Advances in Technology have significantly shaped human history, influencing economies, societies, and cultures. From the printing press to the internet, these innovations transformed communication, transportation, and industry. Understanding these effects is crucial for success in the AP World History: Modern exam, as it reveals the connections between technological progress and major historical events, fostering a comprehensive understanding of global developments.
Learning Objectives
In studying “Advances in Technology and Their Effects” for AP World History: Modern, you should learn to identify key technological innovations, analyze their societal and economic impacts, and evaluate their roles in shaping historical events. It’s also important to explore how these advancements fostered cultural exchanges, providing a comprehensive understanding of their influence on global developments throughout history.
1. The Early Modern Era (1450-1750)
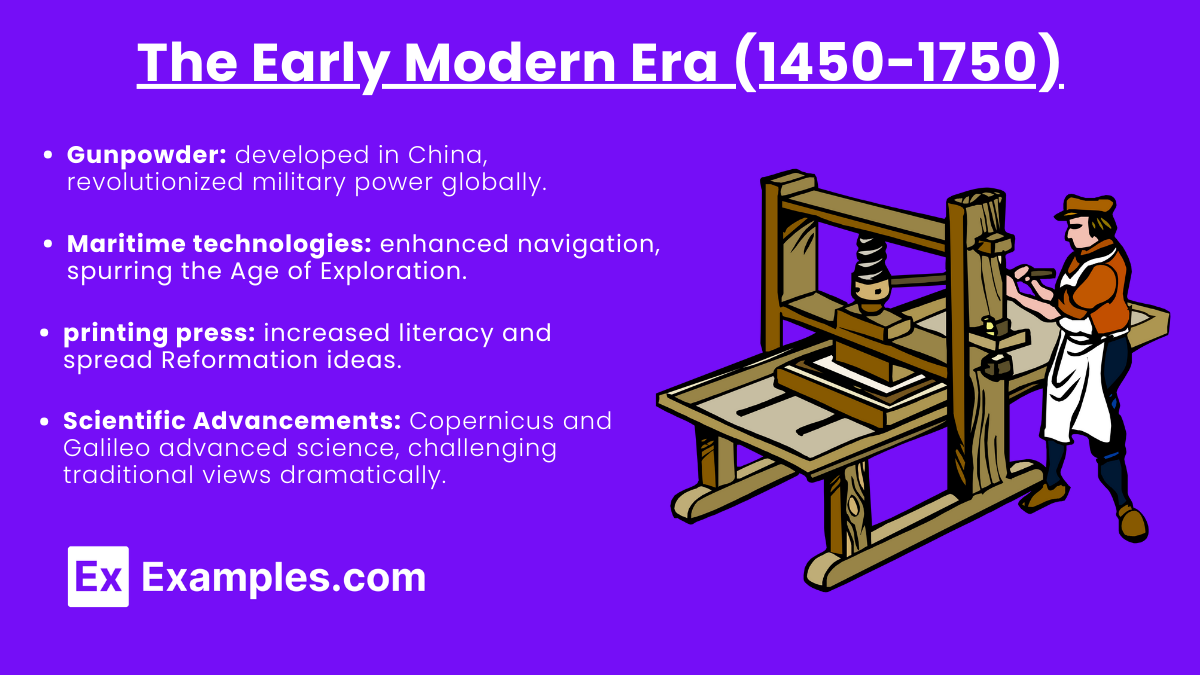
Key Technologies:
- Gunpowder: Originally developed in China, gunpowder transformed military power in Europe and Asia during this period. It enabled the rise of powerful empires like the Ottoman, Mughal, and Safavid Empires (collectively known as the “Gunpowder Empires”).
- Maritime Technologies: The invention of the caravel (a maneuverable ship), compass, and astrolabe significantly improved navigation and led to the Age of Exploration. European powers like Spain and Portugal were able to explore and colonize new territories in Africa, the Americas, and Asia.
- Printing Press: Introduced in Europe by Johannes Gutenberg around 1440, it revolutionized the spread of knowledge. Books became cheaper, literacy rates increased, and it played a crucial role in the Protestant Reformation by spreading Martin Luther’s ideas.
- Scientific Advancements: The Early Modern Era also witnessed significant scientific progress, including advancements in fields like astronomy and medicine. Figures like Copernicus and Galileo challenged traditional views, promoting the Scientific Revolution.
Effects:
- Colonization and Exploration: European powers established colonies in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, leading to the establishment of global trade networks like the Atlantic slave trade and the Columbian Exchange.
- Rise of Powerful Empires: Gunpowder-based weaponry allowed empires like the Ottomans and Mughals to expand their territories and centralize power.
- Cultural Diffusion: The printing press facilitated the spread of Renaissance ideas, scientific discoveries, and religious reforms.
2. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1900)
The Industrial Revolution (1750-1900) marked a transformative period characterized by mechanization, urbanization, and technological advancements, leading to significant changes in production, transportation, and societal structures across the globe.
Key Technologies:
- Steam Engine: James Watt’s improvements to the steam engine in the late 18th century revolutionized transportation and industry, making it possible to power factories and railways.
- Textile Innovations: Inventions like the spinning jenny (James Hargreaves) and power loom (Edmund Cartwright) mechanized textile production, leading to mass production in factories.
- Telegraph: Samuel Morse’s telegraph system allowed for near-instant communication across long distances, revolutionizing diplomacy, business, and personal communication.
Effects:
- Urbanization and Social Change: The Industrial Revolution spurred massive urbanization as people moved to cities to work in factories. It also created new social classes (industrial middle class and working class), which would later lead to social and labor movements.
- Global Trade and Imperialism: Improved transportation and communication facilitated global trade and increased European imperialism. European powers sought raw materials for their factories and new markets for manufactured goods.
- Environmental Impact: Industrialization led to widespread environmental degradation due to deforestation, pollution, and resource extraction.
3. Technology in the 20th Century and Its Effects

Key Technologies:
- The Automobile and Airplane: The development of internal combustion engines revolutionized personal and cargo transportation, and the Wright brothers’ flight in 1903 opened the door to global air travel.
- Electricity: The widespread use of electricity transformed daily life, industries, and communication. It powered factories, homes, and new inventions like the radio and television.
- Computers and the Internet: The invention of computers during World War II and the development of the internet in the late 20th century revolutionized information storage, communication, and global connectivity.
Effects:
- World Wars: New technologies like machine guns, tanks, and airplanes made warfare more destructive. World War I (1914-1918) and World War II (1939-1945) saw unprecedented levels of global conflict and loss of life due to these technologies.
- Cold War and Nuclear Arms Race: After World War II, the U.S. and the Soviet Union emerged as superpowers, each developing massive nuclear arsenals. The fear of nuclear war shaped international politics throughout the Cold War.
- Economic Globalization: Computers and the internet facilitated the rise of a global economy by making international business and trade more efficient. Multinational corporations became increasingly important players in global trade.
- Cultural Change: Advances in transportation and communication (e.g., radio, TV, internet) led to the spread of global culture, including American pop culture. This period also saw the rise of mass media and consumer culture.
4. The 21st Century and Future Technologies
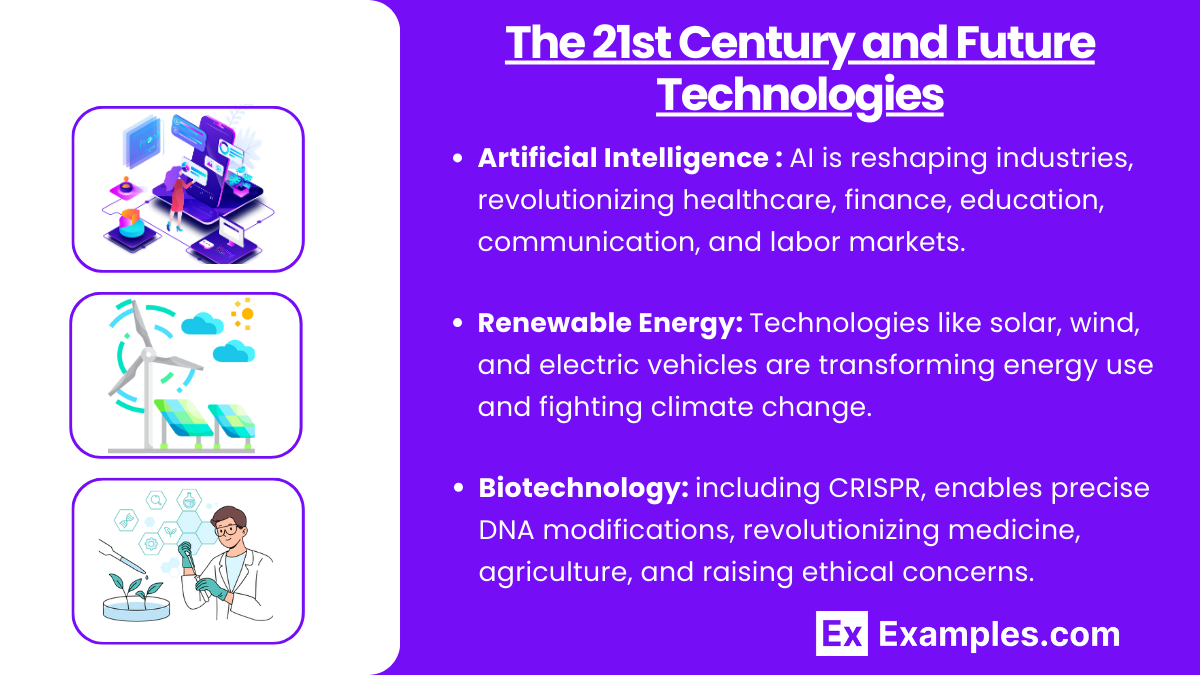
Key Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming industries such as healthcare, finance, and transportation, with the potential to revolutionize fields like education, communication, and labor markets.
- Renewable Energy: Technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles are reshaping energy consumption and are crucial to combating climate change.
- Biotechnology: Advances in genetic engineering, such as CRISPR, allow for precise alterations of DNA, opening possibilities for medical treatments, agriculture, and ethical debates.
Effects:
- Economic Shifts: Automation and AI are transforming the labor market, potentially leading to job displacement in traditional industries but creating new opportunities in technology-driven fields.
- Globalization of Information: The internet continues to play a key role in shaping international relations, with social media fostering movements such as the Arab Spring and global climate activism.
- Environmental Concerns: While technological advances help combat climate change (e.g., renewable energy), they also pose environmental risks (e.g., electronic waste and resource depletion).
5. Overarching Themes and Impacts of Technological Advances

- Increased Global Interdependence: From the Columbian Exchange to the modern internet, technology has continuously connected societies and economies across the globe. This has fostered both cooperation and competition, with empires, nations, and corporations striving for dominance.
- Shifts in Power: Technological advancements have frequently shifted power balances. For example, gunpowder helped rise empires, steam power fueled industrialized nations, and nuclear weapons defined superpower status in the Cold War.
- Environmental and Ethical Challenges: Industrialization and modern technology have often come at a cost to the environment, prompting debates about sustainability and the ethics of progress. Today’s discussions on AI, biotechnology, and climate change reflect these ongoing concerns.
- Cultural Transformations: From the Renaissance to the Information Age, technology has played a crucial role in the diffusion of ideas, art, and knowledge, shaping global culture and identity.
- Economic Disparities: Technological advancements have often widened the gap between wealthy and poorer nations. Industrialized countries have reaped significant economic benefits, while developing regions have struggled to catch up, leading to global inequality and uneven development.
Examples
Example 1: The Printing Press (15th Century)
The printing press enabled mass production of books, increasing literacy rates and spreading Renaissance ideas, which fostered cultural and scientific movements across Europe.
Example 2: The Steam Engine (18th Century)
The steam engine revolutionized transportation and industry, facilitating urbanization and global trade, and creating a new working class during the Industrial Revolution.
Example 3: The Telegraph (19th Century)
The telegraph transformed communication, allowing instant long-distance messaging, which enhanced business transactions, diplomacy, and news dissemination, creating a more interconnected world.
Example 4: The Automobile (20th Century)
The mass production of automobiles revolutionized transportation by increasing personal mobility, promoting suburban growth, creating jobs, and transforming social dynamics, significantly impacting lifestyles and economic development in the 20th century.
Example 5: The Internet (Late 20th Century)
Computers and the internet revolutionized information access and communication, fostering globalization, transforming economies, and creating new social dynamics in the digital age.
MCQs
Question 1
Which invention significantly improved communication in the 19th century?
A) The printing press
B) The telegraph
C) The telephone
D) The radio
Answer: B) The telegraph
Explanation: The telegraph enabled near-instantaneous communication over long distances, transforming business and diplomacy in the 19th century.
Question 2
What was a key effect of the steam engine during the Industrial Revolution?
A) Increased agricultural efficiency
B) Urbanization and factory growth
C) Enhanced military power
D) Decline of transportation
Answer: B) Urbanization and factory growth
Explanation: The steam engine powered factories and transportation, leading to urbanization and the rise of industrial centers.
Question 3
Which technology contributed to the spread of Enlightenment ideas?
A) The television
B) The internet
C) The printing press
D) The radio
Answer: C) The printing press
Explanation: The printing press allowed for the mass production of books, facilitating the dissemination of Enlightenment ideas widely.


