Ecosystem services are the myriad benefits that natural ecosystems provide to humans, playing a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. In the field of ecology, these services encompass everything from the regulation of climate and purification of water to the pollination of crops by diverse flora. The biosphere, which includes all living organisms and their interactions, relies on these services to maintain ecological balance and support human well-being. Understanding and preserving ecosystem services is vital for maintaining the health and functionality of our planet's ecosystems and the broader biosphere.
Free AP Environmental Science Practice Test
Learning Objectives
Learning objectives for ecosystem services include understanding how natural ecosystems support human life and well-being by providing essential benefits. Students should recognize how various organisms, from plants to mammals, contribute to these services, including provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural functions. They should grasp the impact of climate change on these services and the importance of conservation efforts to protect and sustain them. By studying these interactions, students will appreciate the intricate balance within ecosystems and the necessity of preserving ecosystem services for the survival of all life forms, including humans.
Definition
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans receive from functioning ecosystems. These services contribute to human well-being, economic value, and environmental health.
Types of Ecosystem Services
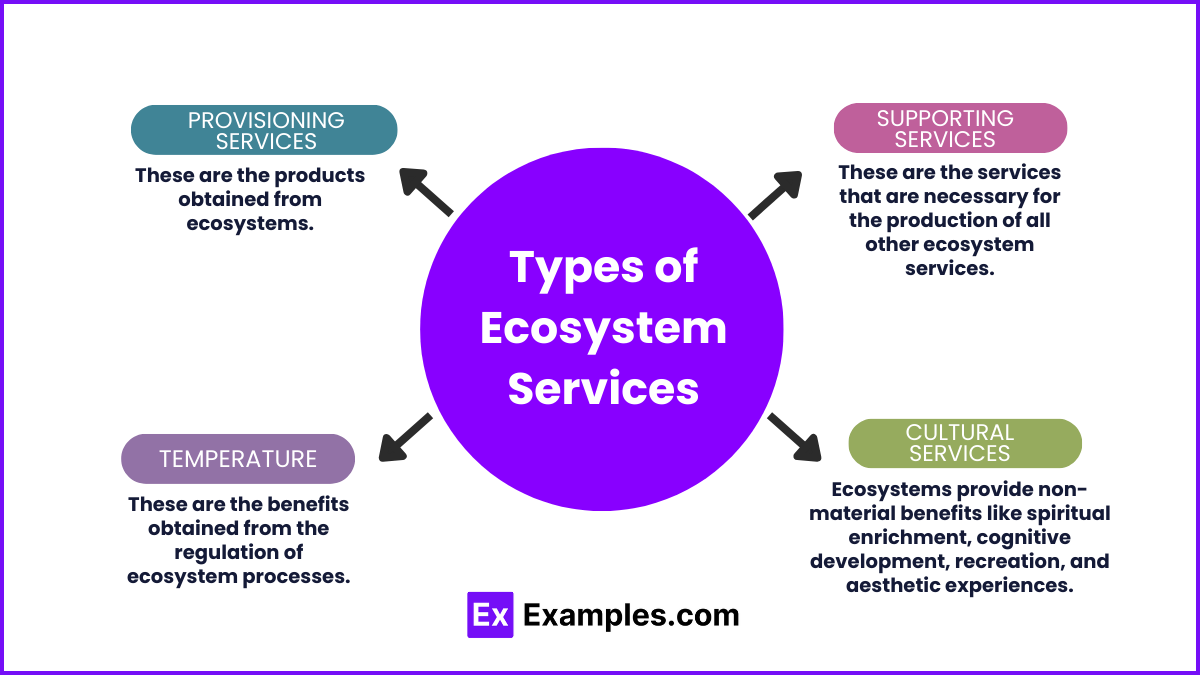
Provisioning Services:
Definition: These are the products obtained from ecosystems.
Examples:
Food: Crops, fruits, fish, and livestock.
Water: Freshwater for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
Raw Materials: Wood, fiber, fuel, and medicinal resources.
Genetic Resources: Genes used for crop and livestock breeding, biotechnology.
Regulating Services:
Definition: These are the benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes.
Examples:
Climate Regulation: Forests and oceans sequester carbon, influencing global climate.
Flood Regulation: Wetlands absorb excess rainwater, reducing flood risks.
Disease Regulation: Natural predators control pest populations; ecosystems regulate pathogens.
Water Purification: Wetlands and riparian zones filter pollutants from water.
Supporting Services:
Definition: These are the services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services.
Examples:
Soil Formation: Decomposition and nutrient cycling enrich soil fertility.
Nutrient Cycling: Movement of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus through ecosystems.
Primary Production: Photosynthesis by plants and algae, producing biomass.
Habitat Provision: Ecosystems provide habitats for various species, maintaining biodiversity.
Cultural Services:
Definition: These are the non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences.
Examples:
Recreation and Tourism: National parks, hiking, bird watching, and ecotourism.
Aesthetic Value: Natural landscapes, scenic views.
Cultural Heritage: Sacred sites, traditional knowledge, and cultural practices.
Education and Inspiration: Ecosystems as sources of learning and creativity.
Importance of Ecosystem Services
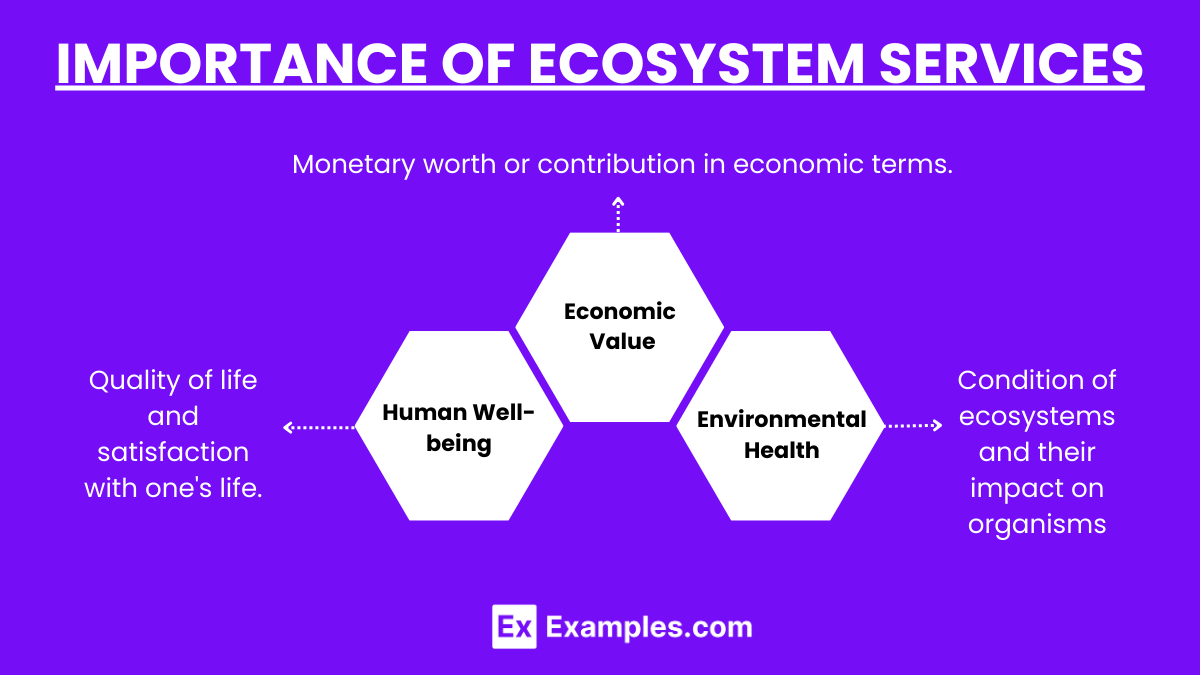
Human Well-being:
Ecosystem services are essential for survival, providing food, clean water, and air.
They support health by regulating disease and providing medicinal resources.
Economic Value:
Ecosystem services contribute to economies through agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism.
Natural resources and services often underpin livelihoods and industries.
Environmental Health:
Healthy ecosystems maintain biodiversity, soil fertility, and water quality.
They contribute to climate stability and resilience against natural disasters.
Threats to Ecosystem Services

Habitat Destruction:
Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion reduce the capacity of ecosystems to provide services.
Example: Loss of wetlands reduces flood control and water purification services.
Climate Change:
Alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting ecosystem functions.
Example: Coral reefs suffering from bleaching events, reducing biodiversity and fishery resources.
Pollution:
Air, water, and soil pollution degrade ecosystems and their services.
Example: Agricultural runoff causing eutrophication, harming aquatic life and water quality.
Overexploitation:
Unsustainable harvesting of resources leads to depletion and ecosystem collapse.
Example: Overfishing reducing fish populations and the economic viability of fisheries.
Invasive Species:
Non-native species disrupt ecosystem balance, outcompeting native species.
Example: Invasive plants reducing biodiversity and altering habitat structure.
Conservation and Sustainable Management

Protected Areas:
Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve ecosystems.
Example: Yellowstone National Park protecting diverse ecosystems and their services.
Sustainable Practices:
Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fisheries to balance resource use and conservation.
Example: Agroforestry integrating trees into farming systems to enhance biodiversity and productivity.
Restoration Ecology:
Restoring degraded ecosystems to recover their functions and services.
Example: Reforestation projects to restore carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
Legislation and Policies:
Enacting laws and regulations to protect ecosystems and their services.
Example: Clean Water Act regulating pollutants to protect water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
Community Involvement:
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts to ensure sustainable use of ecosystem services.
Example: Community-based forest management to balance resource use and conservation.
Ecosystem Valuation:
Assigning economic value to ecosystem services to highlight their importance in decision-making.
Example: Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) schemes compensating landowners for conservation efforts.
Examples of Ecosystem Services
Amazon Rainforest:
Provisioning: Diverse plant species for medicinal use.
Regulating: Carbon sequestration mitigating climate change.
Supporting: Habitat for countless species, maintaining biodiversity.
Cultural: Indigenous cultures and knowledge.
Coral Reefs:
Provisioning: Fish and other seafood.
Regulating: Coastal protection from storms and erosion.
Supporting: Nursery habitats for marine life.
Cultural: Tourism and recreational diving.
Wetlands:
Provisioning: Fish, timber, and peat.
Regulating: Water purification, flood control.
Supporting: Nutrient cycling, habitat for wildlife.
Cultural: Recreational activities like bird watching and fishing.


