Energy conservation methods are essential for maintaining the health of our ecology, ecosystem, and biodiversity within the biosphere. By reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency, we can minimize the negative impacts on natural habitats and promote sustainable practices. These efforts are crucial for preserving the delicate balance of our environment, a key focus of AP Environmental Studies. Understanding and implementing energy conservation methods helps protect our planet's resources and ensures a stable and thriving biosphere for future generations.
Free AP Environmental Science Practice Test
Learning Objectives
By studying energy conservation methods, students will learn how to reduce energy use and its impact on organisms, mitigate climate changes, and preserve flora and fauna. Key objectives include understanding the importance of energy efficiency, exploring renewable energy sources, and recognizing the role of sustainable practices in protecting natural habitats. These skills are essential for promoting a healthier environment and addressing the challenges posed by climate changes on all organisms within various ecosystems.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
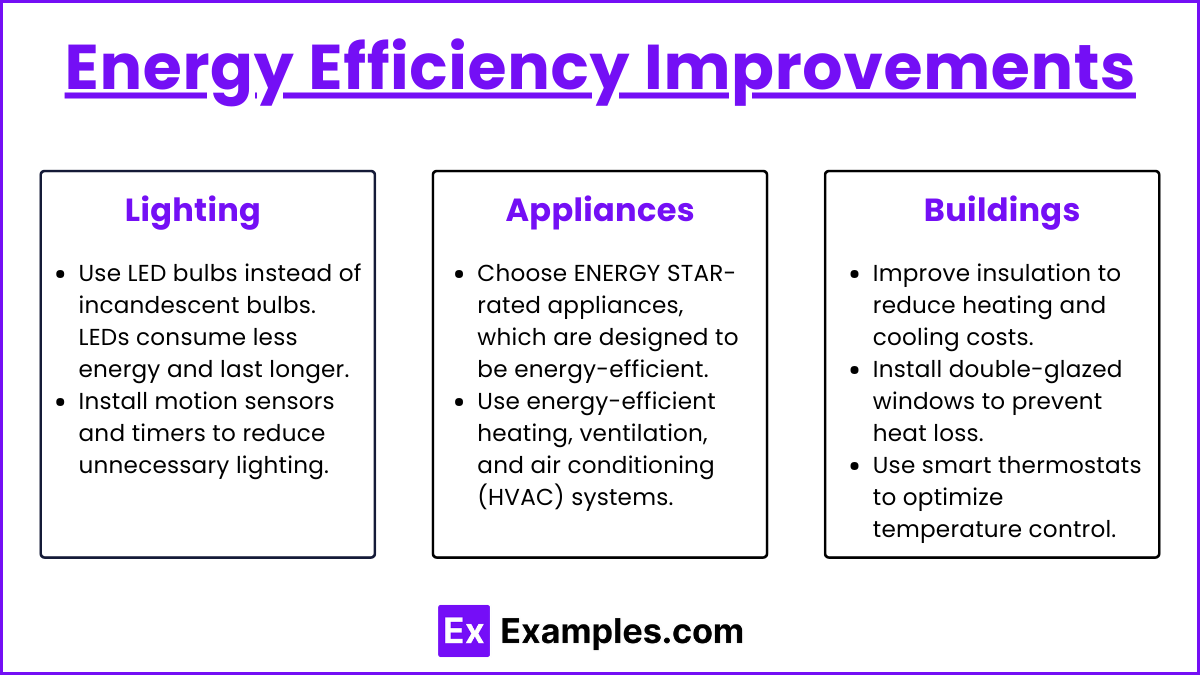
Lighting:
Use LED bulbs instead of incandescent bulbs. LEDs consume less energy and last longer.
Install motion sensors and timers to reduce unnecessary lighting.
Appliances:
Choose ENERGY STAR-rated appliances, which are designed to be energy-efficient.
Use energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Buildings:
Improve insulation to reduce heating and cooling costs.
Install double-glazed windows to prevent heat loss.
Use smart thermostats to optimize temperature control.
Renewable Energy Sources
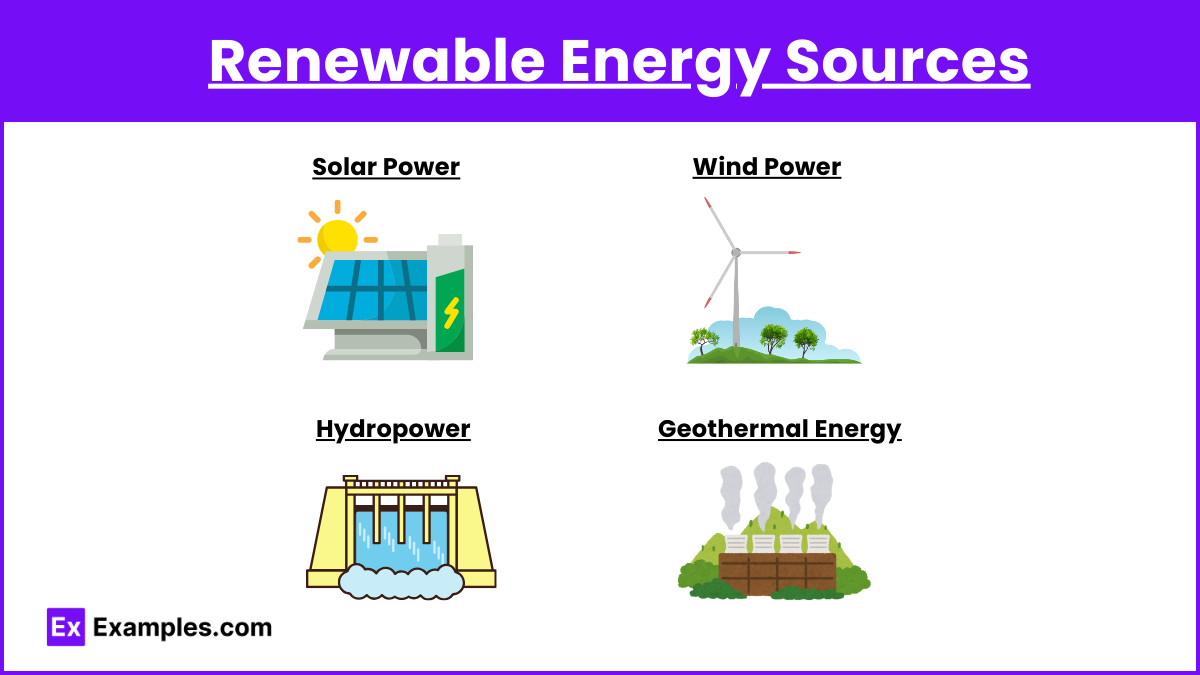
Solar Power:
Install solar panels to harness energy from the sun.
Use solar water heaters for domestic hot water needs.
Wind Power:
Utilize wind turbines to generate electricity.
Implement small-scale wind systems for local energy needs.
Hydropower:
Develop micro-hydro systems for remote areas.
Use tidal and wave energy systems where applicable.
Geothermal Energy:
Use geothermal heat pumps for heating and cooling.
Tap into geothermal reservoirs for electricity generation.
Behavioral Changes
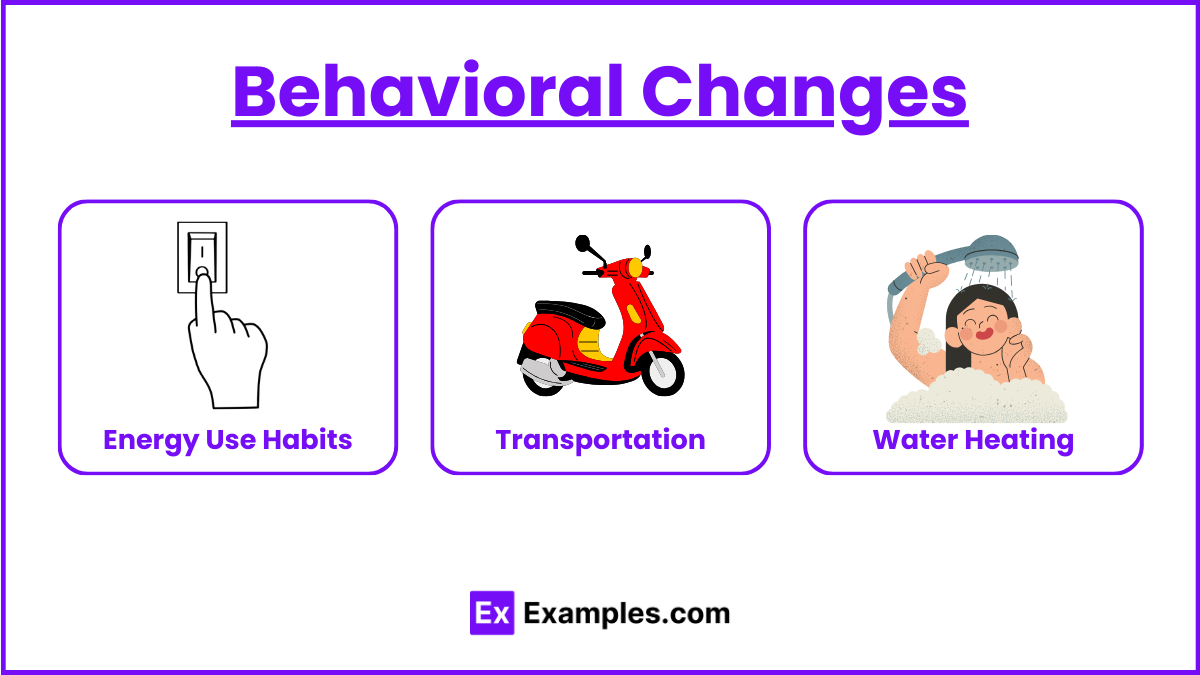
Energy Use Habits:
Turn off lights and appliances when not in use.
Unplug chargers and electronics when not needed.
Transportation:
Use public transportation, carpool, or bike to reduce fuel consumption.
Maintain vehicles regularly to ensure efficient fuel use.
Water Heating:
Take shorter showers and use low-flow showerheads.
Wash clothes in cold water whenever possible.
Government Policies and Incentives
Regulations:
Enforce building codes that mandate energy efficiency standards.
Implement fuel economy standards for vehicles.
Subsidies and Tax Credits:
Provide financial incentives for renewable energy installations.
Offer tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements.
Public Awareness Campaigns:
Educate the public about the benefits of energy conservation.
Promote energy-saving practices through media and community programs.
Technological Innovations
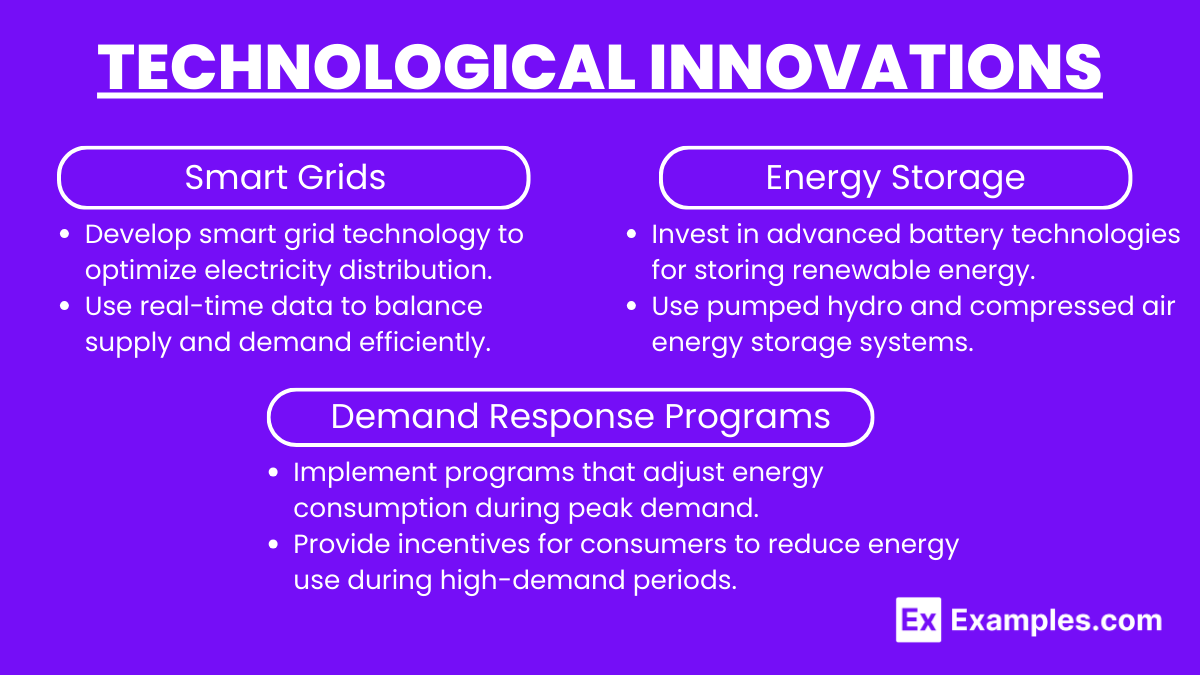
Smart Grids:
Develop smart grid technology to optimize electricity distribution.
Use real-time data to balance supply and demand efficiently.
Energy Storage:
Invest in advanced battery technologies for storing renewable energy.
Use pumped hydro and compressed air energy storage systems.
Demand Response Programs:
Implement programs that adjust energy consumption during peak demand.
Provide incentives for consumers to reduce energy use during high-demand periods.
Sustainable Design and Architecture
Green Building Design:
Design buildings with natural lighting and ventilation to reduce energy use.
Incorporate green roofs and walls to improve insulation and reduce heat islands.
Passive Solar Design:
Orient buildings to maximize solar gain in winter and minimize it in summer.
Use thermal mass materials to store and release solar energy.
Industry and Manufacturing
Energy Management Systems:
Implement energy management systems to monitor and control energy use.
Conduct regular energy audits to identify and rectify inefficiencies.
Process Optimization:
Optimize manufacturing processes to reduce energy consumption.
Recover waste heat for use in other processes.
Agricultural Practices
Efficient Irrigation:
Use drip irrigation and other efficient watering systems to reduce water and energy use.
Sustainable Farming:
Adopt practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and no-till farming to reduce energy inputs.


