Understanding electric systems and charge is fundamental for mastering the principles of electricity and magnetism in the AP Physics exam. This topic covers the behavior of electric charges, electric fields, and the laws governing electric forces and potential. Below are detailed notes along with five examples to help you achieve a high score on your AP Physics exam.
Learning Objectives
By studying Electric Systems and Charge for the AP Physics exam, you should understand the principles of electric charge, electric force, and electric fields. You should be able to analyze electric potential and potential energy in various configurations, apply Coulomb’s law, and understand the behavior of conductors and insulators. Additionally, you should grasp the concepts of electric circuits, including Ohm’s law, resistivity, and the functionality of series and parallel circuits, enabling you to solve complex circuit problems effectively.
Electric Charge
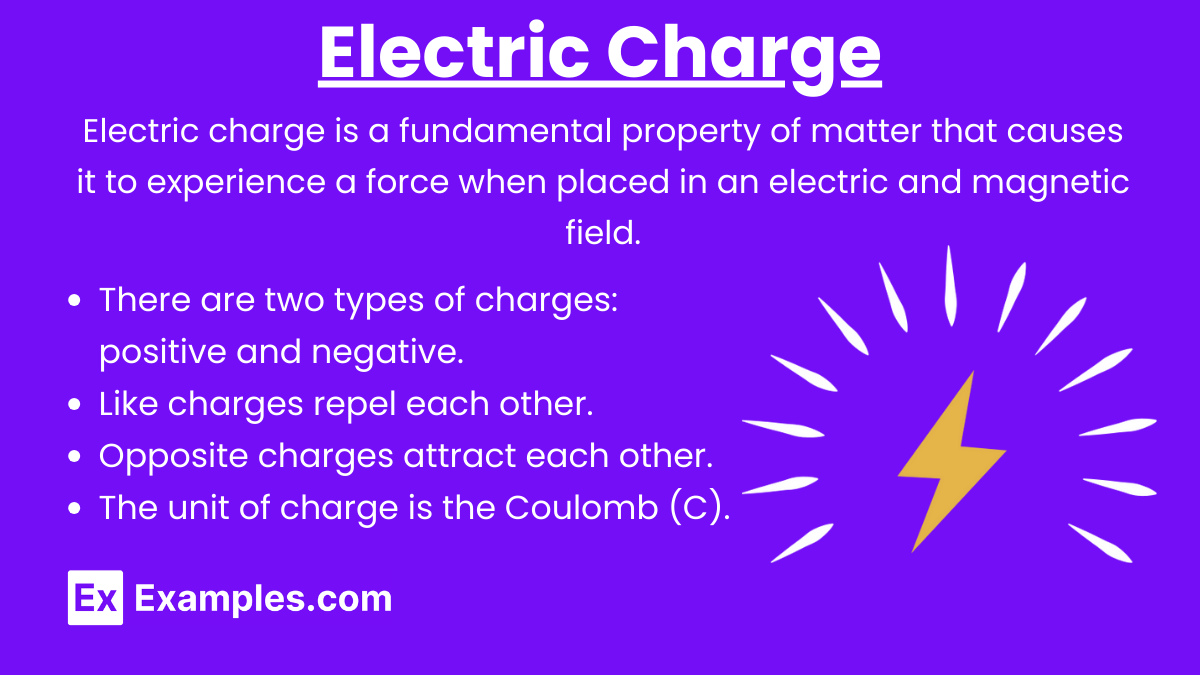
Electric Charge (q): Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electric and magnetic field. There are two types of charges: positive and negative.
Key Points:
- Like charges repel each other.
- Opposite charges attract each other.
- The unit of charge is the Coulomb (C).
Quantization of Charge
Quantization of Charge: Charge is quantized, meaning it occurs in discrete amounts. The smallest unit of charge is the elementary charge eee, where: e = 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹
Conservation of Charge
Conservation of Charge: The total charge in an isolated system remains constant. Charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one object to another.
Coulomb’s Law
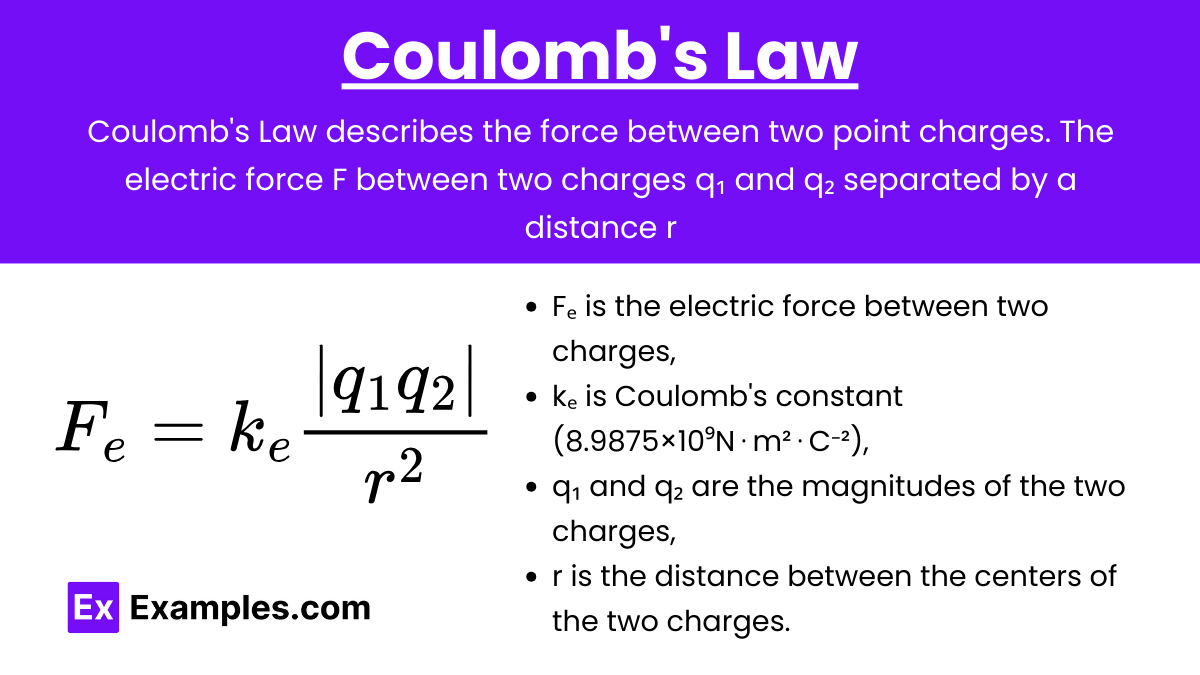
Coulomb’s Law: Coulomb’s Law describes the force between two point charges. The electric force F between two charges q₁ and q₂ separated by a distance r is given by:
where:
- F is the magnitude of the force,
- ke is Coulomb’s constant (8.9875×10⁹ N⋅m²⋅C⁻²),
- q₁ and q₂ are the charges,
- r is the distance between the charges.
Key Points:
- The force is attractive if the charges are of opposite signs and repulsive if they are of the same sign.
- The force acts along the line joining the centers of the two charges.
Electric Field
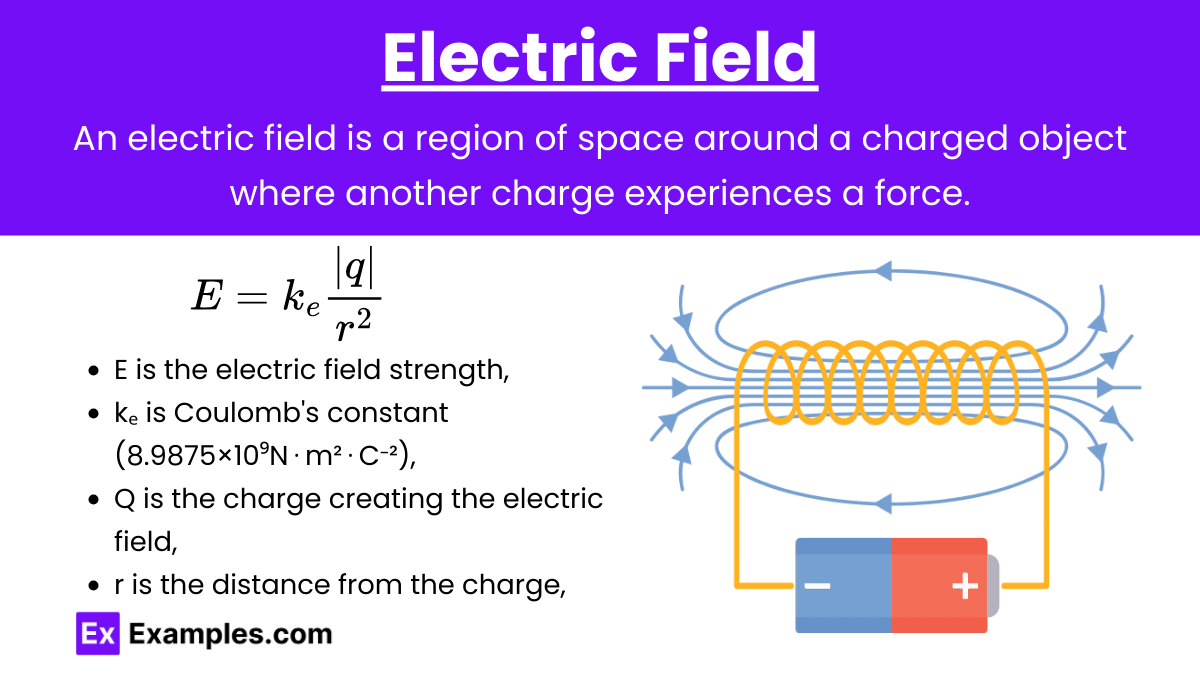
Electric Field (E): An electric field is a region around a charged object where another charged object experiences an electric force. The electric field E due to a point charge q at a distance r is given by:
Key Points:
- The direction of the electric field is away from positive charges and towards negative charges.
- The unit of electric field is Newtons per Coulomb (N/C).
Electric Potential
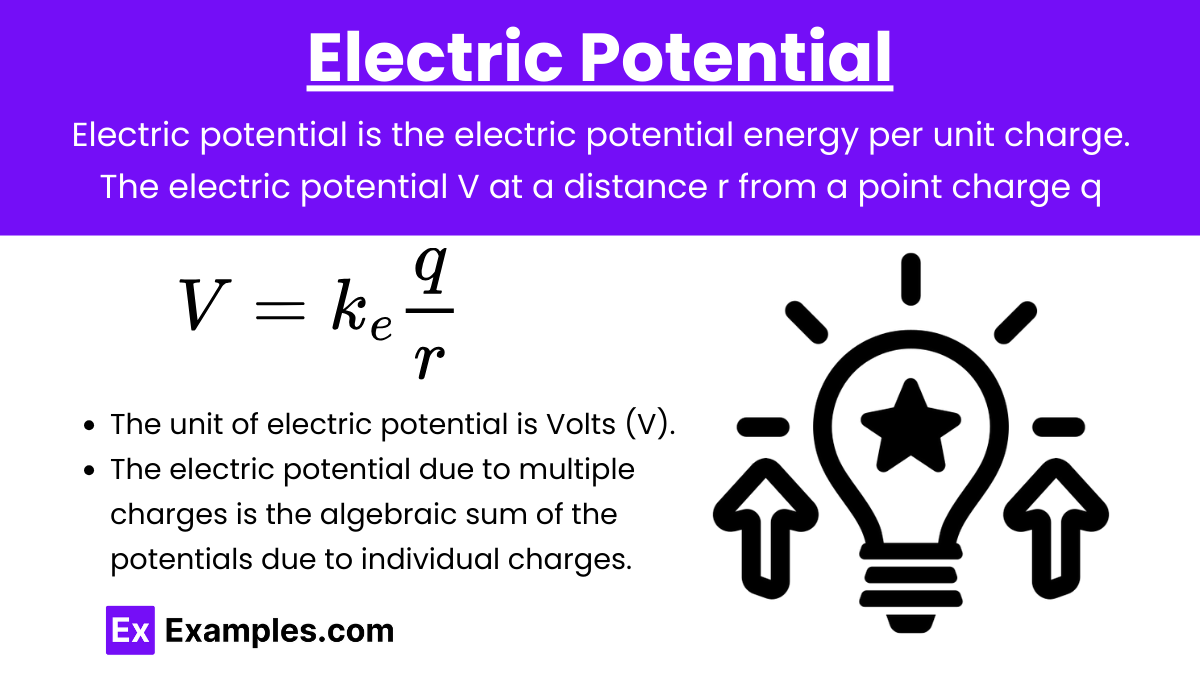
Electric Potential (V): Electric potential is the electric potential energy per unit charge. The electric potential V at a distance r from a point charge q is given by:
Key Points:
- The unit of electric potential is Volts (V).
- The electric potential due to multiple charges is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to individual charges.
Examples of Electric Systems and Charge
Example 1: Calculating Electric Force
Scenario: Two charges, q₁ = +3μC and q₂ = −5μC, are placed 0.2 meters apart. Calculate the electric force between them.
Solution:
Example 2: Electric Field Due to a Point Charge
Scenario: Calculate the electric field at a point 0.1 meters away from a +2μC charge.
Solution:
Example 3: Electric Potential Due to a Point Charge
Scenario: Find the electric potential at a distance of 0.5 meters from a +1C charge.
Solution:
Example 4: Superposition of Electric Fields
Scenario: Two charges, q₁ = +4μC and q₂ = +6μC, are placed 0.3 meters apart. Find the electric field at the midpoint between the charges.
Solution: The electric field due to q₁ at the midpoint is:
The electric field due to q₂ at the midpoint is:
Since both charges are positive, the fields are in opposite directions.
Therefore, the net field at the midpoint is:
Example 5: Potential Energy of a System of Charges
Scenario: Calculate the potential energy of a system with two charges, q₁ = +3μC and q₂ = −3μC, separated by 0.1 meters.
Solution:
Practice Problems
Question 1:
Two point charges, q₁ = +3μC and q₂ = −3μC, are placed 0.5 meters apart in a vacuum. What is the magnitude of the electric force between them? (Use Coulomb’s constant k = 8.99×109N⋅m²/C²)
A) 0.27N
B) 0.54N
C) 1.08N
D) 2.16N
Answer: C) 1.08 N
Explanation:
The electric force F between two point charges is given by Coulomb’s law:
Given:
Calculate the magnitude of the force:
Thus, the correct answer is 1.08 N.
Question 2:
What is the electric potential energy of a system of two charges, q₁ = 4μC and q₂ = 6μC, separated by a distance of 0.3 meters in a vacuum? (Use Coulomb’s constant k=8.99×10⁹N⋅m²/C²)
A) 0.72J
B) 0.96J
C) 1.20J
D) 1.44J
Answer: B) 0.72 J
Explanation:
The electric potential energy U of a system of two point charges is given by:
Given:
Calculate the electric potential energy:
Thus, the correct answer is 0.72 J.
Question 3:
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a 12 V battery and has a capacitance of 5 μF. What is the charge stored on the capacitor?
A) 30μC
B) 50μC
C) 60μC
D) 120μC
Answer: C) 60 μC
Explanation:
The charge Q stored on a capacitor is given by the formula:
Q = CV
where C is the capacitance and V is the voltage.
Given:
- C = 5μF = 5×10⁻⁶F
- V = 12V
Calculate the charge:
Q = 5×10⁻⁶F×12V
Q =60×10⁻⁶C
Q = 60μC
Thus, the correct answer is 60 μC.