What is codominance in genetics?
When one allele completely masks the effect of another
When two alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype
When one allele is partially expressed
When neither allele is expressed

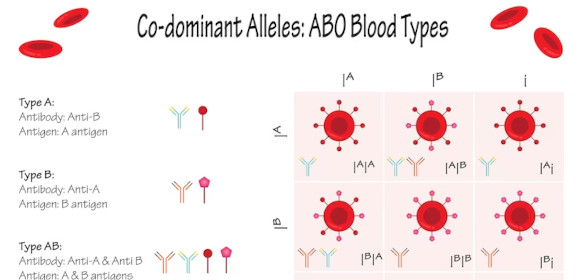
In genetics, people inherit various physical properties, traits, and characteristics from their parents. This also includes various entities and organic beings like plants and animals. Various contexts, biotic factors, and themes like the biosphere, ecosystem, food chain, food web, symbiosis, and biome will also affect the proclivity of the said traits. Codominance is a phenomenon that occurs when the genes will produce a mixed result of the two traits.
Codominance is a specific phenomenon when the child of two parents obtains traits that have both physical characteristics of each parent’s physical trait. For example, when a purple flower and a red flower are cross-bred, codominance might produce a flower with both purple and red flower petals.
The Punnett square is a tool people can use to determine the alleles that the parents will genetically pass on to their offspring. It can also determine the codominant trait that will be present in the whole equation.
Begin by creating a Punnett square that will help you visualize the possible genotypes that the offspring will inherit. Not only that, but this will also provide you with a structure and a framework you can utilize to determine the codominance.
To use the Punnett square you must list down the dominant and recessive traits that the parents will pass on to their offspring. You will list the dominant and recessive traits on the X and Y axis respectively.
Each trait will have a specific allele loadout that is specific to the trait. You must match the alleles in each quadrant in the table. You will end up with 4 different allele combinations in the Punnett square, which will be in the format of AA, Aa, or aa where the uppercase a is the dominant allele and the lowercase a is the recessive allele.
The codominant trait is the trait with a dominant and a recessive allele in the punnett square, which is represented by the Aa combination. You must identify the presence of this allele formation in the Punnett square.
Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon where the recessive trait or dominant trait is repressed, which will mean only the characteristic of the unsuppressed trait will be active. Codominance is a phenomenon where the offspring will receive a trait that is a combination of the recessive and dominant traits of a specific physical characteristic.
There are many observable examples of codominant traits naturally occurring in nature. For example, when a white chicken is paired with a gray rooster, their offspring can have a codominant trait wherein it will have a mix of gray and white feathers on its body.
The person’s eye color is a trait that has an incomplete dominance due to the characteristic’s ability to only manifest a recessive or a dominant gene. A trait can only be considered codominant if both dominant and recessive traits are present in the characteristics.
Codominance is the phenomenon where a specific trait will manifest a blend of both physical characteristics of both dominant and recessive genes the parents have given to their offspring. It is important to know how to identify the possibility of a trait with codominance in their offspring.

In genetics, people inherit various physical properties, traits, and characteristics from their parents. This also includes various entities and organic beings like plants and animals. Various contexts, biotic factors, and themes like the biosphere, ecosystem, food chain, food web, symbiosis, and biome will also affect the proclivity of the said traits. Codominance is a phenomenon that occurs when the genes will produce a mixed result of the two traits.
ohio.k12.ky.us
Details
File Format
Size: 34 KB

mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Details
File Format
Size: 58 KB

nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Details
File Format
Size: 44 KB
dentonisd.org
Details
File Format
Size: 71 KB

par.nsf.gov
Details
File Format
Size: 66 KB

sgasd.org
Details
File Format
Size: 19 KB

bear.wheatlandsd.com
Details
File Format
Size: 41 KB

wsfcs.k12.nc.us
Details
File Format
Size: 25 KB

wesleyschool.org
Details
File Format
Size: 34 KB
kyrene.org
Details
File Format
Size: 51 KB

woodstown.org
Details
File Format
Size: 44 KB
Codominance is a specific phenomenon when the child of two parents obtains traits that have both physical characteristics of each parent’s physical trait. For example, when a purple flower and a red flower are cross-bred, codominance might produce a flower with both purple and red flower petals.
The Punnett square is a tool people can use to determine the alleles that the parents will genetically pass on to their offspring. It can also determine the codominant trait that will be present in the whole equation.
Begin by creating a Punnett square that will help you visualize the possible genotypes that the offspring will inherit. Not only that, but this will also provide you with a structure and a framework you can utilize to determine the codominance.
To use the Punnett square you must list down the dominant and recessive traits that the parents will pass on to their offspring. You will list the dominant and recessive traits on the X and Y axis respectively.
Each trait will have a specific allele loadout that is specific to the trait. You must match the alleles in each quadrant in the table. You will end up with 4 different allele combinations in the Punnett square, which will be in the format of AA, Aa, or aa where the uppercase a is the dominant allele and the lowercase a is the recessive allele.
The codominant trait is the trait with a dominant and a recessive allele in the punnett square, which is represented by the Aa combination. You must identify the presence of this allele formation in the Punnett square.
Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon where the recessive trait or dominant trait is repressed, which will mean only the characteristic of the unsuppressed trait will be active. Codominance is a phenomenon where the offspring will receive a trait that is a combination of the recessive and dominant traits of a specific physical characteristic.
There are many observable examples of codominant traits naturally occurring in nature. For example, when a white chicken is paired with a gray rooster, their offspring can have a codominant trait wherein it will have a mix of gray and white feathers on its body.
The person’s eye color is a trait that has an incomplete dominance due to the characteristic’s ability to only manifest a recessive or a dominant gene. A trait can only be considered codominant if both dominant and recessive traits are present in the characteristics.
Codominance is the phenomenon where a specific trait will manifest a blend of both physical characteristics of both dominant and recessive genes the parents have given to their offspring. It is important to know how to identify the possibility of a trait with codominance in their offspring.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is codominance in genetics?
When one allele completely masks the effect of another
When two alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype
When one allele is partially expressed
When neither allele is expressed
Which of the following is an example of codominance in humans?
Blue eyes
Blue eyes
Sickle-cell anemia
Brown hair
In codominance, what would be the phenotype of an individual with genotype IAIB for the ABO blood group?
Type A blood
Type B blood
Type AB blood
Type O blood
Which of the following organisms can exhibit codominance?
Plants
Animals
Humans
All of the above
In a cross between a red-flowered plant (RR) and a white-flowered plant (WW), which offspring phenotype indicates codominance?
All red flowers
All white flowers
Pink flowers
Red and white spotted flowers
Which scenario best exemplifies codominance?
A rabbit with black fur
A cow with patches of black and white fur
A bird with a mix of blue and green feathers
A dog with solid brown fur
How does codominance differ from incomplete dominance?
Codominance blends traits, incomplete dominance shows both traits
Codominance shows both traits equally, incomplete dominance blends traits
Codominance shows neither trait, incomplete dominance shows one trait
Codominance is only seen in plants, incomplete dominance is seen in animals
If a chicken with black feathers (BB) is crossed with a chicken with white feathers (WW), and the offspring have black and white feathers, what pattern of inheritance is this?
Complete dominance
Incomplete dominance
Codominance
Multiple alleles
Which statement is true about codominant alleles?
One allele is always dominant over the other
Both alleles are expressed equally in the heterozygote
Neither allele is expressed in the phenotype
Codominant alleles can only occur in animals
Which blood type combination shows codominance in the ABO blood system?
AA and BB
AO and BO
AB and OO
AB and AB
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

