Which of the following organisms is an autotroph?
Lion
Mushroom
Oak Tree
Human
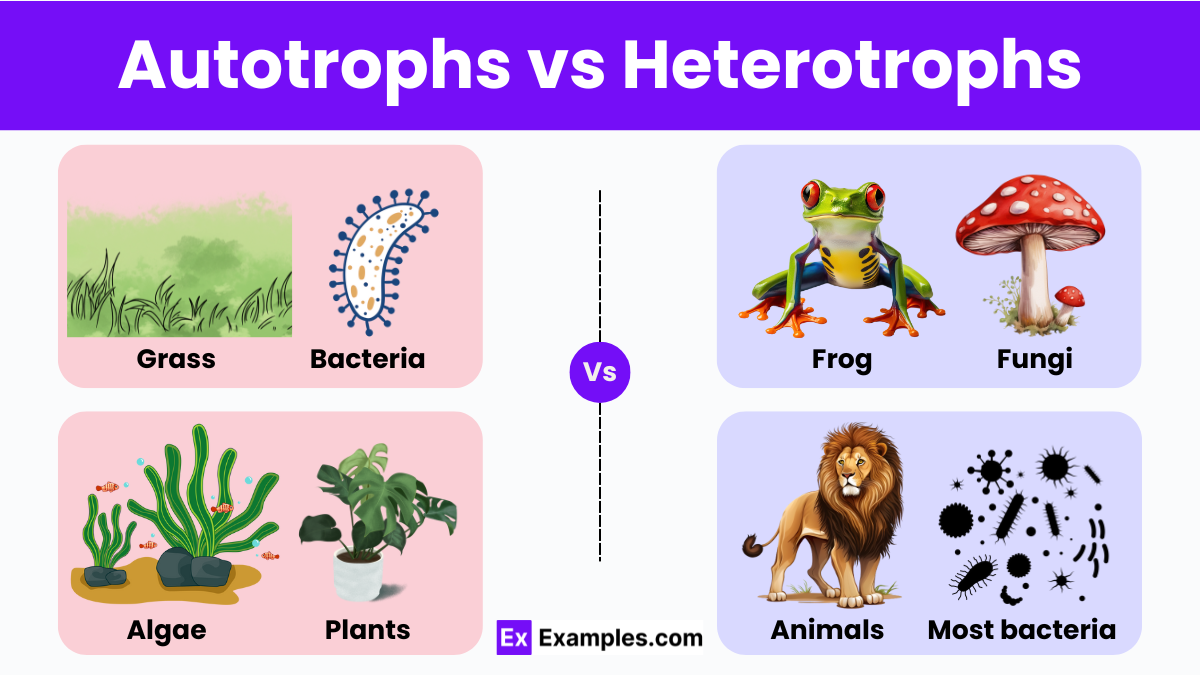
Autotrophs, also known as producers, are organisms that make their own food using sunlight and simple materials like water and carbon dioxide. This process, called photosynthesis, is essential because it starts the food chains that feed all life. Mainly, plants, algae, and certain bacteria have this capability. Heterotrophs, or consumers, cannot make their own food. They must eat plants, other organisms, or organic material to get energy. This group includes animals, fungi, and many bacteria and protists. Heterotrophs depend entirely on the energy initially created by autotrophs.
Autotrophs, commonly known as producers, are self-sufficient organisms that create their own food using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. This remarkable ability allows them to convert inorganic substances like water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, which are vital for their growth and sustenance. The main groups of autotrophs include plants, algae, and certain bacteria, which not only cater to their own energy needs but also produce excess organic compounds that are crucial for other organisms. These producers are the cornerstone of ecosystems, initiating food chains that provide energy for all subsequent levels of life.
Heterotrophs, on the other hand, are known as consumers because they cannot synthesize their own food. Instead, they rely on ingesting or absorbing organic material from other sources, primarily autotrophs or other heterotrophs. This group encompasses a diverse array of organisms, including all animals, fungi, many protists, and bacteria. Heterotrophs’ survival is directly linked to the availability of organic molecules produced by autotrophs, underscoring a deep ecological dependence. Without the continuous input of energy from autotrophs, heterotrophs would face extinction.
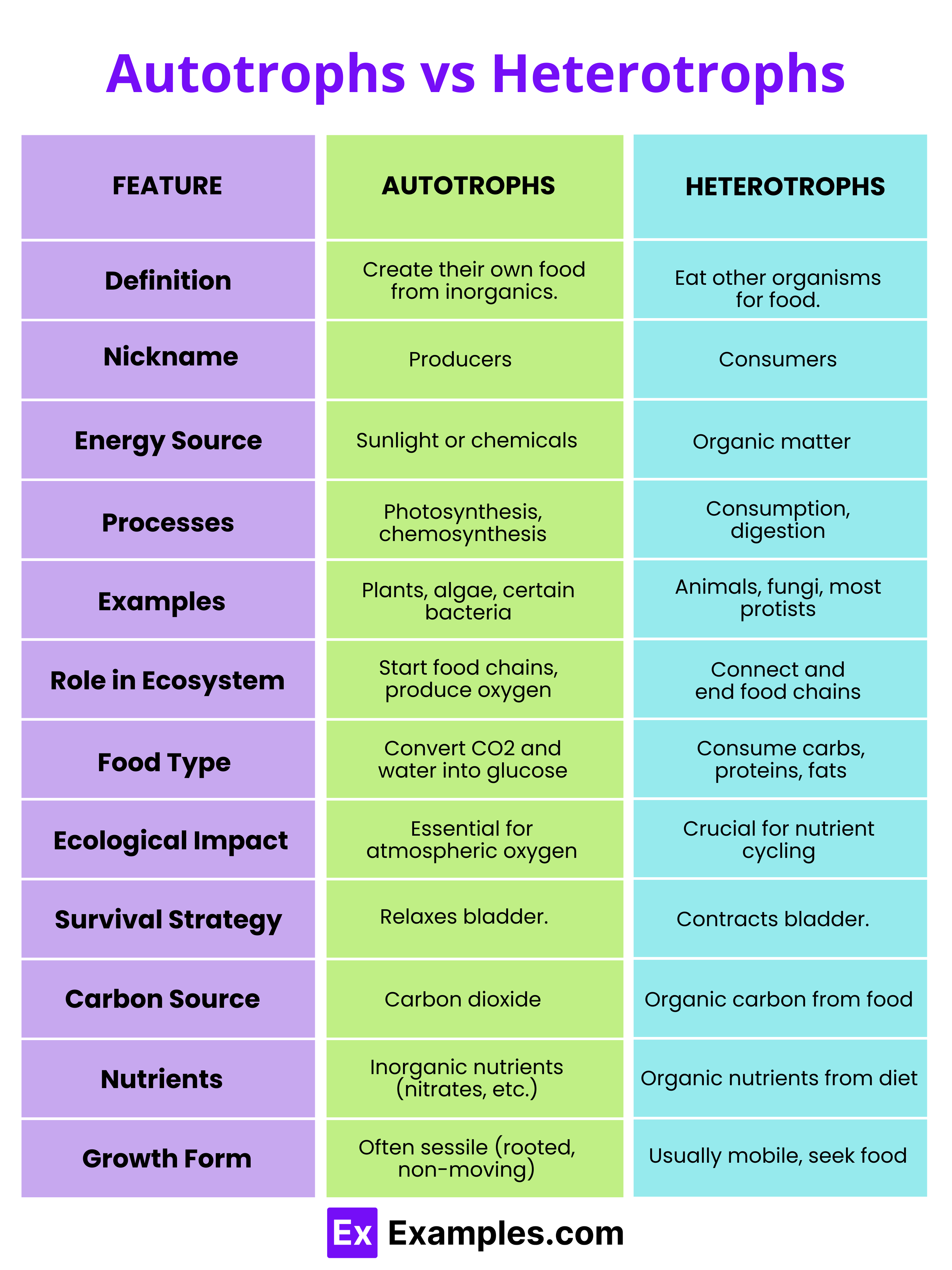
| Feature | Autotrophs | Heterotrophs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organisms that produce their own food using inorganic materials primarily through photosynthesis. | Organisms that cannot synthesize their own food and must consume other organisms or organic material. |
| Also Known As | Producers | Consumers |
| Energy Source | Sunlight, inorganic chemicals | Organic compounds from other organisms |
| Process Used | Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis | Consumption and absorption |
| Primary Examples | Plants, algae, some bacteria | Animals, fungi, many protists, and bacteria |
| Role in Ecosystem | Foundation of food chains; provide energy for other organisms. | Depend on autotrophs for energy; consume organic material to obtain energy. |
| Types of Food | Produce organic molecules themselves from inorganic sources. | Depend on the organic material produced by other organisms. |
| Survival Impact | Can survive independently by producing their own food. | Survival depends on the presence of autotrophs or other food sources. |
| Energy Transformation | Transform solar or chemical energy directly into usable chemical energy. | Rely on the energy stored in the bodies of other organisms. |
| Ecological Dependence | Less directly dependent on other organisms for food, though they may rely on other species for pollination or dispersal. | Utterly dependent on the existence of autotrophs for their energy needs. |
Autotrophs produce their own food via photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, while heterotrophs consume other organisms for energy.
Autotrophs synthesize organic compounds from inorganic substances; heterotrophs must ingest organic material.
Recall: ‘Auto’ means self (autotrophs self-feed), and ‘hetero’ means different (heterotrophs eat different organisms).
Animals are considered heterotrophs as they rely on consuming others for energy.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following organisms is an autotroph?
Lion
Mushroom
Oak Tree
Human
Heterotrophs obtain their energy by:
Producing their own food using sunlight
Consuming other organisms
Chemosynthesis
Direct absorption of sunlight
Which of the following processes is used by autotrophs to produce food?
Respiration
Fermentation
Photosynthesis
Digestion
Which statement best describes heterotrophs?
They produce their own food.
They are primary producers.
They depend on other organisms for food.
They can perform photosynthesis.
Which of the following is an example of a heterotroph?
Algae
Grass
Deer
Cyanobacteria
Autotrophs can be classified into which two categories?
Herbivores and Carnivores
Phototrophs and Chemotrophs
Producers and Consumers
Decomposers and Detritivores
Which of the following organisms is a photoautotroph?
Fungi
Coral
Cyanobacteria
Whale
How do chemoautotrophs obtain energy?
From consuming other organisms
By photosynthesis
Through chemical reactions involving inorganic substances
By absorbing sunlight directly
Which of the following best describes autotrophs?
They are at the top of the food chain.
They are primary producers.
They are exclusively animals.
They feed on other organisms.
Which organism is an example of a chemoautotroph?
Grass
Fish
Deep-sea vent bacteria
Rabbit
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

