answer: C) Bull call spread.
Explanation:
A bull call spread involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and simultaneously selling another call option at a higher strike price. This strategy allows the trader to benefit from a moderate increase in the underlying asset’s price while limiting potential losses. It is typically less expensive than simply buying a call option outright, as the premium received from selling the higher strike call partially offsets the cost of purchasing the lower strike call. The bull call spread is ideal when a trader anticipates a modest rise in the underlying asset’s price, as it maximizes profit potential within that range.
Question 3
What is a “straddle” option strategy designed to achieve?
A) Profit from small price movements in the underlying asset.
B) Benefit from significant price movement in either direction.
C) Reduce the cost of buying options by selling calls.
D) Protect against adverse price movements while still participating in potential gains.
Correct Answer: B) Benefit from significant price movement in either direction.
Explanation:
A straddle involves buying both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is used when a trader expects a significant price movement in the underlying asset but is unsure of the direction (up or down). The straddle profits if the price moves significantly in either direction, as the gains from one of the options can offset the losses from the other. The key to a successful straddle is that the price movement must be substantial enough to cover the total premium paid for both options. If the underlying asset’s price remains stable, the strategy could result in a loss due to the premium spent on the options expiring worthless.


