Modern forces, including globalization, technology, and migration, play a crucial role in shaping cultural patterns worldwide. In AP Human Geography, globalization accelerates the exchange of ideas, goods, and cultural practices, leading to both cultural homogenization and hybridization. Through economic integration, digital media, and international trade, cultural traits like language, fashion, and food spread across borders. While these forces enhance global connectivity, they also raise concerns about the loss of local traditions and cultural identities, creating a dynamic interplay between global influences and regional cultural resilience.
Free AP Human Geography Practice Test
Learning Objectives
For the topic "Modern Forces, such as Globalization, that Affect Cultural Patterns," you should learn how globalization spreads cultural traits and influences cultural homogenization, diffusion, and hybridization. Understand the role of technology, migration, and economic integration in shaping cultural patterns. Examine both the positive effects, like increased diversity and global awareness, and the challenges, such as loss of cultural identity and cultural imperialism. Additionally, explore case studies illustrating these effects, and critically analyze how modern forces impact local and global cultures in various regions.
Modern Forces and Globalization and Their Impact on Cultural Patterns
In AP Human Geography, modern forces such as globalization, technology, and economic integration play crucial roles in shaping cultural patterns worldwide. Globalization, in particular, refers to the process by which people, ideas, goods, and services spread across international boundaries, creating a more interconnected world. This process has profound effects on cultural practices, leading to both homogenization and differentiation.
Globalization

Globalization is the process by which the world becomes increasingly interconnected through the exchange of goods, services, ideas, technologies, and cultural practices across borders. It is driven by advancements in communication, transportation, and trade, leading to a more integrated global economy and culture. As globalization expands, it influences various aspects of life, including economic activities, social structures, and cultural patterns.
Cultural Homogenization: As globalization accelerates, certain cultural traits, such as consumer habits, entertainment, and language, become dominant across the globe. For example, the spread of fast-food chains like McDonald's, global fashion trends, and Western media influence tend to create uniformity across cultures. This results in a phenomenon called cultural homogenization, where local cultures adopt global norms, often at the expense of their unique traditions.
Cultural Diffusion: Globalization increases the flow of cultural practices from one region to another. Ideas such as democracy, human rights, and environmentalism have spread globally through media and international organizations. Technologies like the internet have facilitated the quick exchange of cultural elements such as music, art, and religion.
Language Dominance: English has become a dominant global language in business, technology, and international communication due to globalization. This can lead to a decline in the use of minority languages, potentially threatening linguistic diversity.
Economic Impact on Culture: The global economy, fueled by free trade agreements and multinational corporations, can reshape local economies and cultural patterns. Economic globalization often leads to urbanization, where people move to cities for better job opportunities, altering traditional rural cultures.
Modern Forces Shaping Cultural Patterns
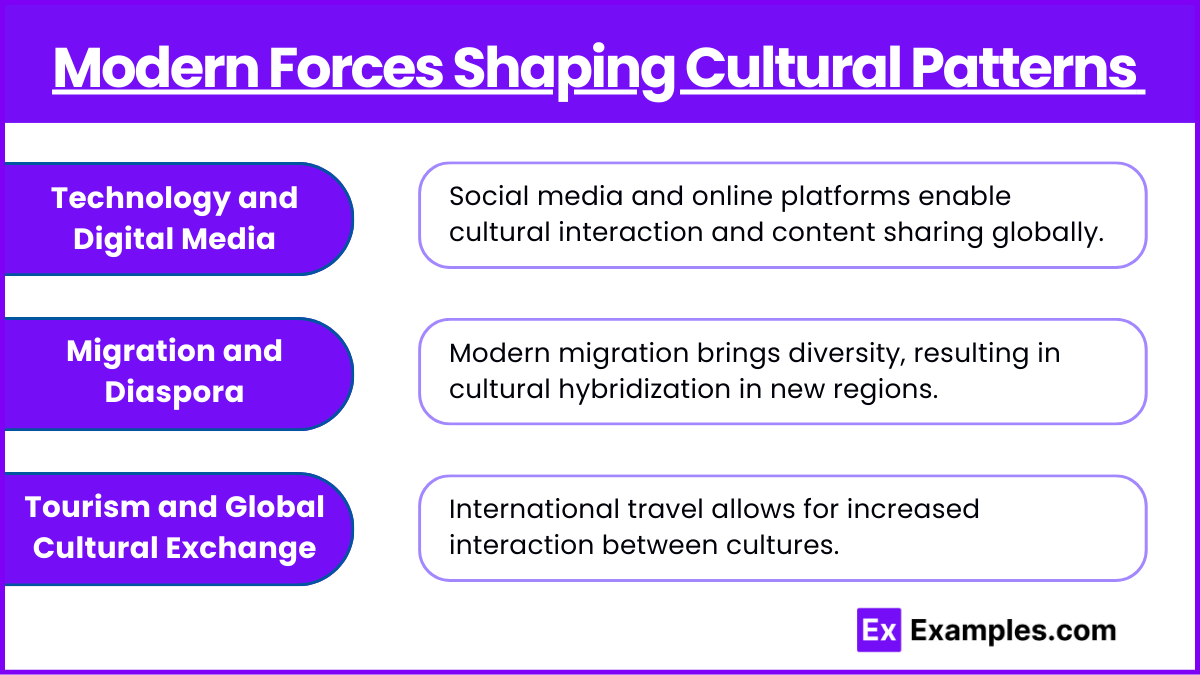
Technology and Digital Media: Social media platforms, streaming services, and online communities create a space where people from different cultures can interact and share cultural content. This exchange can blur the boundaries between cultures, as people have access to a wide variety of cultural products (e.g., K-pop music or Bollywood films) from other regions.
Migration and Diaspora: Modern migration patterns bring diverse groups into new regions, often leading to cultural hybridization. Immigrants introduce their cultural practices, while also adapting to their host countries, resulting in syncretism or blending of cultures. For example, Latin American communities in the United States contribute to a mix of Hispanic-American traditions.
Tourism and Global Cultural Exchange: International travel allows for increased interaction between cultures. Tourists experience local cultures while also bringing their cultural practices with them. This can lead to the commercialization of certain cultural elements, where traditional practices are packaged for tourist consumption (e.g., traditional dances or crafts).
Positive Effects of Globalization on Cultural Patterns
Cultural Diversity and Hybridization: Despite concerns about cultural homogenization, globalization can lead to cultural hybridization. Different cultural practices mix and create new, diverse cultural forms. For example, fusion cuisine, where culinary traditions from different parts of the world are blended, is a result of global cultural exchange.
Global Awareness and Identity: Globalization fosters greater awareness of global issues, leading to the creation of global movements. People identify with transnational communities based on shared values, such as environmental sustainability or human rights, transcending traditional national or cultural identities.
Examples
Example 1. Globalization of Food Culture
Global fast-food chains like McDonald's and Starbucks have spread worldwide, influencing local eating habits and cultures. In many countries, traditional foods are being replaced or supplemented by Western-style fast food, leading to the homogenization of culinary practices. For example, the introduction of McDonald's in India has brought changes to local cuisine, while still incorporating cultural elements like vegetarian menu items to cater to the Indian population. This illustrates how global economic forces reshape local food cultures.
Example 2. Technology and Social Media
Social media platforms such as Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook have become global phenomena, allowing people from different parts of the world to share and consume cultural content. The rapid exchange of music, fashion, and entertainment trends through digital media results in the blending of cultures. For instance, the global popularity of K-pop (Korean pop music) is largely driven by social media, where it has gained a massive international following, influencing fashion and music culture worldwide.
Example 3. Migration and Cultural Syncretism
Modern migration patterns bring people from diverse backgrounds into contact with one another, resulting in the blending of cultural practices. For example, Latin American migration to the United States has introduced elements of Hispanic culture, such as language, food, and religious practices, which are now integrated into American culture. This cultural exchange enriches local cultures but also leads to new, hybrid identities that merge elements from both the migrant and host cultures.
Example 4. International Tourism
Tourism promotes the exchange of cultural practices between locals and visitors. For example, in Bali, Indonesia, local traditions and religious ceremonies have been adapted to meet the expectations of international tourists. While tourism brings economic benefits and global attention to cultural practices, it can also lead to the commercialization or dilution of traditions as they are modified to appeal to a broader audience.
Example 5. Economic Globalization and Language Shifts
The dominance of English as the global language of business, science, and technology is a significant force in cultural globalization. Countries around the world emphasize English-language education to participate in the global economy. For example, in countries like China and Japan, English is taught from a young age to enhance international business opportunities. This focus on a global lingua franca can sometimes lead to the decline of local languages and traditions, contributing to cultural homogenization.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1
Which of the following is a primary result of cultural globalization?
A) Cultural isolation increases as people adopt traditional practices.
B) Local languages and customs become more widely practiced.
C) Global cultural homogenization occurs, reducing cultural diversity.
D) National borders become more significant in protecting cultural identities.
Answer: C) Global cultural homogenization occurs, reducing cultural diversity.
Explanation: Globalization often leads to cultural homogenization, where global cultural norms, especially from dominant cultures like the West, spread across the world. This results in a blending or loss of unique local traditions and customs, as many societies adopt similar practices in areas such as entertainment, food, and language. For example, the spread of Western fast-food chains and media leads to a more uniform global culture, potentially reducing cultural diversity. The other options are incorrect because globalization tends to reduce, rather than increase, cultural isolation, and it can challenge the preservation of local languages and customs.
Question 2
Which of the following modern forces most directly contributes to the spread of cultural practices across the world?
A) Increased migration
B) Urbanization in developing countries
C) The growth of multinational corporations
D) The expansion of social media and digital platforms
Answer: D) The expansion of social media and digital platforms
Explanation: The expansion of social media and digital platforms plays a significant role in cultural diffusion by allowing individuals from different parts of the world to share their cultural practices in real-time. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube enable the rapid spread of music, fashion, language, and values, leading to the globalization of cultural practices. While the other forces, like migration and multinational corporations, also contribute to cultural spread, digital platforms have the most immediate and widespread impact by connecting billions of people daily and promoting global cultural exchanges.
Question 3
Which of the following best describes the process of cultural hybridization in the context of globalization?
A) One culture completely replaces another as a result of migration and technological advances.
B) Local cultures adopt and adapt elements of global cultures to create new cultural forms.
C) Global cultures eliminate local cultures through economic and political dominance.
D) Local cultures resist all external influences to maintain their traditional practices.
Answer: B) Local cultures adopt and adapt elements of global cultures to create new cultural forms.
Explanation: Cultural hybridization refers to the process where local cultures combine elements from global influences with their own traditions to create something new. An example would be fusion cuisine, where culinary traditions from different parts of the world mix to form unique dishes. This differs from cultural homogenization, which is the reduction of cultural diversity, and from cultural dominance, where one culture overrides another. Hybridization acknowledges the agency of local cultures in adapting and reshaping external influences, rather than passively absorbing or rejecting them.


