Which of the following best describes a national park?
An area for the conservation of specific animal species
A protected area where human activities are strictly regulated
A place where hunting is allowed
A private property


Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are crucial for conservation but serve different functions. Wildlife sanctuaries focus on protecting specific species or habitats, often allowing limited human activity to coexist with wildlife. In contrast, national parks aim to preserve ecosystems on a broader scale, offering more structured environments for public recreation and education, all under stricter legal protections. This article highlights the distinct roles and regulations of each, emphasizing their importance in biodiversity conservation.
A wildlife sanctuary primarily aims to protect particular species of wildlife. It offers a safe habitat where animals can live in a protected environment, usually focusing on endangered or threatened species.
Keoladeo National Park, also known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary in Rajasthan, India, is a prime example of a wildlife sanctuary dedicated to the conservation of avian species. Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, it provides a diverse habitat conducive to over 370 species of birds, including the critically endangered Siberian Crane during its migratory season. This sanctuary not only supports significant biodiversity but also offers educational and ecotourism opportunities, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices to address challenges like water management and climate change impacts. Keoladeo illustrates the vital role of wildlife sanctuaries in global conservation efforts.
National parks are areas designated to protect the natural environment and provide recreation opportunities for the public. They encompass larger areas than wildlife sanctaries and often include ecosystems with high biodiversity.
Yellowstone National Park, established in 1872, is one of the most iconic examples of a national park in the United States. Spanning across Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho, Yellowstone is renowned for its vast wildlife, including grizzly bears, wolves, and herds of bison and elk, as well as its geothermal features like the famous Old Faithful geyser. This park not only serves as a refuge for numerous species but also provides a wide range of recreational activities such as hiking, camping, and sightseeing, all while promoting conservation education and ecological research.
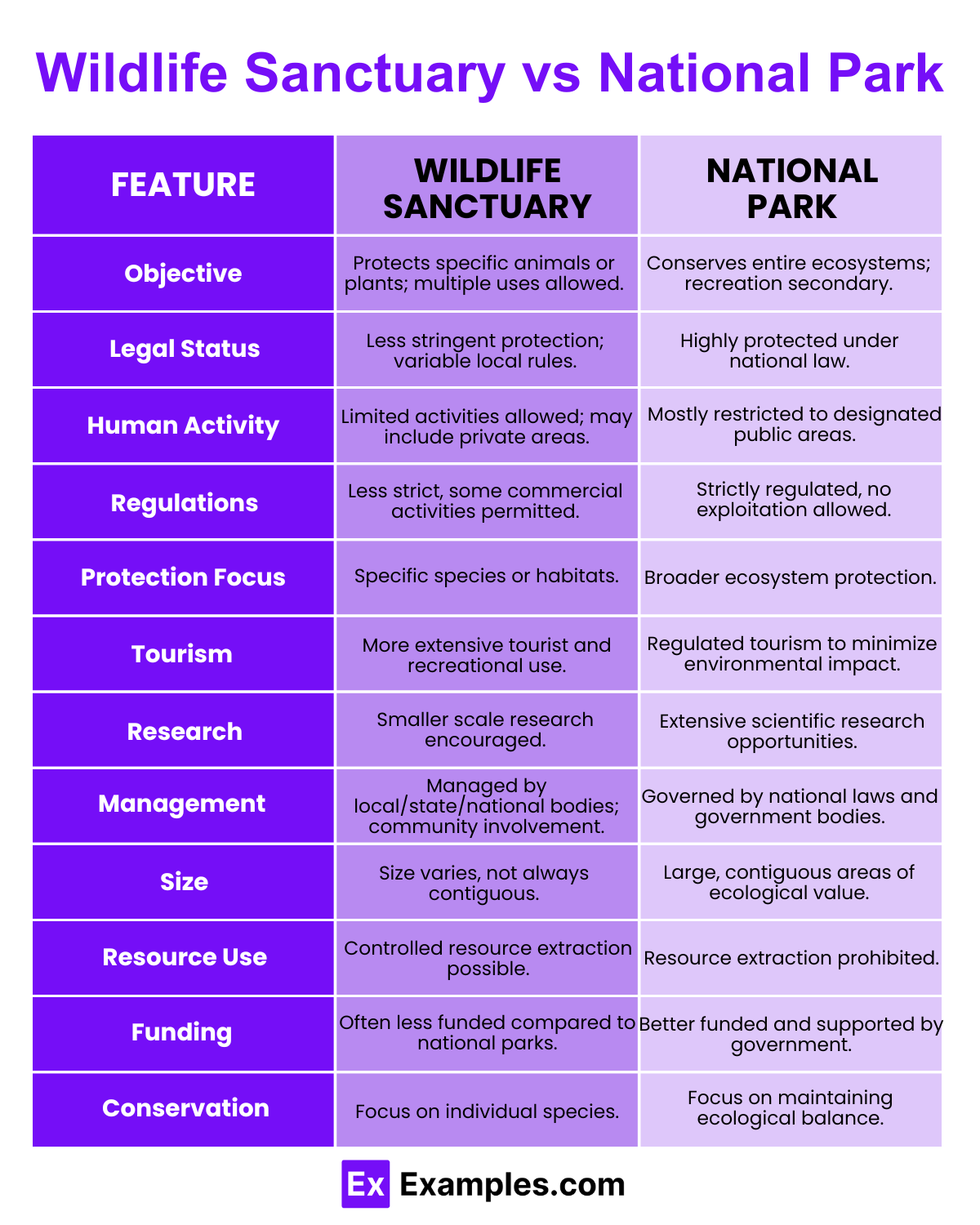
| Aspect | Wildlife Sanctuary | National Park |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A wildlife sanctuary is a protected area that is established for the purpose of conserving wildlife. It allows limited human activity. | A national park is a protected area designated to conserve the natural environment and its wildlife. It often restricts human activities more strictly than sanctuaries. |
| Objective | The primary objective is to ensure the conservation of specific wildlife species, which can include both flora and fauna. Limited human activity is permitted as long as it does not adversely affect the wildlife. | The main goal is to preserve biodiversity, landscapes, and ecosystems in a more holistic manner. This includes educational, recreational, and research purposes with stricter regulations. |
| Legal Regulations | Wildlife sanctuaries are protected under the governing country’s wildlife protection acts but may have fewer restrictions compared to national parks. | National parks have strict regulations under the applicable national laws to ensure the protection of the natural habitat and encompass larger areas of protection. |
| Human Activities | Limited human activities such as grazing, firewood collection, and forestry are sometimes permitted if they do not interfere with conservation efforts. | Human activities are more controlled, with restrictions on grazing, hunting, and forestry. Recreational activities like hiking and sightseeing are managed to minimize ecological impact. |
| Area Coverage | Often covers a smaller area than national parks. The area can be expanded or reduced based on the conservation needs. | Generally covers a larger area that includes ecosystems that are significant for conservation. The boundaries are less likely to be altered frequently. |
| Flora and Fauna | Focuses more on the protection of specific animals and their habitats. Plant life is protected as well, but secondarily to fauna. | Protects entire ecosystems, which includes a wider variety of plants and animals as a collective unit. |
| Public Access | Public access is usually more restricted than in national parks, aimed primarily at protecting wildlife. | While public access is allowed, it is regulated to ensure that it does not affect the natural environment. Educational and recreational visits are common, but with strict supervision. |
| Management | Managed by local or national entities that may allow for some sustainable resource extraction under strict regulation. | Managed by national governments and often has higher funding and resources for conservation, research, and public education. |
| Examples | Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary in India, Gir National Park (Wildlife Sanctuary part) in India. | Yellowstone National Park in the USA, Kruger National Park in South Africa. |
Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks share several fundamental similarities that underscore their roles in conservation and environmental protection:
Both wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are established with the primary goal of conserving nature. They serve as safe havens for flora and fauna, helping to protect ecosystems from the adverse effects of industrialization and human encroachment.
In both types of protected areas, human activities are regulated to minimize impact on the natural environment. This includes guidelines on tourism, educational activities, and sometimes even research, ensuring that such activities are conducted in a way that does not harm the wildlife or the habitat.
Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks enjoy legal protection under various national and sometimes international laws. These legal frameworks help to ensure long-term preservation of their ecological wealth and provide mechanisms for enforcement against poaching, habitat destruction, and illegal wildlife trade.
Both sanctuaries and parks play crucial roles in biodiversity conservation. They protect different species and their habitats, contributing to the maintenance of ecological balance. This is vital for the preservation of biodiversity, which benefits environmental health globally.
Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are important educational resources. They offer recreational opportunities that allow people to connect with nature, which is essential for raising awareness about environmental issues and promoting conservation efforts.
Management of both wildlife sanctuaries and national parks typically involves monitoring of the resident wildlife, habitat management practices, and efforts to engage local communities in conservation efforts. This integrated management helps in maintaining the ecological integrity of these protected areas.
National parks focus on preserving ecosystems, landscapes, and for public enjoyment. Wildlife refuges prioritize habitat conservation mainly for wildlife protection.
Wildlife sanctuaries offer animals a natural habitat and focus on conservation, while zoos primarily engage in exhibition with some conservation efforts.
A national park is a protected area, established by government, to conserve wildlife and natural resources, and for public education and recreation.
India has 106 national parks and over 550 wildlife sanctuaries, each serving to protect the country’s diverse flora and fauna.
Madhya Pradesh has the most wildlife sanctuaries in India, boasting a significant number of these conservation areas.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following best describes a national park?
An area for the conservation of specific animal species
A protected area where human activities are strictly regulated
A place where hunting is allowed
A private property
What is a primary purpose of a wildlife sanctuary?
Recreation and tourism
Conservation of wildlife and their habitat
Industrial development
Urban expansion
Which activities are generally permitted in wildlife sanctuaries but not in national parks?
Industrial activities
Scientific research
Hunting and poaching
Limited human habitation
National parks are often established by:
Private organizations
Local communities
State or national governments
Individual landowners
Which of the following is typically a characteristic of a national park?
Focus on a single species
Limited public access
High level of tourist facilities
Allowing commercial exploitation
Which type of protected area typically allows more human activity?
National park
Wildlife sanctuary
Both allow the same level of activity
Neither allows human activity
The establishment of national parks is often aimed at:
Promoting urban development
Protecting biodiversity and natural resources
Encouraging industrial growth
Expanding agricultural land
Which of the following activities is strictly prohibited in national parks?
Tourism
Wildlife photography
Mining and logging
Bird watching
Which of the following can be a common feature of both wildlife sanctuaries and national parks?
Allowing commercial fishing
Protecting endangered species
Urban development
Industrial activities
Who typically manages national parks?
Private corporations
Government agencies
Local communities
Environmental NGOs
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

