Which of the following is considered a macronutrient?
Iron
Vitamin C
Carbohydrates
Sodium

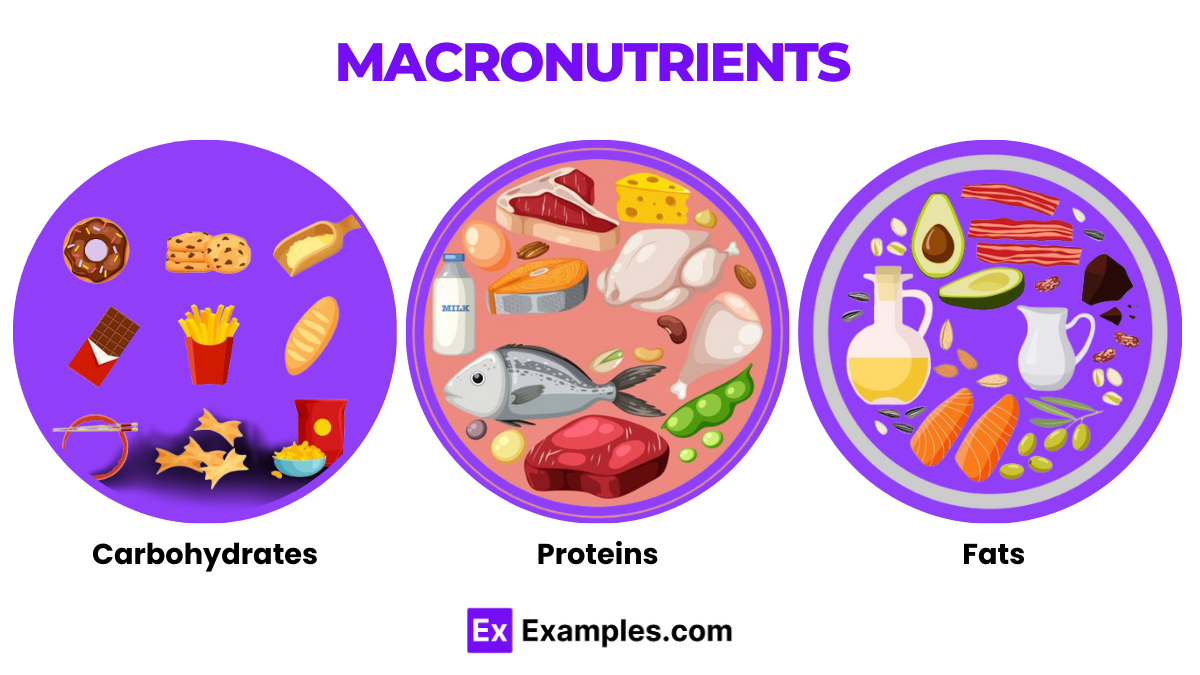
Macronutrients are the essential nutrients required in larger amounts that are crucial for energy production and overall health. These include fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Each macronutrient serves distinct functions: fats are vital for supporting cell growth and protecting organs, proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, and carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body. It’s important to maintain a balanced intake of these nutrients to ensure optimal health and effective bodily functions. While the exact balance can vary based on individual needs, a general guideline is to follow proportions similar to those recommended in dietary guides like the national Eatwell guide, which helps in achieving a well-rounded diet.
Macronutrients, commonly referred to as “macros,” are essential nutrients that the human body requires in large amounts to sustain energy levels, support metabolic processes, and maintain structural integrity. The three primary macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Each macronutrient also contributes calories:
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body. They break down into glucose, which fuels our cells, tissues, and organs. Foods rich in carbohydrates include fruits, vegetables, grains, and sugary snacks. We categorize carbohydrates as simple or complex, depending on their chemical structure and how quickly the body absorbs them. Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like fruit and candy, provide quick energy. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, present in whole grains and legumes, offer sustained energy due to their longer digestive times.
Proteins serve as the building blocks for muscles, skin, enzymes, and hormones. They are vital for repairing tissues and supporting immune function. Dietary proteins are composed of amino acids, some of which are essential because the body cannot synthesize them; they must be ingested through food. High-protein foods include meat, fish, dairy, legumes, and nuts. Consuming a variety of protein sources ensures that we obtain all the essential amino acids our bodies require.
Fats, often misunderstood, are essential for several body functions. They provide energy, protect our organs, support cell growth, and help in the absorption of nutrients. Fats also play a key role in hormone production and the maintenance of healthy skin and hair. There are several types of fats: saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Unsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocado, and fish, are considered beneficial for heart health. Saturated fats, typical in butter and lard, should be consumed in moderation. Trans fats, mostly in processed foods, are best avoided due to their negative effects on cholesterol levels and heart health.
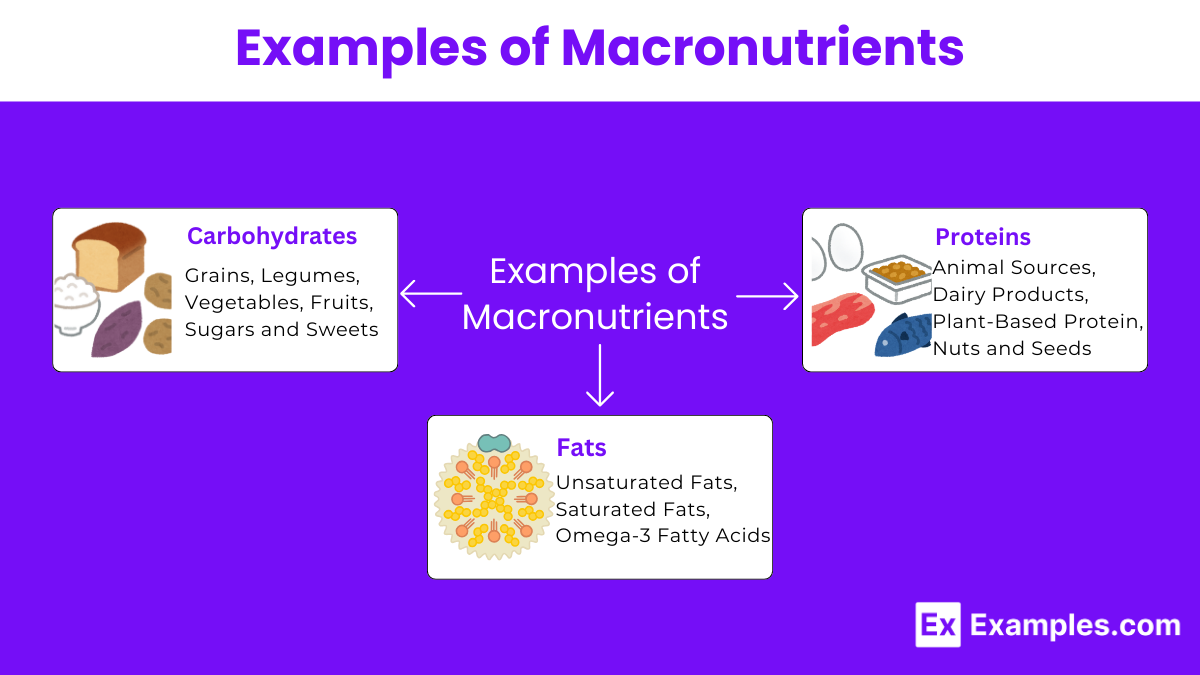
Macronutrients are essential nutrients that the human body requires in large amounts to maintain its functions and energy levels. They are fundamental to providing the energy necessary for daily activities and supporting overall health. The three primary categories of macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, each serving unique roles within the body. Below, we explore each of these macronutrients, providing examples and discussing their importance.
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by the body’s cells for energy. Common sources of carbohydrates include:
Proteins are crucial for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They are also vital in the creation of hormones, enzymes, and other body chemicals. Protein-rich foods include:
Fats are necessary for long-term energy storage, insulation, and protection of vital organs. They also play a crucial role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Examples of healthy fats include:
Carbohydrates provide the primary energy source for your body. During digestion, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which serves as a fundamental energy supply for all cells. In particular, the brain relies heavily on glucose as its main source of fuel. Additionally, carbohydrates play a key role in the health of the digestive system and aid in the regulation of blood glucose levels.
Proteins are crucial for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. Enzymes, which catalyze all biochemical reactions, and hormones, which regulate physiological processes, are primarily made of proteins. Proteins also play significant roles in immune function, as they are essential components of antibodies and immune system cells.
Fats are essential for numerous bodily functions. They provide a concentrated source of energy, with one gram of fat yielding about nine calories, more than twice the calories provided by carbohydrates or proteins. Fats are vital for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and are also crucial for cushioning organs and insulating the body. Additionally, fats contribute to cell membrane structure and the production of important hormones.
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are found in:
Proteins are crucial for the growth and repair of tissues, and they play an integral role in immune function and hormone production. Protein sources include:
Fats are necessary for energy, supporting cell growth, protecting organs, and keeping the body warm. They are also essential for absorbing certain nutrients. Sources of healthy fats include:
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are essential macronutrients that serve key roles in the human body. Carbohydrates, found in grains like rice and oats, fruits such as bananas, and vegetables like potatoes, are the primary source of energy, breaking down into glucose to fuel brain function and physical activities. Proteins, crucial for the growth and repair of tissues, are abundant in both animal sources like chicken and fish, and plant sources such as tofu and quinoa. Fats, necessary for energy storage and nutrient absorption, vary from saturated fats in dairy products to unsaturated fats in avocados and olive oil, each playing a critical role in maintaining overall health.
Macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are essential for plant health, supporting everything from amino acid production and energy conversion to cell structure and metabolism. Similarly, micronutrients such as iron, manganese, boron, and others play crucial roles in chlorophyll formation, enzyme activation, and overall physiological functions, though they are required in smaller amounts. These nutrients together ensure plants perform vital processes such as photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and nitrogen fixation efficiently
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body. They fuel the brain, kidneys, heart muscles, and central nervous system. Here are some key benefits of carbohydrates:
Proteins are critical for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They also play roles in hormonal and enzyme systems. Here are the benefits of proteins:
Fats are often misunderstood, but they are crucial for overall health. They serve several vital functions in the body:
Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals crucial for body functions but not produced internally.
A popular macro ratio for weight loss is 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fats.
Yes, all three macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats) are essential for balanced health and proper body function.
No single macronutrient is most important; carbohydrates, proteins, and fats each play unique, vital roles in health.
Lean chicken, fish, beans, and legumes are among the healthiest protein sources, offering essential nutrients with lower fat.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is considered a macronutrient?
Iron
Vitamin C
Carbohydrates
Sodium
Which macronutrient is primarily responsible for muscle repair and growth?
Proteins
Fats
Carbohydrates
Vitamins
What is the main function of carbohydrates in the human body?
To build muscle mass
To store vitamins
To provide energy
To regulate water balance
Which macronutrient contains the highest amount of calories per gram?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fats
Water
Which of the following macronutrients is important for insulating the body and protecting organs?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fats
Water
Which macronutrient is a key component of enzymes and hormones?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fats
Minerals
Which macronutrient can be stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen?
Fats
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Vitamins
What is the primary function of dietary fats in the body?
To strengthen bones
To support cell growth and absorb certain vitamins
To transport oxygen
To form DNA
Which macronutrient should make up the largest portion of a balanced diet?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fats
Water
Which of the following macronutrients is considered essential for the structure of cell membranes?
Proteins
Fats
Carbohydrates
Minerals
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

