What is the primary difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Number of chromosomes
Type of membrane
Shape of the cell
Size of the nucleus

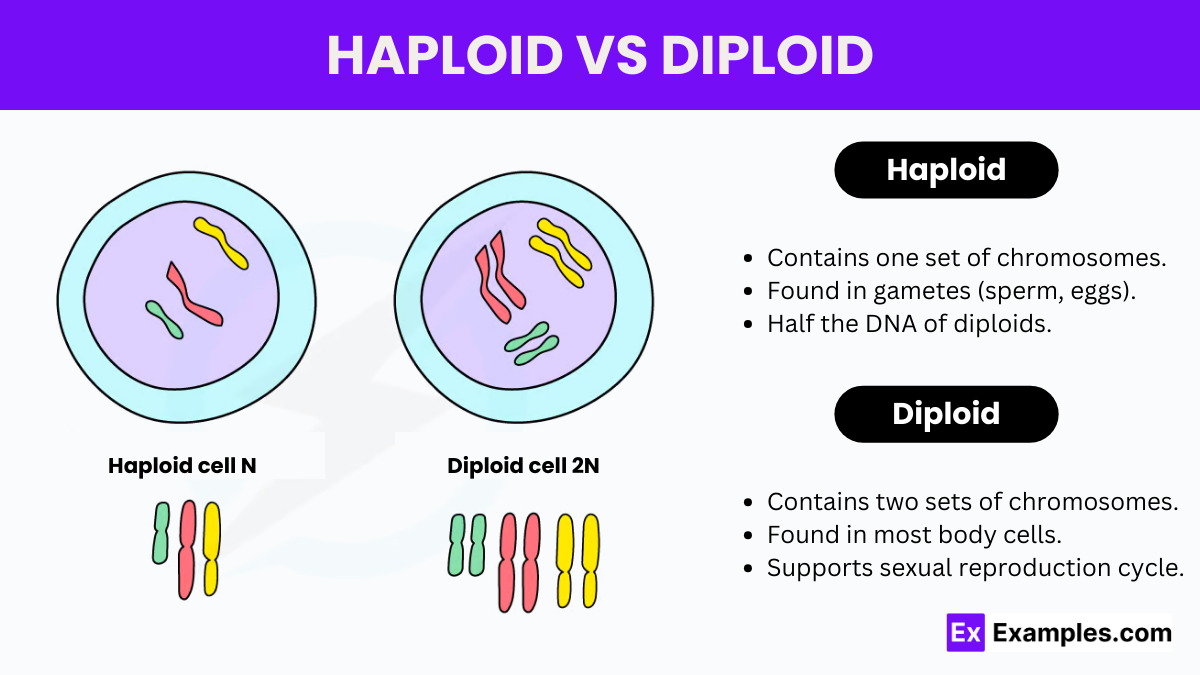
Haploid and diploid represent two fundamental types of chromosomal configurations in organisms, essential for understanding the basics of genetics and reproduction. Both terms describe the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell’s nucleus and are key to how organisms grow, reproduce, and evolve. Despite serving the primary function of genetic material storage and management, the ways in which these two chromosomal setups function and contribute to life processes are markedly different.
Haploid cells contain one complete set of chromosomes, which means each chromosome is unique with no pairs. Haploid is symbolized as ‘n’. Commonly, haploid cells are seen in the reproductive cells (gametes) of both animals and plants. These cells play a crucial role in sexual reproduction, where they ensure genetic diversity through recombination and fusion of gametes.
Diploid cells, symbolized as ‘2n’, have two complete sets of chromosomes—one from each parent. This configuration is typical in somatic cells (non-reproductive) of most animals and plants. Diploid cells are crucial for asexual reproduction and developmental processes, where cell division needs to preserve genetic information across generations.
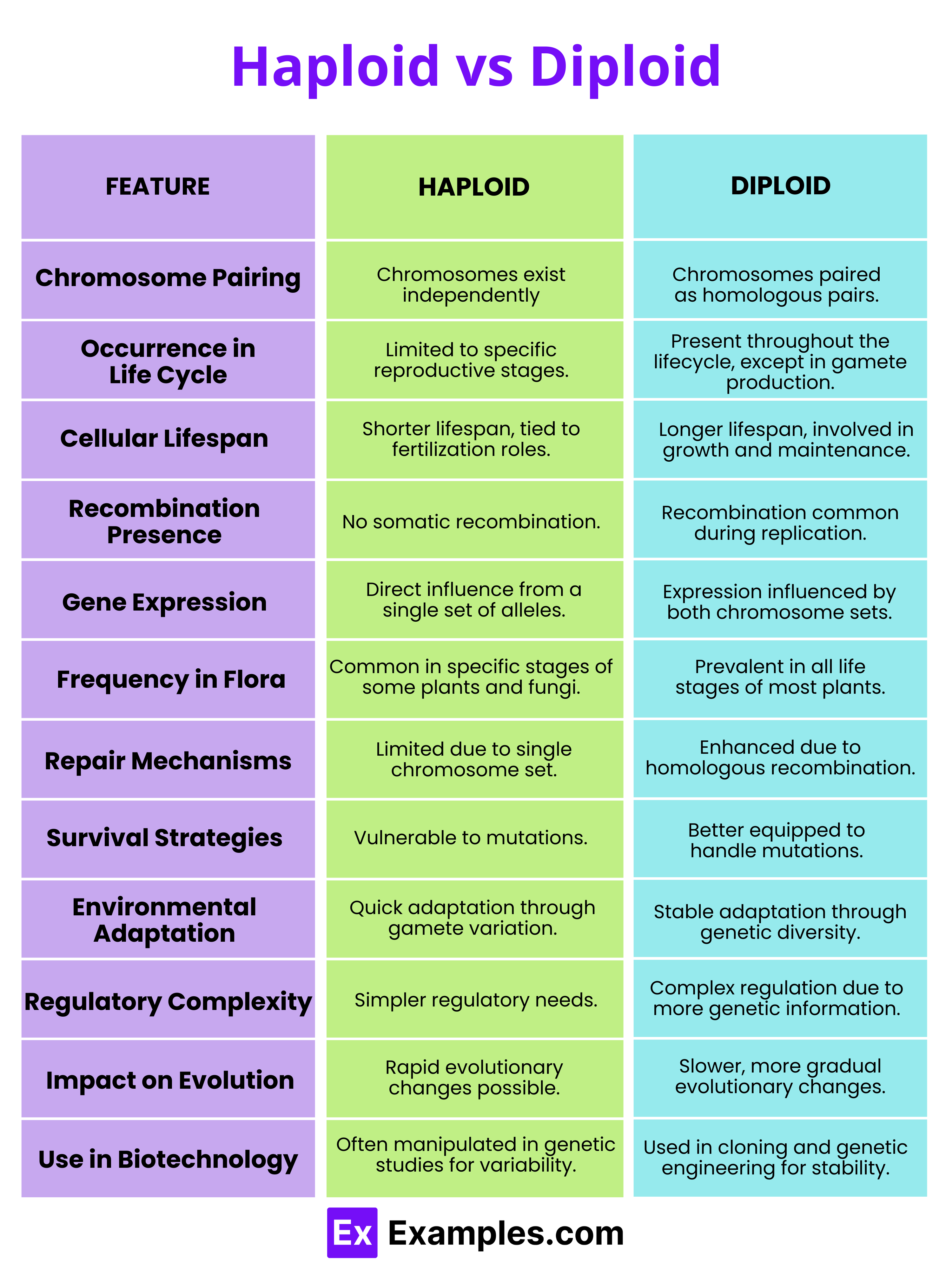
| Aspect | Haploid | Diploid |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Chromosome Sets | Contains one set of chromosomes (n). | Contains two sets of chromosomes (2n). |
| Cell Division Process | Formed by the process of meiosis. | Undergo mitosis. |
| Role in Organisms | In higher organisms like humans, used primarily for sex cells. | In higher organisms like humans, all other cells beside sex cells are diploid. |
| Examples of Cells | Gametes (male or female germ cells). | Blood cells, skin cells, muscle cells (known as somatic cells). |
| Genetic Material | Carries half the genetic material necessary for a complete organism. | Contains the full genetic complement required for a viable organism. |
| Stability | Less genetic stability due to having a single set of chromosomes. | More genetically stable with pairs of homologous chromosomes providing a backup. |
| Function in Reproduction | Involved in the formation of gametes for sexual reproduction. | Involved in general growth and repair through mitotic processes. |
| Genetic Diversity | Promotes genetic diversity through sexual reproduction. | Ensures genetic stability and consistency through asexual reproduction and growth. |
| Role in Development | Limited to reproduction and not involved in general developmental processes. | Crucial for the development, growth, and maintenance of the body. |
| Cellular Examples in Humans | Sperm and egg cells. | Most body cells, including cells in the heart, liver, and brain. |
Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes (2n), common in somatic cells; haploid cells (n) have one, seen in gametes.
Sperm is haploid, containing one set of chromosomes, essential for sexual reproduction.
No, haploid refers to cells with one set of chromosomes, not four; the term “haploid” derives from “single.”
Egg cells are haploid, carrying a single set of chromosomes to combine with sperm during fertilization.
Skin cells are diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes, typical of most body cells for genetic stability.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Number of chromosomes
Type of membrane
Shape of the cell
Size of the nucleus
Which of the following cells is haploid?
Muscle cell
Skin cell
Sperm cell
Nerve cell
What is the chromosome number of diploid human cells?
23
32
46
64
During which process do cells become haploid?
Mitosis
Meiosis
Binary fission
Budding
Which type of cell division results in the formation of diploid cells?
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
Mitosis
Binary fission
In humans, which cells are diploid?
Gametes
Somatic cells
Red blood cells
Platelets
Which phase of meiosis reduces the chromosome number from diploid to haploid?
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Which of the following is true about diploid cells?
They have half the number of chromosomes of haploid cells.
They are produced by meiosis.
They contain two sets of chromosomes.
They only occur in plants.
What is the diploid number of chromosomes in a fruit fly, if its haploid number is 4?
2
4
6
8
In plants, which structure is typically haploid?
Root
Leaf
Pollen
Stem
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

