Which of the following is a unicellular organism?
Mushroom
Algae
Bacteria
Fern

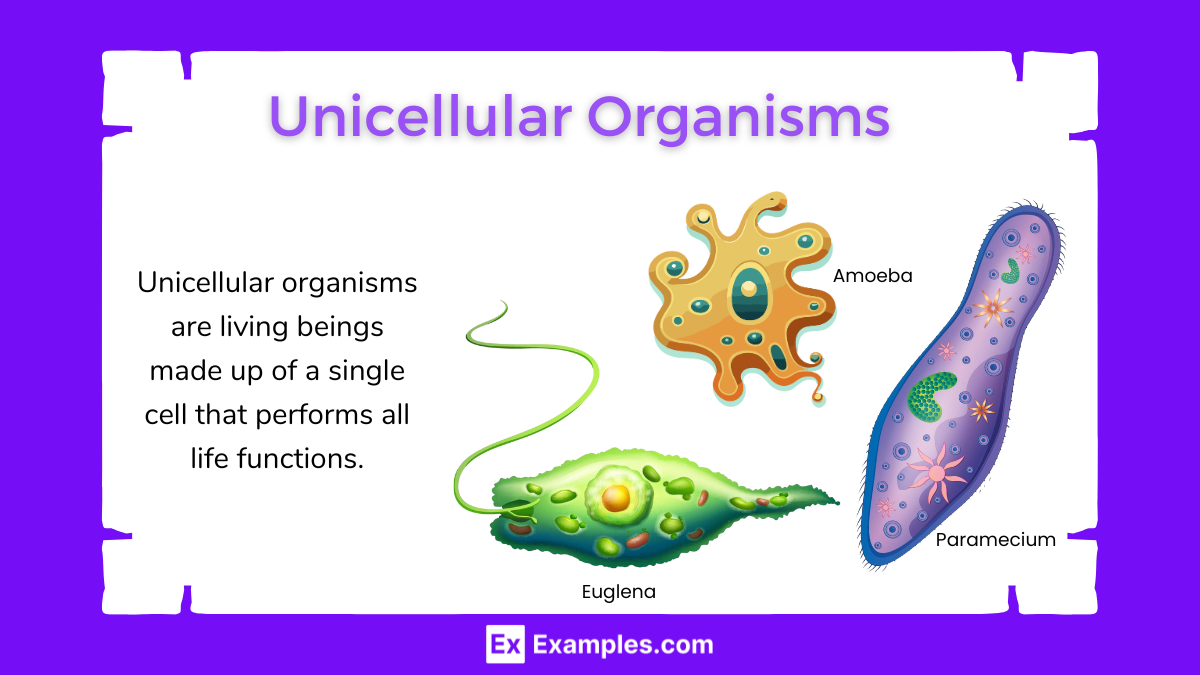
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell that performs all the necessary functions for life. These organisms represent the simplest form of life, yet they exhibit remarkable diversity and complexity. Bacteria, archaea, protozoa, and some algae and fungi fall into this category. They thrive in various environments, from deep oceans to the human gut, showcasing incredible adaptability. Unicellular organisms play essential roles in ecosystems, such as decomposing organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and forming the base of many food chains. Understanding these organisms provides insight into the origins and evolution of life on Earth.
Unicellular organisms, also known as single-celled organisms, are living entities that consist of only one cell. This single cell performs all the necessary functions for the organism’s survival, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and response to environmental stimuli. Unicellular organisms are the simplest form of life and can be found in various environments, from extreme conditions like hot springs and deep-sea vents to more common habitats like soil, water, and inside other organisms.
Unicellular organisms have diverse cell structures, but they generally fall into two main categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Here is an overview of their key structural components:
Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria and archaea are the main examples of prokaryotic unicellular organisms.
Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Examples include protozoa, algae, and fungi.
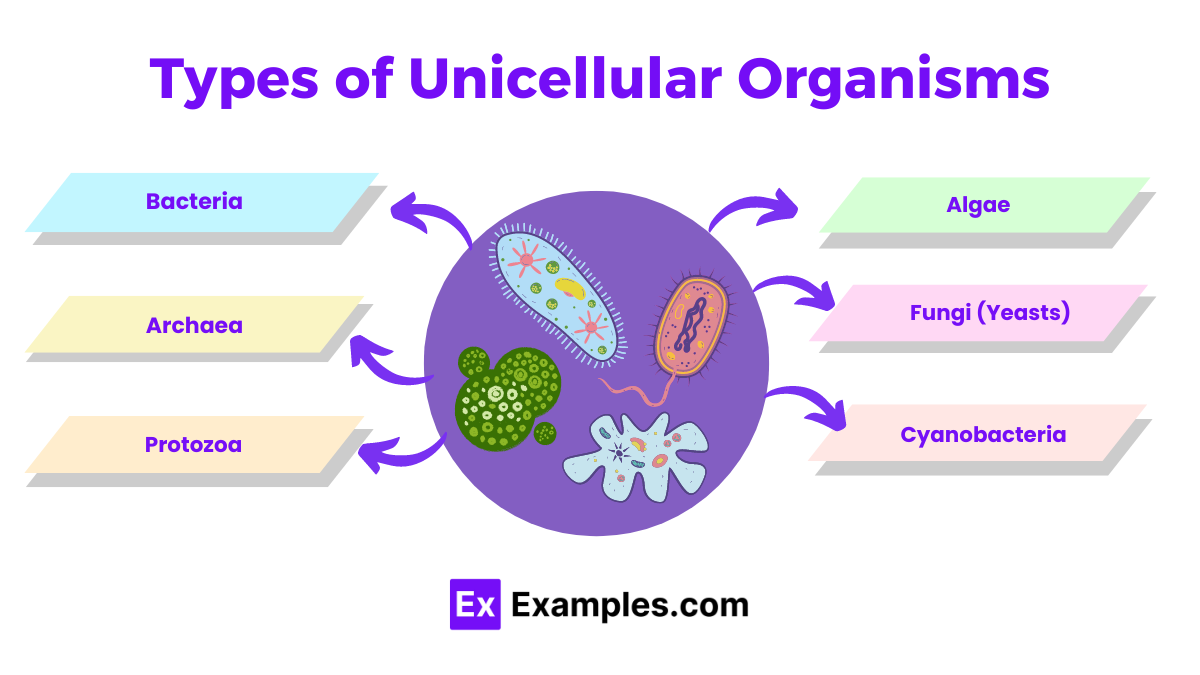
Unicellular organisms, also known as single-celled organisms, are living entities that consist of a single cell. These organisms perform all necessary functions for life within one cell. They are incredibly diverse and can be found in almost every environment on Earth. Here are the primary types of unicellular organisms:
Bacteria are among the most well-known and diverse unicellular organisms. They can be found in various environments, including soil, water, and inside other organisms.
Archaea are similar to bacteria but have distinct genetic and biochemical characteristics. They often inhabit extreme environments.
Protozoa are a diverse group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They often exhibit animal-like behaviors such as movement and predation.
Algae are primarily photosynthetic unicellular organisms. They can be found in aquatic environments and are critical to the food chain.
Yeasts are unicellular fungi. They are important in fermentation processes and can also be pathogenic.
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are photosynthetic bacteria that contribute significantly to oxygen production.
| Type | Cell Type | Notable Features | Examples | Reproduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic | No nucleus, diverse habitats | E. coli, Streptococcus | Binary fission |
| Archaea | Prokaryotic | Unique membrane lipids | Halobacterium, Thermoplasma | Binary fission |
| Protozoa | Eukaryotic | Animal-like behaviors | Amoeba, Paramecium | Mostly asexual |
| Algae | Eukaryotic | Photosynthetic, aquatic | Chlamydomonas, Diatoms | Asexual and sexual |
| Fungi (Yeasts) | Eukaryotic | Fermentation, pathogenic | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Budding, sexual |
| Cyanobacteria | Prokaryotic | Photosynthetic, oxygen production | Anabaena, Spirulina | Binary fission |
Unicellular organisms reproduce primarily through asexual means, ensuring rapid population growth and adaptation. Some unicellular organisms also engage in sexual reproduction under certain conditions. Here are the main methods of reproduction in unicellular organisms:
In unicellular organisms, nutrition involves the intake of nutrients, their digestion, and assimilation to sustain life processes. Here are the key points:
Examples of unicellular organisms include amoebas, which use pseudopodia to engulf food, and paramecia, which use cilia to direct food into an oral groove.
Unicellular organisms utilize two main types of respiration:
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen. It is the most efficient way to produce energy, yielding more ATP (adenosine triphosphate) compared to anaerobic processes. The general equation for aerobic respiration is: Glucose+Oxygen→Carbon Dioxide+Water+Energy (ATP)Glucose+Oxygen→Carbon Dioxide+Water+Energy (ATP)
Examples:
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. This process is less efficient, producing less ATP and often resulting in byproducts like alcohol or lactic acid. The general equation for anaerobic respiration in yeasts is: Glucose→Ethanol+Carbon Dioxide+Energy (ATP)Glucose→Ethanol+Carbon Dioxide+Energy (ATP)
Examples:
Unicellular organisms are typically composed of either prokaryotic cells (like bacteria and archaea) or eukaryotic cells (like many protozoa, unicellular algae, and fungi such as yeasts). Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and various organelles.
Unicellular organisms are living beings made up of a single cell that performs all life functions.
Examples include bacteria, archaea, protozoa, unicellular algae, and yeasts.
They reproduce primarily through asexual methods like binary fission, budding, or spore formation.
They thrive in diverse environments, from soil and water to extreme conditions like hot springs and deep-sea vents.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus (e.g., bacteria), while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus (e.g., protozoa).
They acquire nutrients through absorption, engulfing particles, or photosynthesis.
Yes, many move using structures like flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia.
They play crucial roles in ecosystems, such as decomposing matter, producing oxygen, and forming the base of food webs.
Identification methods include microscopy, staining, culture techniques, molecular methods, and biochemical tests.
They can be autotrophic (self-feeding via photosynthesis) or heterotrophic (feeding on organic matter).
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a unicellular organism?
Mushroom
Algae
Bacteria
Fern
What structure do most unicellular organisms use for movement?
Nucleus
Cilia or flagella
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Which of these is a function of the cell membrane in unicellular organisms?
Producing energy
Controlling movement of substances in and out of the cell
Storing genetic information
Replicating DNA
Amoebas move and capture food using:
Flagella
Cilia
Pseudopodia
Chloroplasts
Which process do unicellular organisms use to reproduce?
Binary fission
Pollination
Photosynthesis
Respiration
What is the main function of the nucleus in a unicellular organism?
Locomotion
Digestion
Storing genetic material
Photosynthesis
Which of the following is an example of a eukaryotic unicellular organism?
Bacteria
Virus
Yeast
Archaea
Unicellular organisms that can perform photosynthesis are known as:
Heterotrophs
Autotrophs
Parasites
Decomposers
Which unicellular organism is often used in baking and brewing?
Paramecium
Amoeba
Yeast
Bacteria
The study of unicellular organisms falls under which branch of biology?
Botany
Zoology
Microbiology
Ecology
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

