What is the primary function of Vitamin D in the human body?
Promotes red blood cell production
Enhances calcium absorption
Supports immune system function
Assists in protein synthesis

Vitamin D, often hailed as the “Sunshine Vitamin,” is unique because our bodies can produce it when exposed to sunlight. It’s also found in certain foods and supplements. This nutrient undergoes a two-step process in the body to become active, supporting crucial functions like calcium absorption for strong bones and immune system regulation. Available in two dietary forms, D2 and D3, Vitamin D’s absorption is efficient and essential for maintaining optimal health. While measuring Vitamin D levels can be challenging due to testing variability, it’s a key indicator of bone health and overall well-being. Vitamin D is a vital nutrient that supports a range of bodily functions, from bone health to immune response, underscoring its importance in our daily lives.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, supporting immune system health, and regulating muscle function. It’s unique because your body can produce it when exposed to sunlight. Besides sun exposure, you can obtain Vitamin D from certain foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, as well as dietary supplements. This vitamin plays a crucial role in calcium absorption in the gut, which is vital for bone growth and remodeling. Its importance extends beyond bone health, as emerging research suggests links to reduced risks of chronic diseases, including certain cancers and heart disease.
Vitamin D is classified as a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it can dissolve in fats and oils. This property allows Vitamin D to be stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver, making it available for use when needed, especially when sunlight exposure or dietary intake is limited. Fat-soluble vitamins differ from water-soluble ones, which need to be regularly consumed because they are not stored in the body to the same extent. Vitamin D’s role in calcium absorption, bone health, and immune function highlights its importance in maintaining overall health.
Vitamin D includes compounds like vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol), which are crucial for calcium, magnesium, and phosphate absorption. Both have a similar steroid structure, with vitamin D3 formed in the skin from 7-dehydrocholesterol under UV light and vitamin D2 coming from plants and fungi. The main difference between D2 and D3 lies in their side chains.
Once ingested or synthesized, vitamin D is converted in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the main circulating form. It’s further processed in the kidneys to the active form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which interacts with receptors in the body to regulate various biological functions, including calcium metabolism and immune response.
There are two main types of Vitamin D: Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol). Both types are crucial for maintaining optimum health, but they have different sources and functions in the body.
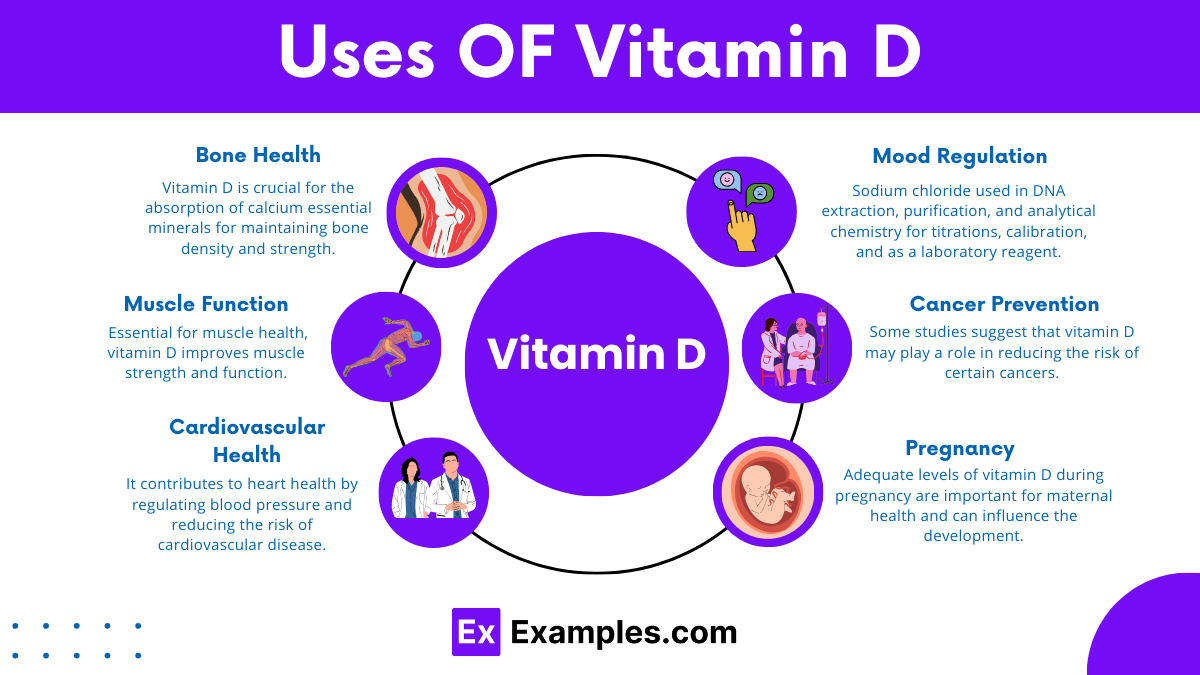
Vitamin D supports bone health, immune function, and calcium absorption, playing a key role in overall physical well-being.
Signs include fatigue, bone pain, muscle weakness, mood changes, and frequent infections, indicating potential deficiency.
To boost Vitamin D levels, seek sunlight exposure, consume fortified foods and fatty fish, and consider supplements.
Opt for Vitamin D3 as it’s more effective at raising and maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels in the body.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of Vitamin D in the human body?
Promotes red blood cell production
Enhances calcium absorption
Supports immune system function
Assists in protein synthesis
Which of the following is a natural source of Vitamin D?
Apples
Carrots
Salmon
Rice
How does the body produce Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight?
By absorbing ultraviolet B (UVB) rays
By absorbing ultraviolet A (UVA) rays
By converting Vitamin C
By converting cholesterol in the skin
What condition is commonly associated with Vitamin D deficiency in children?
Osteoporosis
Rickets
Scurvy
Pellagra
Which vitamin is often fortified in milk and other dairy products?Vitamin A
Vitamin A
Vitamin B12
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
What is a common symptom of Vitamin D deficiency?
Fatigue
Headaches
Muscle cramps
Joint pain
Which of the following foods is a poor source of Vitamin D?
Fortified cereal
Orange juice
Beef liver
Spinach
What is the recommended way to maintain adequate Vitamin D levels in people who have limited sun exposure?
Increase intake of Vitamin C
Take Vitamin D supplements
Eat more fruits
Use sunscreen
Which organ in the body is primarily responsible for converting Vitamin D to its active form?
Liver
Kidneys
Heart
Pancreas
What is the term for the condition where bones become brittle due to Vitamin D deficiency in adults?
Osteomalacia
Rickets
Scurvy
Beriberi
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

