30+ Relative Pronoun Examples
Relative pronouns are key tools in English grammar that connect clauses to nouns, adding detailed information without starting new sentences. These pronouns include “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.” For instance, in the sentence “The teacher who loves books is speaking,” the word “who” links additional information about the teacher directly to the noun, enriching the sentence’s context and meaning. Understanding and using relative pronouns correctly can make your writing clearer and more engaging.
What are Relative Pronoun
List of Relative Pronouns
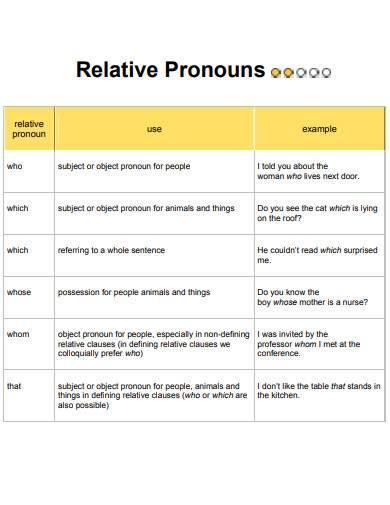
- Who: Refers to people and acts as the subject of the relative clause.
- Whom: Also refers to people but is used as the object of the relative clause.
- Whose: Indicates possession and relates to both people and things.
- Which: Refers to animals and things and can introduce additional information about them.
- That: Can refer to people, animals, or things and is used in restrictive clauses, which are essential to the meaning of the sentence.
Types of Relative Pronouns
- Possessive Relative Pronoun:
- Whose: The only possessive relative pronoun, it shows ownership and can relate to both people and objects. Example: “The student whose book was stolen was very upset.”
- Compound Relative Pronouns:
- Whoever/Whomever/Whosoever: These are compound forms used for emphasis or in complex sentences. “Whoever” and “Whosoever” act as subjects, while “Whomever” acts as an object. Example: “Whoever arrives first will get a seat.”
Examples on Relative Pronouns

- Who
- The girl who won the race is my cousin.
- The athletes who train daily perform better.
- He is the doctor who helped me recover.
- The children who play in the park seem happy.
- She is the leader who inspires us all.
- Whom
- The man whom I saw yesterday is my uncle.
- The customer whom you spoke with left a review.
- The actor whom we met is very down-to-earth.
- She is someone whom I respect deeply.
- The player whom they recruited scored the winning goal.
- Whose
- The boy whose dog was lost is over there.
- The woman whose article you read is a famous journalist.
- They found the cat whose owner moved away.
- The author whose books we love will visit our school.
- That’s the company whose products are eco-friendly.
- Which
- This is the book which inspired the movie.
- The car, which was parked outside, is gone.
- I read the report, which was very enlightening.
- They visited the castle, which is hundreds of years old.
- She wore the dress, which she had made herself.
- That
- The cake that she baked was delicious.
- I remember the day that we first met.
- The movie that we saw last night was exciting.
- This is the house that Jack built.
- The ideas that they proposed were innovative.
1. The Relative Pronoun
2. Relative Pronouns Worksheets
3. Printable Relative Pronouns
How To Use Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are crucial elements in English grammar, serving to connect clauses and provide additional information about nouns. Understanding how to use these pronouns effectively can enhance your writing and speaking skills by making your sentences more complex and informative.
Who
Use “who” to refer to the subject of a clause when talking about people.
Whom
Use “whom” when referring to the object of a clause. It is typically used in formal writing or speech.
Whose
“Whose” is used to indicate possession for both people and things.
Which
“Which” is used for animals and things. It can introduce non-essential clauses (using commas) or essential clauses.
That
“That” is a versatile relative pronoun used for people, animals, and things. It is typically used in restrictive clauses (without commas) where the information is essential to the meaning of the sentence.
Tips for Using Relative Pronoun
- Identify the Antecedent: Ensure that the pronoun clearly refers to a noun mentioned earlier in the sentence.
- Choose the Correct Pronoun: Determine whether the pronoun is acting as a subject, object, or possessive.
- Punctuation: Use commas to offset non-restrictive clauses introduced by relative pronouns, which provide extra information that could be omitted without changing the sentence’s fundamental meaning.
- Formality: “Whom” is often replaced by “who” in casual conversation, but in formal writing, it is important to use “whom” correctly when it is the object of the clause.
Exercises
- The woman _______ baked the cake is my aunt.
- The laptop _______ screen is broken belongs to Jake.
- I cannot find the papers _______ I placed on your desk.
- He hired an assistant _______ can speak three languages.
- The house _______ we bought has a lovely garden.
- This is the player _______ won the match yesterday.
- The book, _______ cover is blue, is my favorite.
- That’s the dog _______ followed me home.
- The lady to _______ you spoke is my mother.
- There is a professor at the university _______ teaches Ancient History.
Answers
- 1: who
- 2: whose
- 3: that
- 4: who
- 5: that
- 6: who
- 7: whose
- 8: that
- 9: whom
- 10: who
What are the three most common relative pronouns?
The three most common relative pronouns are “who,” “which,” and “that.” These words help connect details to nouns in sentences.
What are the rules for relative pronouns?
The rules for relative pronouns include matching the pronoun to its antecedent in number and function, and choosing “who” for subjects and “whom” for objects.
Why use relative pronouns?
They combine sentences smoothly, adding clarity and detail without repetition.
Can “that” replace “who” or “which”?
Yes, “that” can often replace “who” or “which” in restrictive clauses.
Do relative pronouns always need antecedents?
Yes, relative pronouns must refer back to a noun or pronoun mentioned earlier.
What are relative pronouns for kids?
Relative pronouns for kids include “who” for people, “which” for things, and “that” for both, simplifying how we add information about nouns.
What makes “whom” different from “who”?
“Whom” is used as the object of a verb or preposition, while “who” is used as a subject.
Are there any unusual relative pronouns?
Yes, “whichever,” “whoever,” and “whomever” are compound forms used for emphasis or in complex contexts.
Can relative pronouns introduce all types of clauses?
They primarily introduce adjective clauses that modify nouns or pronouns.
What’s the difference between “whose” and “who’s”?
“Whose” is a possessive pronoun; “who’s” is a contraction for “who is” or “who has.”