Biodiversity encompasses the variety of life forms on Earth, including the diversity within species, between species, and among ecosystems. It is vital for maintaining ecological stability, providing ecosystem services, and supporting cultural, economic, and scientific endeavors. Biodiversity ensures the resilience of ecosystems, enabling them to adapt to changes and recover from disturbances. However, it is under threat from human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, overexploitation, and the introduction of invasive species. Understanding and conserving biodiversity is essential for sustaining the natural systems that humans and all life depend on.
Learning Objectives
Learning objectives for biodiversity include understanding the types of biodiversity (genetic, species, ecosystem), recognizing its importance for ecological stability, ecosystem services, and human well-being. Students should be able to identify threats to biodiversity such as habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, overexploitation, and invasive species. Additionally, they should learn about conservation strategies like protected areas, sustainable practices, restoration ecology, and community involvement. By mastering these concepts, students will appreciate the critical role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems and the necessity of protecting it for future generations.
Definition
- Biodiversity refers to the variety of life in all its forms and levels of organization, including the diversity of species, genetic variation within species, and the variety of ecosystems.
Types of Biodiversity
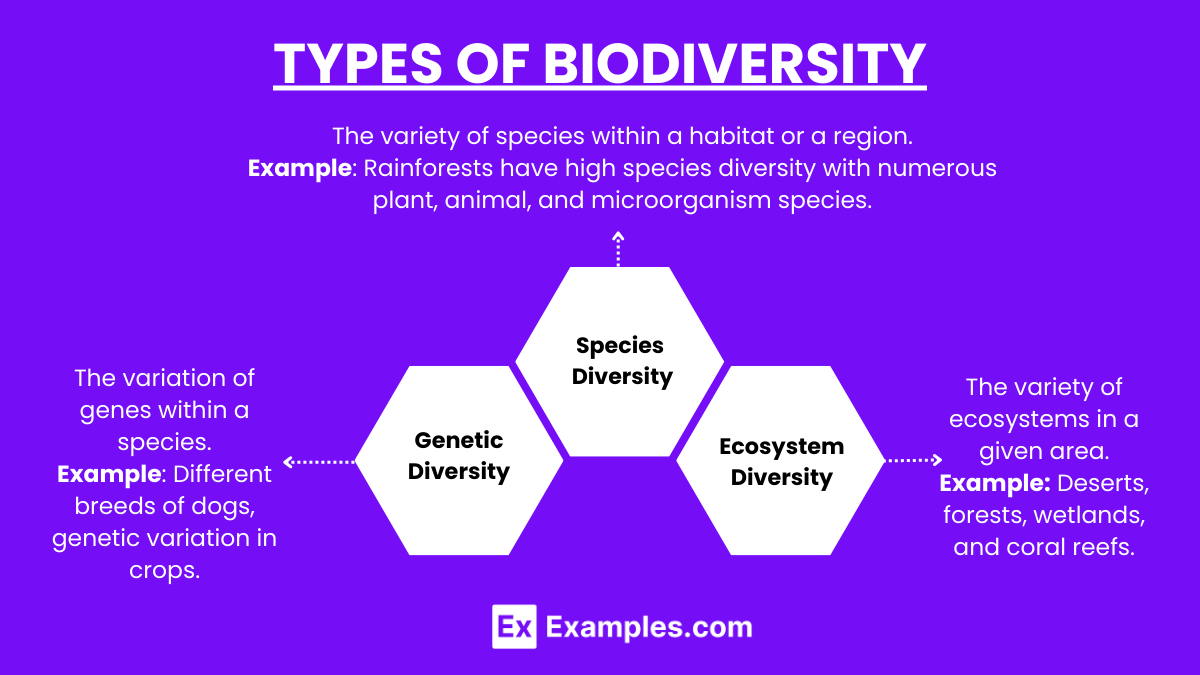
- Genetic Diversity:
- The variation of genes within a species.
- Important for adaptability and survival of species.
- Example: Different breeds of dogs, genetic variation in crops.
- Species Diversity:
- The variety of species within a habitat or a region.
- Measured by species richness (number of species) and species evenness (abundance of species).
- Example: Rainforests have high species diversity with numerous plant, animal, and microorganism species.
- Ecosystem Diversity:
- The variety of ecosystems in a given area.
- Includes different habitats, biological communities, and ecological processes.
- Example: Deserts, forests, wetlands, and coral reefs.
Importance of Biodiversity
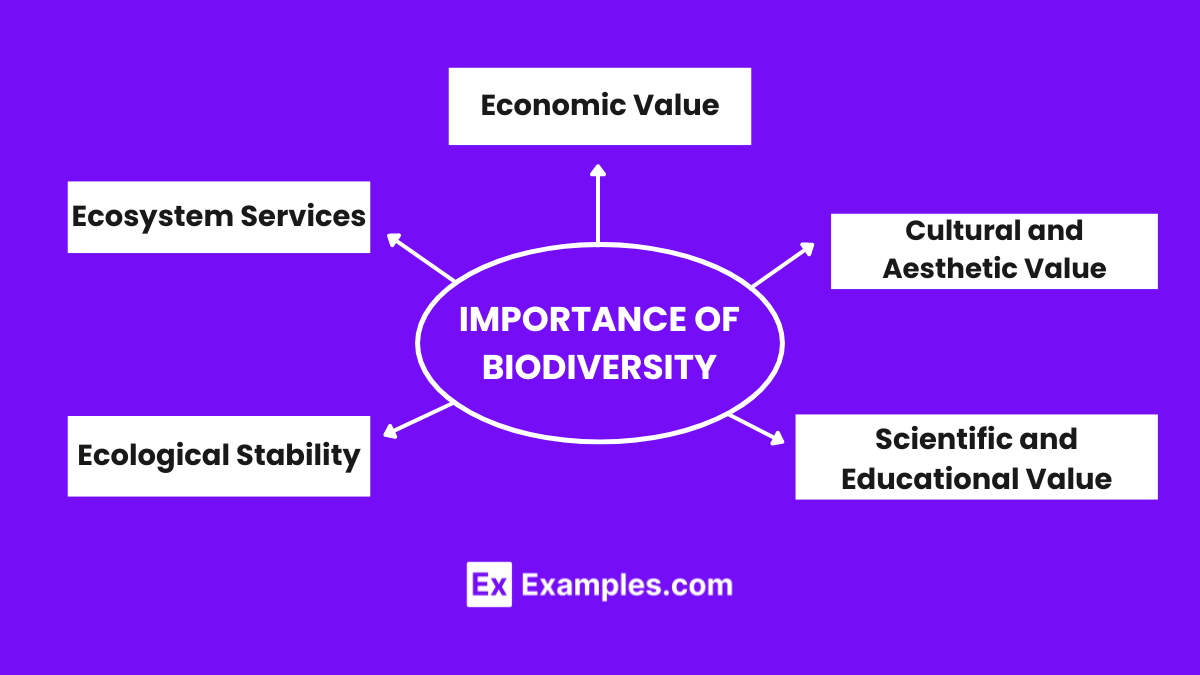
- Ecological Stability:
- Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances and environmental changes.
- Example: Diverse plant species in a forest can better withstand pests and diseases.
- Ecosystem Services:
- Biodiversity provides essential services like pollination, nutrient cycling, water purification, and climate regulation.
- Example: Bees pollinating crops, wetlands filtering water.
- Economic Value:
- Biodiversity supports industries like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism.
- Example: Many medicines are derived from plant compounds.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value:
- Biodiversity enriches cultures, traditions, and provides recreational opportunities.
- Example: National parks, wildlife watching.
- Scientific and Educational Value:
- Biodiversity is a source of scientific discovery and education.
- Example: Research on unique species leading to new technologies or medicines.
Threats to Biodiversity
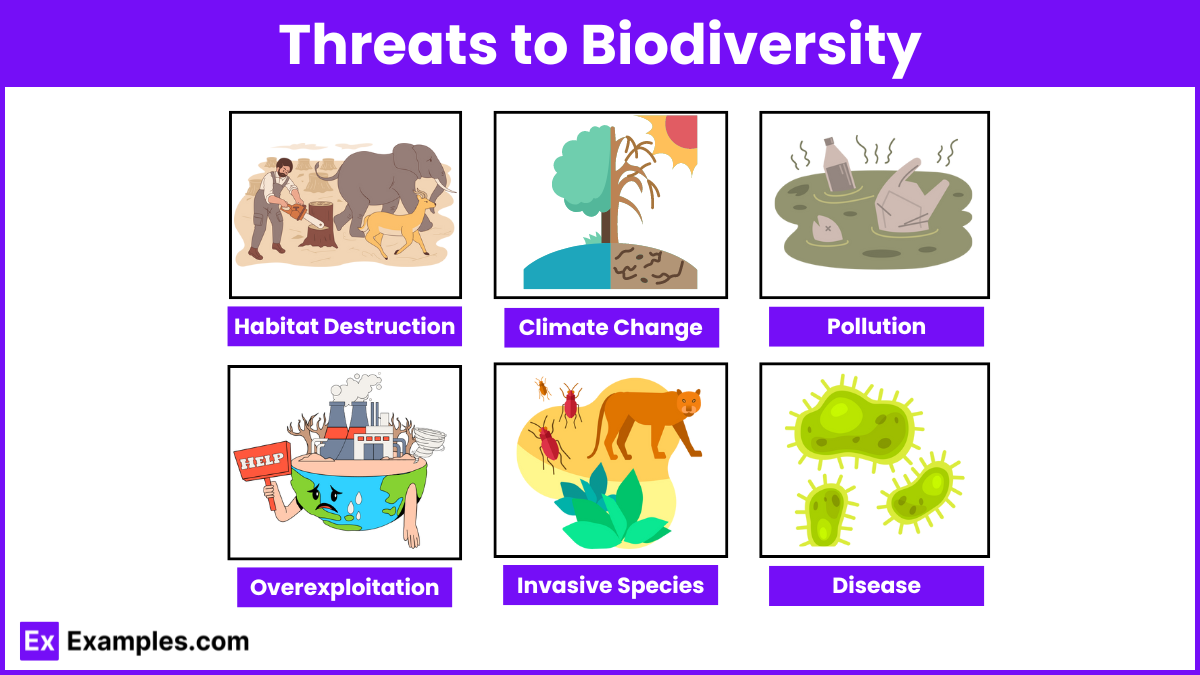
- Habitat Destruction:
- Conversion of natural habitats to agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure.
- Example: Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest.
- Climate Change:
- Alters habitats and threatens species adapted to specific climates.
- Example: Coral bleaching due to rising ocean temperatures.
- Pollution:
- Contaminates air, water, and soil, affecting all levels of biodiversity.
- Example: Pesticides harming pollinators like bees.
- Overexploitation:
- Unsustainable hunting, fishing, and harvesting of species.
- Example: Overfishing leading to the decline of fish populations.
- Invasive Species:
- Non-native species that outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species.
- Example: Zebra mussels in the Great Lakes.
- Disease:
- Pathogens that can decimate populations of species.
- Example: Chytridiomycosis affecting amphibians worldwide.
Conservation of Biodiversity
- Protected Areas:
- Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas.
- Example: Yellowstone National Park.
- Legislation:
- Laws and regulations to protect species and habitats.
- Example: Endangered Species Act (ESA) in the U.S.
- Sustainable Practices:
- Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fisheries.
- Example: Certification schemes like Fair Trade and Marine Stewardship Council (MSC).
- Restoration Ecology:
- Restoring degraded ecosystems to their natural state.
- Example: Reforestation projects.
- Captive Breeding and Reintroduction:
- Breeding endangered species in captivity and reintroducing them into the wild.
- Example: California condor recovery program.
- Community Involvement:
- Engaging local communities in conservation efforts.
- Example: Community-based wildlife management.
Measurement of Biodiversity
- Species Richness:
- The number of different species in a specific area.
- Species Evenness:
- The relative abundance of each species in a specific area.
- Simpson’s Diversity Index:
- A measure that accounts for both richness and evenness.
- Shannon-Weiner Index:
- Another measure of species diversity that considers both the number of species and their evenness.
Biodiversity Hotspots
- Areas with exceptionally high levels of species diversity and endemism that are under threat.
- Example: The Amazon Rainforest, Madagascar, the Coral Triangle.
Ecosystem Services
- Provisioning Services:
- Products obtained from ecosystems like food, water, and raw materials.
- Regulating Services:
- Benefits from ecosystem processes that regulate the environment, such as climate regulation and flood control.
- Supporting Services:
- Necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, like soil formation and nutrient cycling.
- Cultural Services:
- Non-material benefits obtained from ecosystems like recreation, spiritual, and cultural values.
Human Activities and Biodiversity
- Agriculture:
- Both a cause of habitat destruction and a field where biodiversity can be beneficial (e.g., crop diversity).
- Urbanization:
- Leads to habitat fragmentation and loss of biodiversity.
- Industrialization:
- Pollution and resource extraction impact biodiversity.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Balancing development and biodiversity through strategies like sustainable development and green infrastructure.