18+ BPO Examples
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) involves contracting specific business tasks to third-party service providers. Companies use BPO to improve efficiency and reduce costs. A well-crafted contractor proposal is essential to secure BPO contracts, outlining services and job objectives clearly. BPO services range from customer support to payroll processing, allowing companies to focus on core activities. By partnering with BPO firms, businesses can leverage specialized expertise and advanced technologies, ensuring streamlined operations and enhanced productivity.
What Is Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)?
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is the practice of contracting non-core business functions to third-party providers. It enhances efficiency and reduces costs, allowing companies to focus on core activities. BPO providers offer specialized services and product knowledge for streamlined operations.
BPO Examples
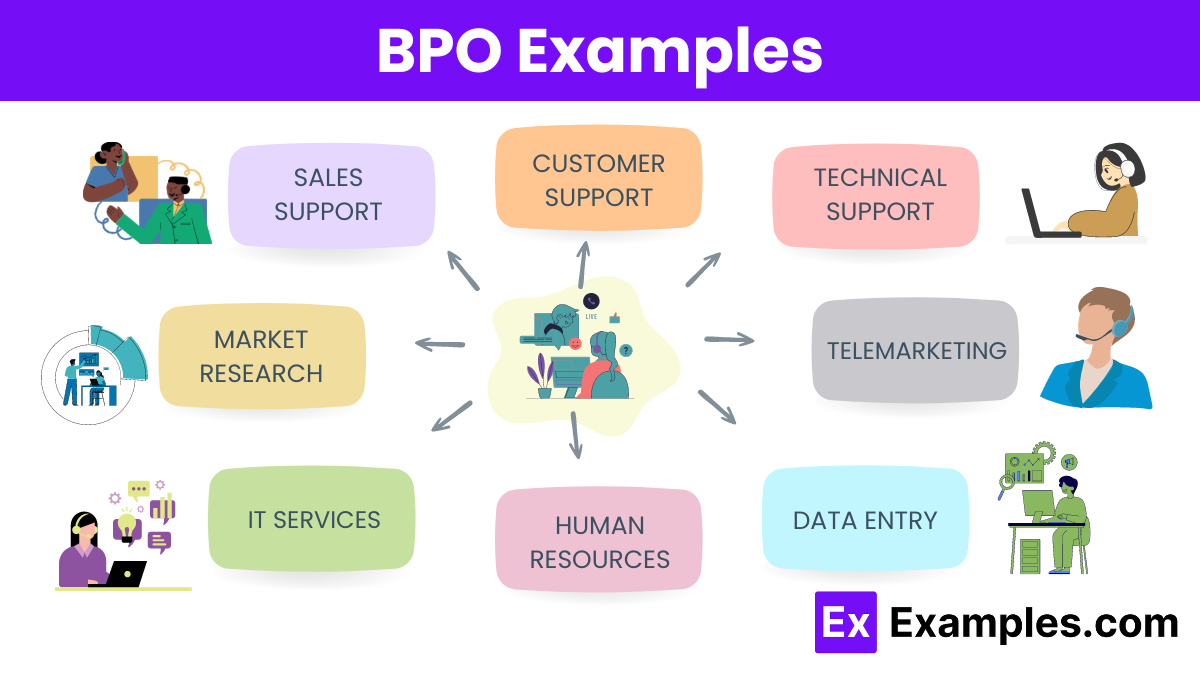
- Customer Support – Handling customer inquiries and issues through phone, email, or chat services.
- Technical Support – Providing assistance for technical problems and troubleshooting software or hardware issues.
- Telemarketing – Conducting sales calls and marketing campaigns to promote products or services.
- Data Entry – Entering and managing data for various business processes and databases.
- Finance and Accounting – Managing accounts payable, receivable, payroll, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources – Administering HR functions like recruitment, payroll, and employee benefits.
- IT Services – Offering IT support, infrastructure management, and software development services.
- Back Office Operations – Managing administrative tasks such as data processing, document management, and compliance.
- Supply Chain Management – Coordinating logistics, inventory control, and vendor management.
- Medical Transcription – Converting voice-recorded medical reports into written text.
- Legal Process Outsourcing – Handling legal research, document review, and contract management.
- Insurance Processing – Managing claims processing, policy administration, and customer service for insurance companies.
- Procurement – Handling purchasing activities, vendor negotiations, and contract management.
- Market Research – Conducting surveys, data analysis, and reporting on market trends.
- Sales Support – Providing administrative support to sales teams, including order processing and customer follow-up.
- Content Creation – Developing and managing content for websites, blogs, and social media.
- Quality Assurance – Ensuring products or services meet specified quality standards through testing and inspection.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – Managing customer data and improving customer interactions.
- Training and Development – Providing employee training programs and professional development resources.
- Help Desk Services – Offering support for IT-related issues and user assistance for software and hardware.
Types of BPO
- Front Office BPO – Handles customer-facing services such as customer support, sales, and marketing.
- Back Office BPO – Manages internal business functions like accounting, data entry, and human resources.
- Offshore BPO – Outsourcing services to a company located in a different country, often for cost savings.
- Onshore BPO – Outsourcing services within the same country to a different city or region.
- Nearshore BPO – Outsourcing services to a neighboring country with a similar time zone and cultural affinity.
- IT-Enabled Services BPO – Focuses on technology-related services such as software development, IT support, and data management.
- Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) – Involves high-value tasks such as research, data analysis, and legal services.
- Human Resource Outsourcing (HRO) – Manages HR functions like recruitment, payroll, and employee benefits.
- Finance and Accounting BPO – Handles financial tasks including bookkeeping, invoicing, and financial reporting.
- Legal Process Outsourcing (LPO) – Provides legal support services such as document review and legal research.
- Supply Chain Management BPO – Manages logistics, procurement, and inventory control.
- Healthcare BPO – Focuses on medical billing, transcription, and claims processing.
- Insurance BPO – Handles tasks like policy administration, claims processing, and customer service.
- Telecommunication BPO – Manages customer support and technical assistance for telecom companies.
- Content Creation and Moderation BPO – Develops and manages digital content for websites and social media platforms.
- Procurement BPO – Oversees purchasing activities, vendor negotiations, and contract management.
- Sales and Marketing BPO – Conducts telemarketing, lead generation, and market research activities.
- Research and Analytics BPO – Provides data analysis, market research, and business intelligence services.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) BPO – Manages customer data and enhances customer interactions and relationships.
- Help Desk and Technical Support BPO – Offers IT support and user assistance for software and hardware issues.
What Are the Types of BPO Companies?
- E-commerce BPO: Manages online retail operations and support.
- Data Entry BPO: Focuses on data management and entry services.
- Engineering Services BPO: Provides engineering solutions and support.
- Real Estate BPO: Offers services in real estate management and support.
- Publishing BPO: Provides publishing and editorial services.
- Training and Development BPO: Provides employee training and development programs.
- Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) : Involves high-value tasks such as research, data analysis, and legal services, integrating knowledge management.
- Logistics BPO: Manages logistics and distribution services.
- Audit Services BPO: Conducts financial and operational audits.
- Legal Process Outsourcing (LPO) : Provides legal support services such as document review and legal research.
BPO Services
- Customer Service : Handling customer inquiries and issues via phone, email, or chat; often detailed in a customer service proposal.
- Technical Support : Providing assistance with technical problems related to products or services.
- Data Entry : Inputting and managing data for various business processes.
- Payroll Processing : Managing employee salaries, generating salary slips, and ensuring timely payments.
- Human Resources Management : Overseeing recruitment, employee records, and HR compliance.
- Accounting and Finance : Managing financial records, bookkeeping, and financial reporting.
- Telemarketing : Conducting outbound sales calls to generate leads and promote products or services.
- Lead Generation : Identifying and qualifying potential customers for sales teams.
- Market Research : Gathering and analyzing data on market trends and consumer behavior.
- Order Processing : Handling orders from receipt to delivery, including inventory management.
What Is a BPO Call Center?
- Service Offering: A BPO call center provides customer service, technical support, telemarketing, and other phone-based services.
- Client Engagement: Companies outsource their customer communication needs to BPO call centers to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Operations Management: Call centers manage inbound and outbound calls, emails, and live chats, often following a structured committee meeting agenda for planning and performance reviews.
- Technology Use: Utilizes advanced technologies like CRM software, automated dialing systems, and analytics tools to enhance service quality.
- Performance Metrics: Monitors key performance indicators (KPIs) such as call resolution time, customer satisfaction, and agent productivity to ensure high service standards.
How Does Business Process Outsourcing Work?
- Identify Functions: Companies identify non-core functions that can be outsourced, such as customer service, accounting, or IT support.
- Select Provider: They select a BPO provider specializing in the required services and ensure compliance with standards like the office safety inspection checklist.
- Contract Agreement: Both parties negotiate and sign a contract outlining service levels, costs, and performance metrics.
- Transition Process: The BPO provider takes over the functions, using their resources and expertise to manage the tasks efficiently.
- Ongoing Management: Regular monitoring and performance reviews ensure the outsourced processes meet the agreed standards and objectives.
What is the Difference Between Outsourcing and BPO?
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracting out specific tasks or services to a third party. | Contracting out entire business processes to a third party. |
| Scope | Can involve any function or task, such as IT services, manufacturing, etc. | Typically involves back-office functions like HR, finance, customer service, etc. |
| Focus | Task-specific. | Process-specific. |
| Examples | IT support, janitorial services, legal services. | Customer service, payroll processing, data entry. |
| Objective | Reduce costs, access expertise, increase efficiency. | Improve efficiency, streamline processes, focus on core activities. |
| Duration | Can be short-term or long-term, depending on the task. | Generally long-term, involving ongoing processes. |
| Control | Limited control over the outsourced task. | More integrated and requires closer collaboration and control over processes. |
| Customization | Often standardized solutions. | Often tailored to the specific needs of the business process. |
| Risk | Varies depending on the task and provider. | Higher risk due to the dependency on the provider for critical business processes. |
| Impact on Business | Less impactful on core business functions. | Significant impact on core business operations and efficiency. |
Benefits of Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces operational and labor costs by outsourcing tasks to regions with lower labor costs.
- Focus on Core Activities: Allows companies to concentrate on their primary business functions and strategic initiatives.
- Access to Expertise: Provides access to specialized skills, technologies, and industry expertise not available in-house.
- Scalability: Enables businesses to scale operations up or down quickly based on demand.
- Improved Service Quality: Enhances customer service and operational efficiency through specialized providers.
- Flexibility: Offers flexible staffing solutions, allowing businesses to adjust resources as needed.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines processes and improves productivity by leveraging best practices and technologies.
- Risk Management: Helps manage and mitigate risks associated with business processes through specialized providers.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of BPO
| Aspects | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Reduces operational and labor costs. | Hidden costs and expenses may arise. |
| Focus on Core Activities | Allows companies to concentrate on core business functions. | Potential loss of control over outsourced tasks. |
| Access to Expertise | Provides access to skilled professionals and advanced technologies. | Risk of relying too much on external expertise. |
| Scalability | Easily scales operations up or down based on demand. | Can lead to dependency on the service provider’s capacity and availability. |
| Efficiency | Increases efficiency and productivity by leveraging specialized skills. | Quality of service can vary between providers. |
| Time Zone Advantages | Enables 24/7 operations due to global time differences. | Coordination across different time zones can be challenging. |
What services are commonly outsourced in BPO?
Services include customer support, data entry, human resources, IT support, and accounting.
How does BPO differ from general outsourcing?
BPO focuses on entire business processes, while general outsourcing can include any task or service.
What are the benefits of BPO?
Benefits include cost savings, improved efficiency, access to expertise, and scalability.
What is the difference between offshore and onshore BPO?
Offshore BPO involves outsourcing to another country, while onshore BPO involves outsourcing within the same country.
What is nearshore BPO?
Nearshore BPO involves outsourcing services to a neighboring country with similar time zones and cultural affinity.
What are some examples of front-office BPO services?
Examples include customer support, telemarketing, and sales.
What are some examples of back-office BPO services?
Examples include data entry, payroll processing, and accounting.
How does BPO improve efficiency?
BPO providers use specialized expertise and advanced technologies to streamline processes and enhance productivity.
What is Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)?
KPO is a type of BPO that involves outsourcing high-value tasks like research, data analysis, and legal services.
Is BPO only for large companies?
No, businesses of all sizes can benefit from BPO to streamline operations and reduce costs.


