In the realm of AP English Language and Composition, mastering the application of cause-effect and narrative methods is crucial for developing analytical and persuasive essays. These techniques enable writers to elucidate the relationships between events and craft compelling stories that engage readers. The cause-effect method allows students to explore the reasons behind occurrences and their subsequent outcomes, enhancing the logical flow of their arguments. Meanwhile, the narrative method leverages storytelling to illustrate points vividly and memorably. Understanding and effectively utilizing these methods not only enriches writing but also bolsters the ability to convey complex ideas with clarity and impact.
Learning Objectives
By studying the application of cause-effect and narrative methods, students will achieve several critical learning objectives. They will enhance their critical thinking skills by analyzing the complex relationships between events and their outcomes. Through the synthesis of ideas, students will learn to construct a rhetorical essay that seamlessly integrates cause-effect analysis with narrative techniques. Crafting a strong thesis statement will guide their writing, ensuring clarity and focus. Additionally, students will develop rhetorical writing abilities, using storytelling to engage readers and effectively convey their arguments. Mastery of these methods will enable students to produce essays that are both logically sound and compellingly written.
Cause-Effect Method
Definition
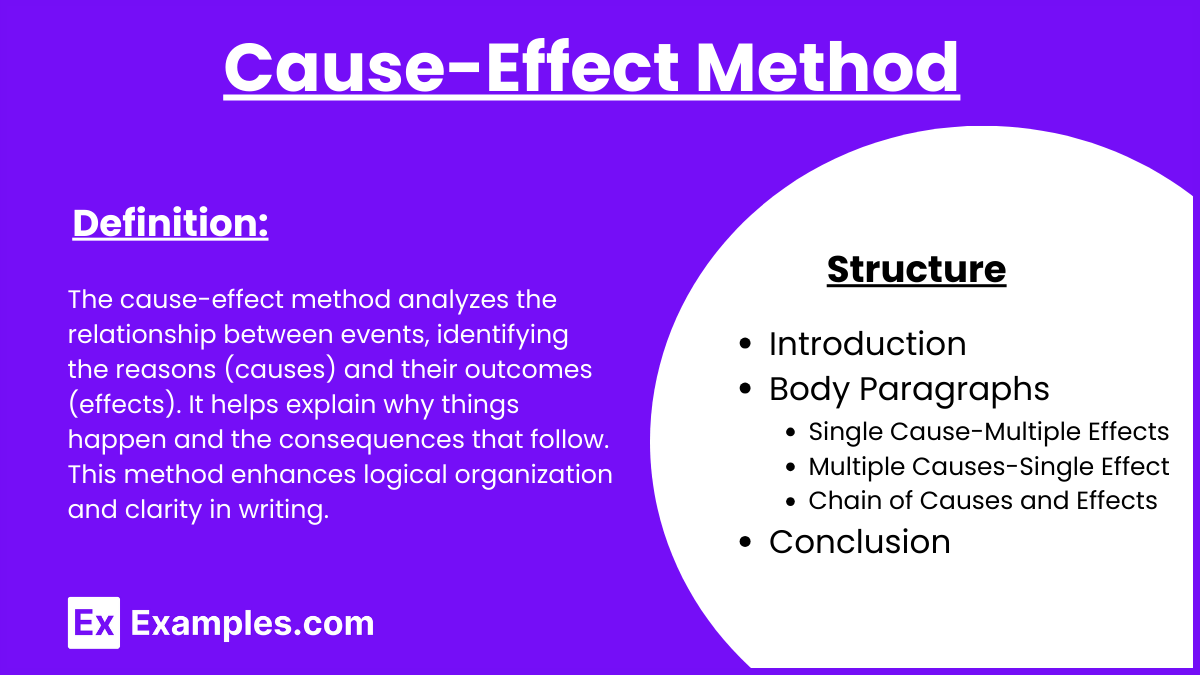
The cause-effect method explores the reasons (causes) why things happen and the outcomes (effects) that result. It is used to explain relationships between events or phenomena.
Key Components
- Cause: The event or situation that triggers something else to happen.
- Effect: The outcome or result of the cause.
Structure
- Introduction: Present the topic and state whether you will discuss causes, effects, or both.
- Body Paragraphs:
- Single Cause-Multiple Effects: Start with a cause and discuss several effects.
- Multiple Causes-Single Effect: Start with an effect and discuss several causes.
- Chain of Causes and Effects: Describe a series of events where one cause leads to an effect, which then becomes the cause for another effect.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and reinforce the cause-effect relationship.
Writing Tips
- Clearly distinguish between causes and effects.
- Use transitional words like “because,” “since,” “therefore,” “consequently,” and “as a result.”
- Provide concrete examples and evidence to support the cause-effect relationship.
- Avoid logical fallacies like assuming causation from mere correlation.
Narrative Methods

Definition
The narrative method involves telling a story to illustrate a point or support an argument. It uses descriptive and sensory details to engage the reader.
Key Components
- Plot: The sequence of events in the story.
- Characters: The individuals involved in the story.
- Setting: The time and place where the story occurs.
- Theme: The underlying message or main idea of the story.
Structure
- Introduction: Introduce the narrative and its significance to the overall argument or topic.
- Body Paragraphs:
- Chronological Order: Present events in the order they occurred.
- Flashbacks/Flash-forwards: Jump back and forth in time to add depth to the story.
- Conclusion: Reflect on the narrative, connecting it back to the main argument or theme.
Writing Tips
- Use vivid and sensory details to create a strong image in the reader’s mind.
- Develop a clear and engaging plot with a beginning, middle, and end.
- Establish relatable and dynamic characters.
- Keep the narrative focused and relevant to the main argument or theme.
- Use dialogue and action to show rather than tell.
Combining Both Methods
In many essays, especially those requiring analytical and persuasive skills, combining cause-effect and narrative methods can be highly effective. For instance, you might start with a narrative anecdote to illustrate a point, then delve into an analysis of the causes and effects of the situation described.
Example
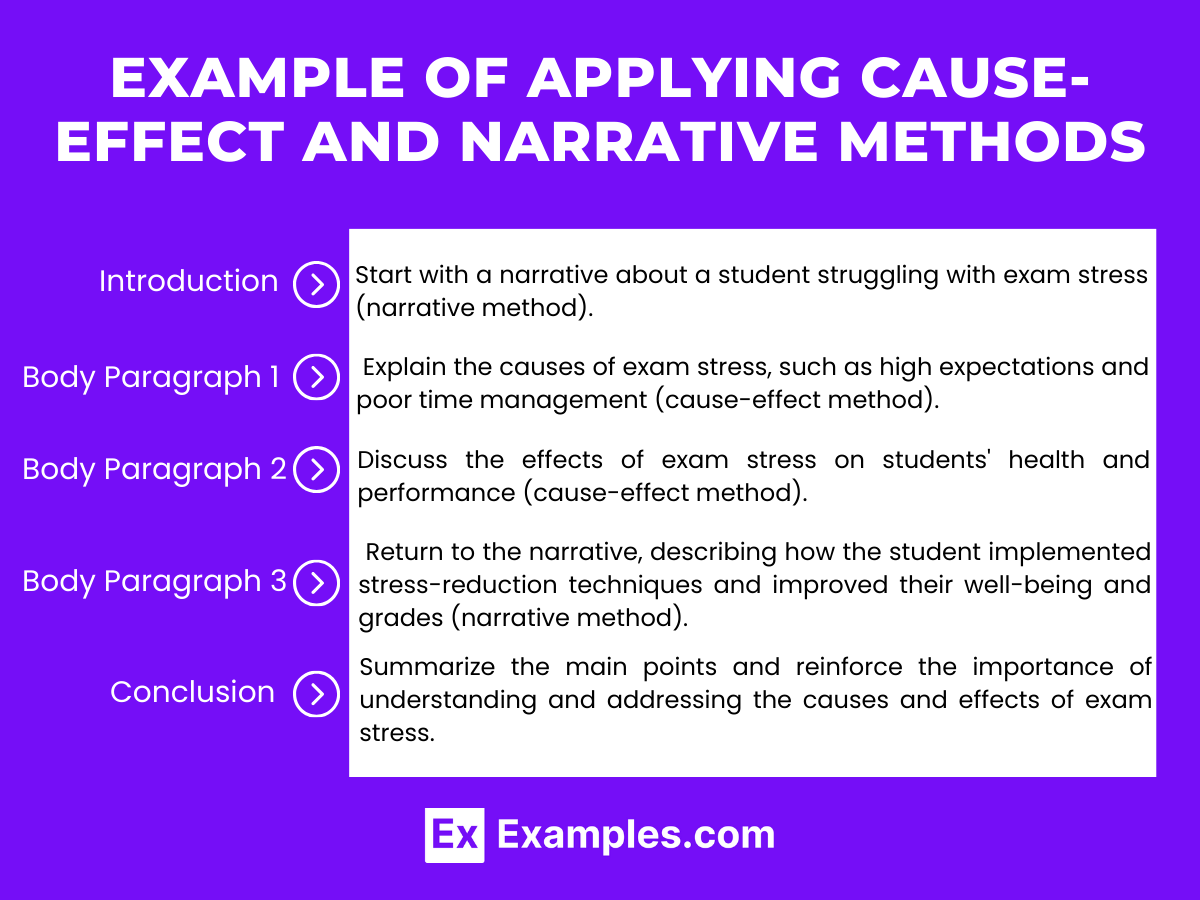
Introduction: Start with a narrative about a student struggling with exam stress (narrative method).
Body Paragraph 1: Explain the causes of exam stress, such as high expectations and poor time management (cause-effect method).
Body Paragraph 2: Discuss the effects of exam stress on students’ health and performance (cause-effect method).
Body Paragraph 3: Return to the narrative, describing how the student implemented stress-reduction techniques and improved their well-being and grades (narrative method).
Conclusion: Summarize the main points and reinforce the importance of understanding and addressing the causes and effects of exam stress.


