Which of the following is a characteristic of flowering plants?
They produce seeds in cones
They reproduce through spores
They produce flowers
They have no vascular system

Plants are fundamental to life on Earth, providing oxygen, food, and shelter. They can be categorized into two primary groups: flowering plants (angiosperms) and non-flowering plants (gymnosperms, ferns, mosses, and algae). Flowering plants produce seeds enclosed within fruits, showcasing a wide array of flowers that attract pollinators. Non-flowering plants, on the other hand, reproduce through spores or naked seeds, and do not produce flowers. Understanding the differences between these two groups helps appreciate the diversity and complexity of the plant kingdom. This article explores the distinct characteristics, reproductive methods, and examples of flowering and non-flowering plants.
Flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, represent the largest and most diverse group in the plant kingdom. They possess distinct features that set them apart from other plant groups.
Flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process involving flowers, pollination, fertilization, and seed formation.
Non-flowering plants encompass a diverse group of plants that do not produce flowers. These plants, including gymnosperms, ferns, mosses, and algae, reproduce through different mechanisms compared to flowering plants.
Non-flowering plants play essential roles in their ecosystems and have various uses for humans:
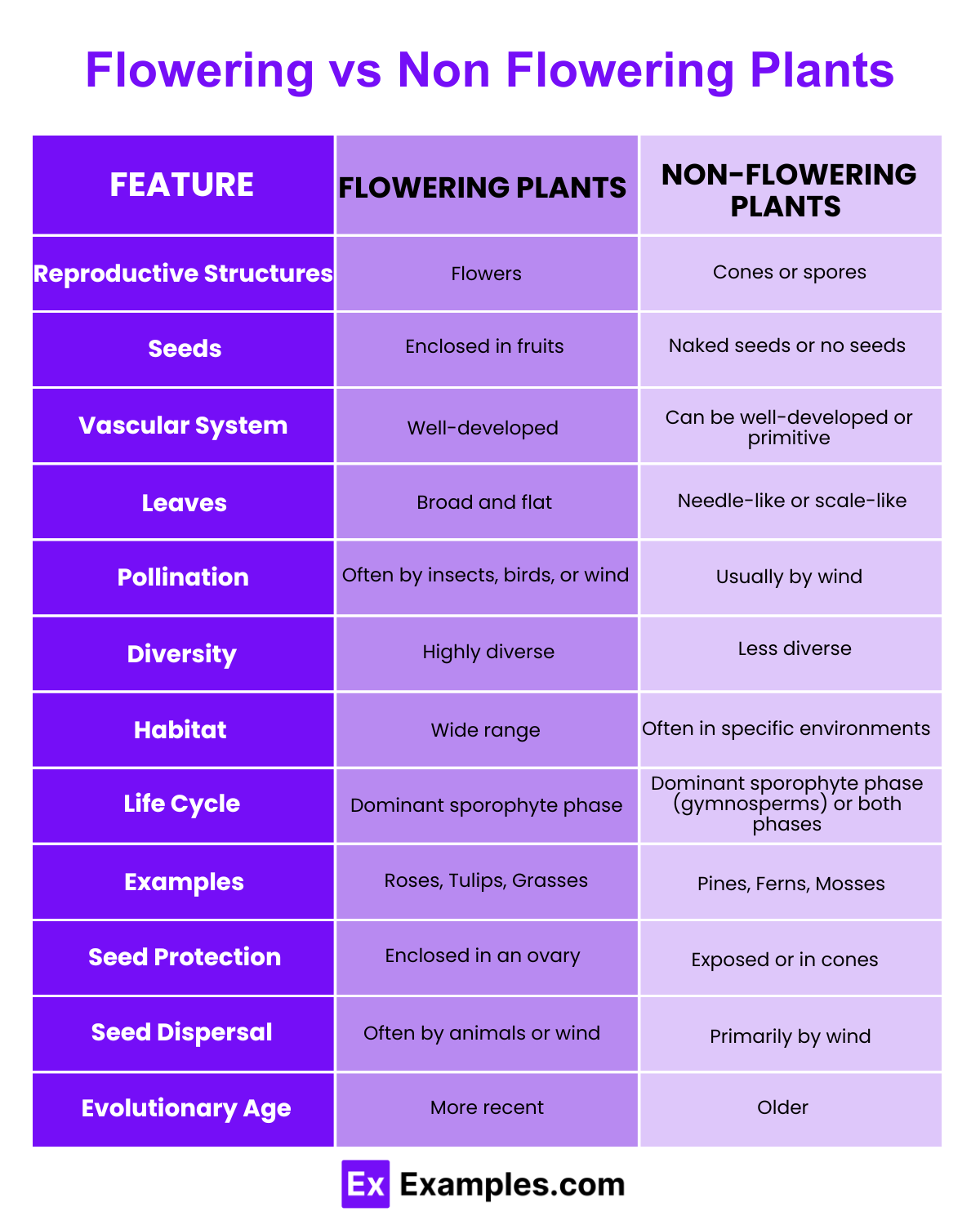
| Feature | Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) | Non-Flowering Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Reproductive Structures | Flowers | Spores or naked seeds |
| Seed Enclosure | Seeds enclosed within fruits | Seeds not enclosed (naked seeds) |
| Pollination | Typically involves flowers and pollinators | Usually does not involve flowers or pollinators |
| Examples | Roses, oak trees, tomatoes, sunflowers | Pines, ferns, mosses, algae |
| Vascular System | Well-developed vascular system (xylem and phloem) | Varies: Some have vascular systems (gymnosperms), others do not (mosses, algae) |
| Leaf Structure | Broad, flat leaves | Needle-like, scale-like, or frond-like leaves; some lack true leaves (mosses, algae) |
| Habitat | Wide range, including terrestrial and aquatic | Wide range, including terrestrial, aquatic, and extreme environments |
| Economic Importance | Major sources of food, medicine, timber, and ornamental plants | Timber, paper, biofuel, food, cosmetics |
| Ecological Role | Provide oxygen, habitats, and food for various organisms | Soil formation, erosion prevention, habitat and food sources |
| Fertilization | Double fertilization (produces zygote and endosperm) | Single fertilization (produces only the zygote) |
Despite their differences, flowering and non-flowering plants share several key similarities. These common features highlight their fundamental roles in the plant kingdom and their evolutionary connections.
Flowering plants, or angiosperms, produce flowers and seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are the most diverse plant group.
Non-flowering plants, or gymnosperms, reproduce through spores or naked seeds not enclosed in a fruit. Examples include ferns and conifers.
Flowering plants reproduce sexually through pollination, leading to seed formation within fruits.
Non-flowering plants reproduce via spores or seeds that are exposed, often on cones or other structures.
Examples of flowering plants include roses, lilies, and apple trees.
Examples of non-flowering plants include ferns, mosses, and pine trees.
The main difference is that flowering plants produce flowers and fruits, while non-flowering plants do not.
No, not all trees are flowering plants. Some, like pine trees, are non-flowering.
No, non-flowering plants do not produce fruits; they produce seeds or spores directly.
Flowering plants are more diverse due to their advanced reproductive structures and strategies, including flowers and fruits, which enhance seed dispersal.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a characteristic of flowering plants?
They produce seeds in cones
They reproduce through spores
They produce flowers
They have no vascular system
Which group of plants is known as gymnosperms?
Flowering plants
Non-flowering plants
Ferns
Mosses
An example of a flowering plant is:
Pine tree
Rose bush
Fern
Moss
Non-flowering plants reproduce through:
Seeds enclosed in fruit
Flowers
Spores or naked seeds
Buds
Which part of a flowering plant contains the reproductive organs?
Roots
Stems
Leaves
Flowers
Which of the following is an example of a non-flowering plant?
Sunflower
Pine tree
Tulip
Dandelion
Which of the following produces seeds within a fruit?
Ferns
Mosses
Angiosperms
Gymnosperms
What do gymnosperms use for reproduction?
Flowers
Cones
Fruits
Tubers
Which of the following is a key difference between flowering and non-flowering plants?
Presence of a vascular system
Ability to photosynthesize
Method of seed production
Root structure
Which plant group is known for producing colorful petals to attract pollinators?
Ferns
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Mosses
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

