Which type of muscle is under conscious control?
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
All of the above

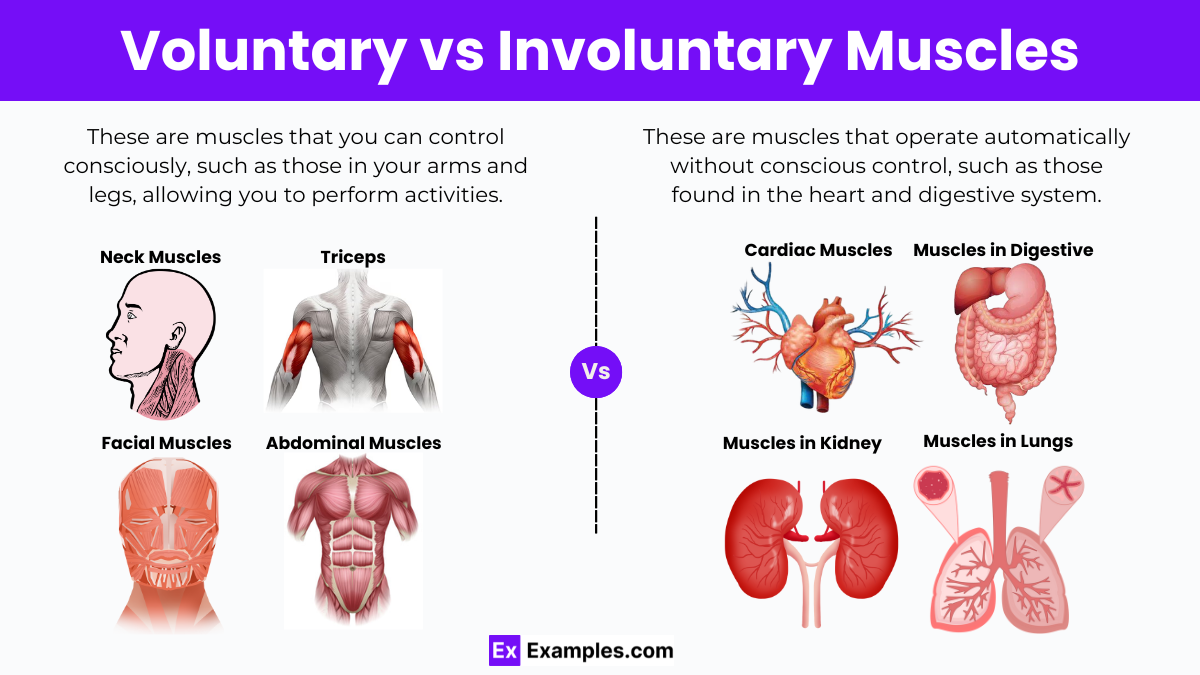
The human body boasts over 600 muscles, constituting approximately 35% of our body mass. These muscles are essential for movement and are categorized based on our ability to control them consciously. Voluntary muscles, such as those in our arms, are under our direct control and respond to conscious commands—think of moving your hand to catch a ball or bending your arm. In contrast, involuntary muscles operate without our conscious input. These muscles are crucial for automatic bodily functions, such as heartbeats and the digestion process, where smooth muscle in the digestive tract helps move food via peristalsis. Both types of muscles are vital, each fulfilling specialized roles that enable various body functions, seamlessly integrating into our daily lives without the need for constant awareness.
You can control voluntary muscles, such as those in your arms and legs. They are long, tube-shaped, and contain multiple nuclei. These muscles attach to your bones and skin and help you move by contracting and relaxing. The brain and the somatic nervous system control these muscles, allowing you to perform actions like walking, picking up objects, and smiling. However, because they exert a lot of effort, voluntary muscles can become tired and need breaks to recover.
Involuntary muscles operate without your conscious control and are present in many internal organs like your heart and stomach. There are two types:
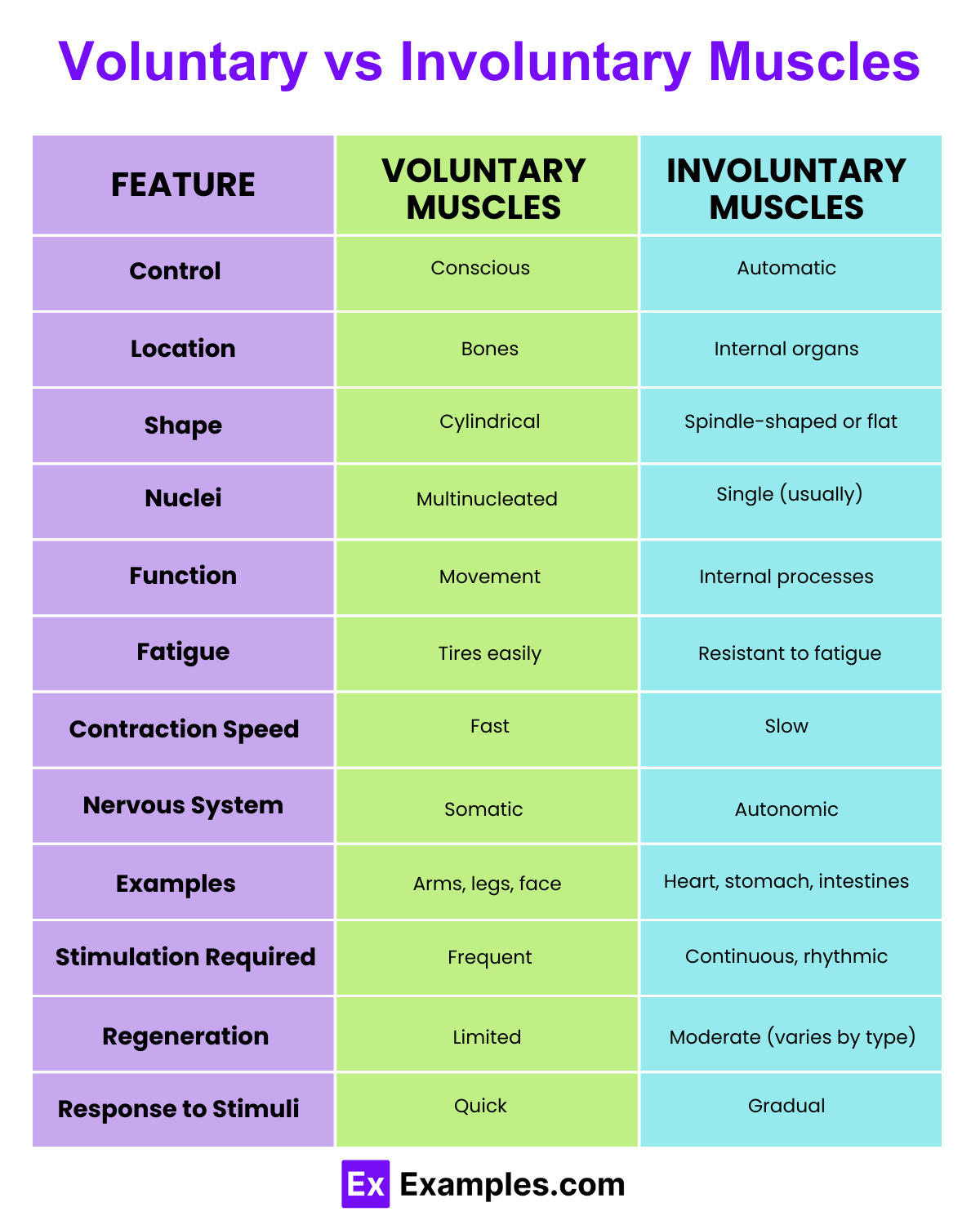
| Feature | Voluntary Muscles | Involuntary Muscles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Muscles that can be controlled consciously. | Muscles that operate without conscious control. |
| Control | Under conscious control. | Automatically controlled by the autonomic nervous system. |
| Types of Muscles | Mainly skeletal muscles. | Smooth muscles and cardiac muscles. |
| Location | Attached to bones and mainly found in arms, legs, and the body’s external parts. | Found in the walls of internal organs such as stomach, intestines, and blood vessels; also includes the heart. |
| Function | Responsible for movements like walking, grabbing, talking, and facial expressions. | Manage functions like digestion, blood flow, and respiration. |
| Appearance | Striated with a regular pattern of light and dark bands. | Non-striated (smooth muscles) and striated (cardiac muscles). |
| Speed of Contraction | Fast and forceful contractions. | Slower and sustained contractions. |
| Fatigue | Tends to fatigue easily. | Designed for endurance, rarely fatigues. |
| Examples | Muscles in arms like biceps and triceps; muscles in legs like quadriceps. | Stomach muscles, muscles in the walls of blood vessels, heart muscles. |
| Stimulation | Usually stimulated by the nervous system through voluntary signals. | Stimulated automatically or through hormonal or involuntary neural signals. |
| Regeneration Ability | Limited regeneration ability; relies on muscle hypertrophy. | Varies; smooth muscles can regenerate better than skeletal muscles. |
| Response to Exercise | Increases in size and strength with exercise. | Does not significantly change in size with exercise, but function can improve. |
Voluntary muscles are consciously controlled, like arm and leg muscles. Involuntary muscles operate automatically, such as heart and digestive muscles.
Examples include the heart muscle, stomach muscles, intestinal muscles, bladder muscles, and muscles in blood vessel walls.
Voluntary motor muscles are consciously controlled for actions like walking. Involuntary motor muscles function autonomously, regulating internal processes.
The three types of muscles are skeletal (voluntary), smooth (involuntary), and cardiac (involuntary).
Voluntary: biceps, triceps, quadriceps, hamstrings, and facial muscles. Involuntary: cardiac muscle, smooth muscles in intestines, bladder, respiratory muscles, and muscles in arteries.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which type of muscle is under conscious control?
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
All of the above
Which muscle type is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body?
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Voluntary muscle
Which of the following is an example of an involuntary muscle?
Biceps
Triceps
Heart
Hamstrings
Where are smooth muscles primarily found?
Attached to bones
In the walls of internal organs
In the heart
In the brain
Which of the following muscles are not controlled voluntarily?
Quadriceps
Deltoid
Intestinal muscles
Pectorals
What type of muscle tissue is involved in facial expressions?
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
Involuntary muscle
Which statement is true about involuntary muscles?
They are consciously controlled.
They include muscles like biceps and triceps.
They operate automatically without conscious effort.
They are only found in the limbs.
The primary function of voluntary muscles is to:
Pump blood
Digest food
Enable body movement
Regulate breathing
Which muscle type is striated and found in the heart?
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Voluntary muscle
Voluntary muscles are primarily controlled by which part of the nervous system?
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Central nervous system
Enteric nervous system
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

