In the AP English Language and Composition exam, utilizing comparison-contrast methods is a critical skill for analyzing texts and constructing compelling arguments. This method involves examining the similarities and differences between two or more subjects to highlight their unique qualities and interrelationships. By mastering comparison-contrast techniques, students can enhance their critical thinking abilities, create well-organized essays, and present balanced perspectives. This approach not only enriches their analytical writing but also strengthens their ability to convey complex ideas effectively and persuasively.
Free AP English Language and Composition Practice Test
Learning Objectives
By studying the use of comparison-contrast methods, students will achieve several key learning objectives. They will learn to identify and analyze the similarities and differences between two or more subjects, enhancing their critical thinking and analytical skills. Students will understand how to structure their essays using point-by-point and block methods, ensuring clear and logical organization. They will develop the ability to craft strong thesis statements that incorporate comparative analysis, and use appropriate transitional words and phrases to guide readers through their arguments. Additionally, students will learn to balance their discussions, providing equal attention to each subject, and support their points with relevant evidence and examples. Mastery of these techniques will enable students to produce well-argued, coherent and persuasive essays in the AP English Language and Composition exam.
Understanding Comparison-Contrast Methods
Definition
Comparison-contrast methods involve analyzing the similarities (comparison) and differences (contrast) between two or more subjects, ideas, or texts.
Purpose
Highlight Differences: Identify distinctive characteristics of each subject.
Show Similarities: Reveal common features or themes.
Analyze Relationships: Understand how subjects relate to or differ from each other.
Structure of Comparison-Contrast Essays
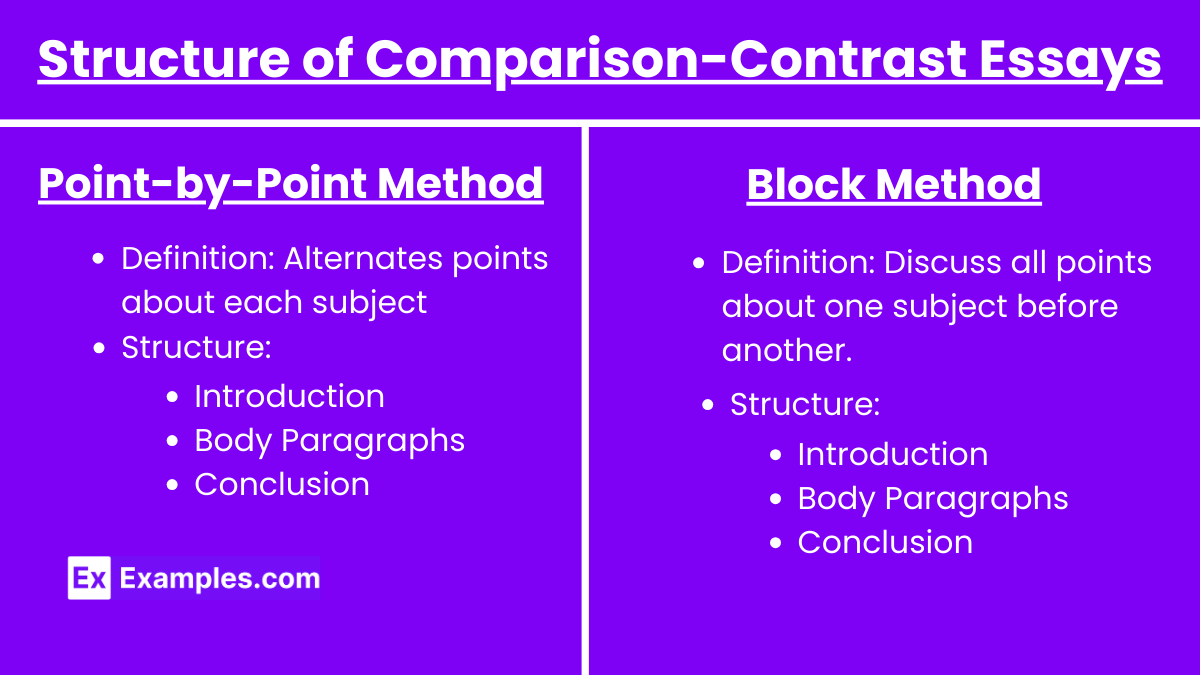
Point-by-Point Method
Definition: Alternates points about each subject.
Structure:
Introduction: Introduce the subjects and state the thesis.
Body Paragraphs: Discuss each point for both subjects alternately.
Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the thesis.
Block Method
Definition: Discusses all points about one subject, then all points about the other.
Structure:
Introduction: Introduce the subjects and state the thesis.
Body Paragraphs:
Subject A: Discuss all points.
Subject B: Discuss all points.
Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the thesis.
Crafting a Comparison-Contrast Essay
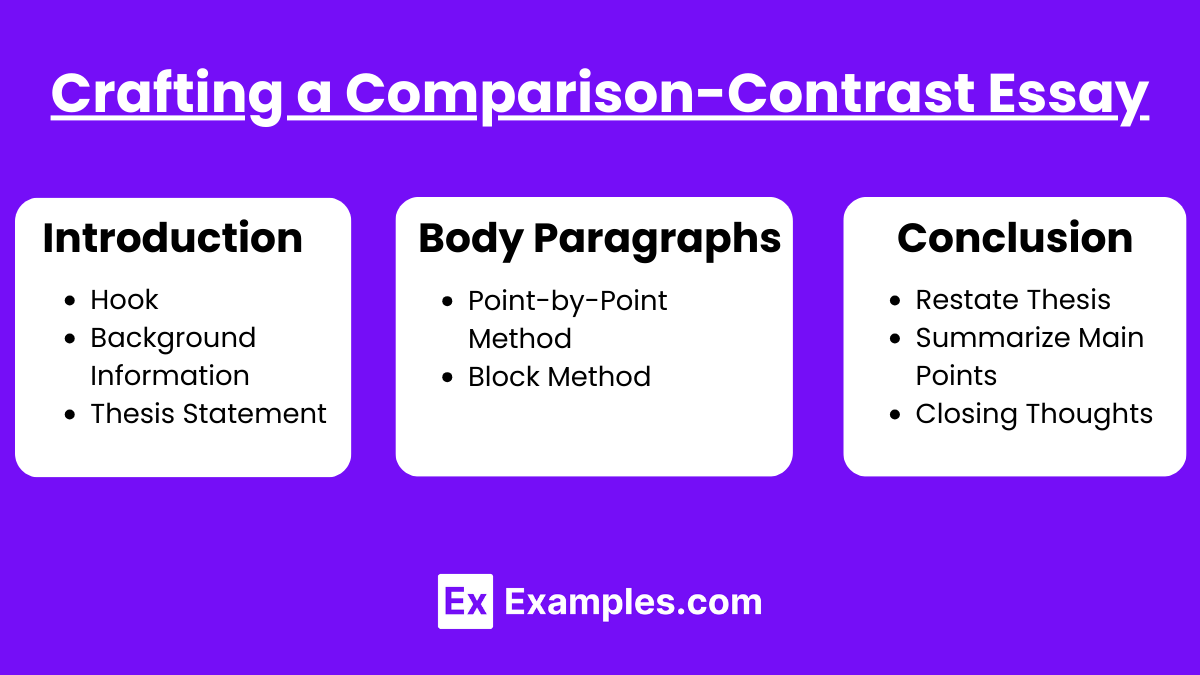
Introduction
Hook: Engage the reader with an interesting fact or question.
Background Information: Provide context for the subjects being compared.
Thesis Statement: Clearly state the purpose of the comparison and the main points to be discussed.
Body Paragraphs
Point-by-Point Method:
Topic Sentence: Introduce the point of comparison.
Comparison: Discuss the similarity.
Contrast: Discuss the difference.
Example: Provide specific examples for each subject.
Block Method:
Subject A: Discuss all points with examples.
Subject B: Discuss all points with examples.
Conclusion
Restate Thesis: Reiterate the main argument or purpose.
Summarize Main Points: Review the key similarities and differences.
Closing Thoughts: Provide a final insight or call to action.
Techniques for Effective Comparison-Contrast Writing

Transitional Words and Phrases
For Comparisons: similarly, likewise, in the same way, just as, both, also
For Contrasts: however, on the other hand, in contrast, whereas, but, yet
Developing Strong Arguments
Balance: Ensure equal discussion for both subjects.
Clarity: Make sure comparisons and contrasts are clear and easy to follow.
Support: Use evidence, examples, and quotes to back up points.
Examples
Example 1: Comparing Two Novels
Thesis: "Although both 'Pride and Prejudice' and 'Jane Eyre' explore themes of social class and gender, they differ significantly in their portrayal of marriage and independence."
Point-by-Point Method:
Marriage: Compare and contrast how each novel addresses marriage.
Independence: Compare and contrast the protagonists' journeys toward independence.
Block Method:
'Pride and Prejudice': Discuss themes of social class, gender, marriage, and independence.
'Jane Eyre': Discuss themes of social class, gender, marriage, and independence.
Example 2: Comparing Historical Events
Thesis: "The French Revolution and the American Revolution were driven by similar ideals of liberty and equality, but differed in their outcomes and methods."
Point-by-Point Method:
Ideals: Compare the driving ideals.
Methods: Contrast the methods used.
Outcomes: Contrast the outcomes of each revolution.
Block Method:
French Revolution: Discuss ideals, methods, and outcomes.
American Revolution: Discuss ideals, methods, and outcomes.