This comprehensive AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based Cheat Sheet provides essential formulas, key concepts, and critical information across all units of the AP Physics 1 curriculum. By summarizing complex topics into easy-to-understand points, it helps students efficiently review and reinforce their knowledge. The inclusion of specific formulas and example problems aids in the application of theoretical concepts, ensuring students are well-prepared for both multiple-choice and free-response questions on the exam. With clear, concise explanations and organized sections, this cheat sheet is an invaluable study aid for achieving a high score on the AP Physics 1 exam.







Download AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based Cheat Sheet – Pdf
Unit 1: Kinematics
- Vector vs. Scalar: Vectors include directions.
- Displacement vs. Distance
- Velocity vs. Speed: Include direction for velocity.
- Acceleration: (also a vector)
- Key Equations:
- Projectile Motion
- Position-Time Graphs: Slope = velocity
- Velocity-Time Graphs: Slope = acceleration
- Acceleration-Time Graphs
- Gravity:
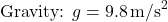
Unit 2: Dynamics
- Equilibrium: Net force = 0
- Newton’s Laws:
- 1st: Law of Inertia
- 2nd: F = ma
- 3rd: Action-Reaction
- Friction:
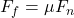
- Ramps/Inclined Planes: Free body diagrams
- Force Body Diagrams
- Net Force Calculation
Unit 3: Circular Motion & Gravitation
- Centripetal Force: Not an actual force, net force
- Centripetal Acceleration:
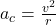
- Universal Gravitation:
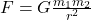
- Uniform Circular Motion: Constant speed
- Gravitational Mass vs. Inertial Mass
Unit 4: Energy
- Work: W = Fd
- Parallel: (+) Work
- Antiparallel: (−) Work
- Energy Types:
- Kinetic Energy:
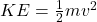
- Potential Energy:
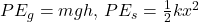
- Kinetic Energy:
- Mechanical Energy: Sum of kinetic and potential energy
- Power:
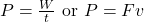
- Conservation of Energy
- Graphs & Diagrams
Unit 5: Momentum
- Momentum: p = mv
- Impulse: J = Ft
- Conservation of Momentum
- Collisions:
- Elastic: Kinetic Energy and Momentum conserved
- Inelastic: Momentum conserved
- Center of Mass
Unit 6: Simple Harmonic Motion
- Spring & Pendulum
- Key Relationships:
- Hooke’s Law: F = kx
- Period Equations:
- Pendulum:
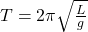
- Spring:
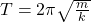
- Pendulum:
Unit 7: Torque & Rotational Motion
- Rotational Kinematics: θ,ω,α
- Similar to linear kinematics with rotational symbols
- Torque: tau = rF \sin \theta \)
- Moment of Inertia:
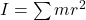
- Angular Momentum:
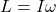
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
FRQ Tips
- FRQ Breakdown:
- Experimental Design: Data analysis
- Quantitative & Qualitative Translation: Concept application
- Paragraph Argument: Cohesive argument in physics
- Solving Tips:
- Correct equations and observations
- Direct/indirect relationships
- Citing information
- Basic physics application
- Clear and concise claims

