15+ Annual Budget Examples
Budget management plays a very crucial role in keeping a small business, household, or single person’s financial resources safe. In the business aspect, the process can help set the marketing and sales budget. This is by thoroughly flicking through any of its project preparation, breakdown, and financial summary. Budgeting can be done periodically. Few organizations or individuals prefer to have them on a weekly, bi-weekly, and monthly basis. However, the majority of businesses would rather adopt the yearly budget cycle. The logic behind it is simply because it comes with various benefits. Learn more about the benefits of annual budgeting by reading this article.
15+ Annual Budget Examples
1. Annual Operating Budget
2. Annual IT Budget
3. Simple Annual Budget

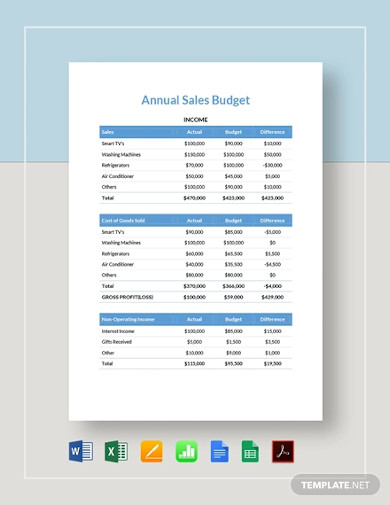
4. Annual Sales Budget
5. HR Annual Budget

6. Corporate Annual Budget

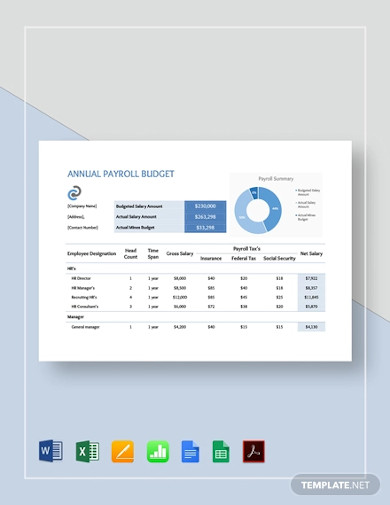
7. Annual Payroll Budget
8. Annual Travel Budget

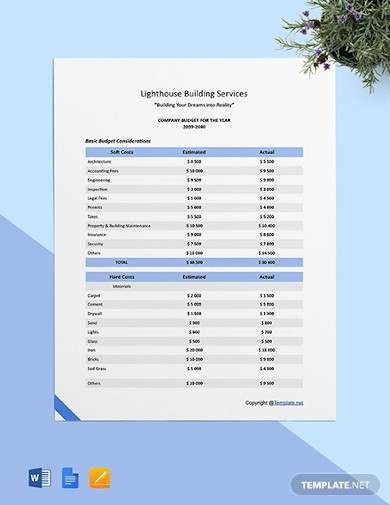
9. Basic Annual Construction Budget
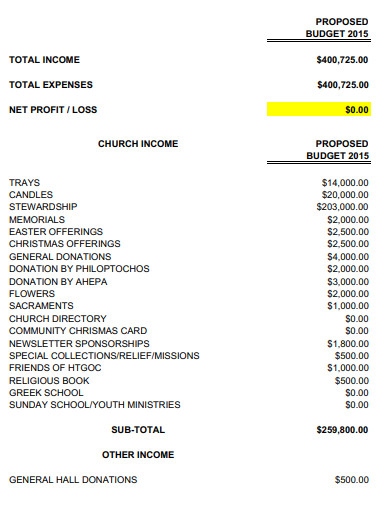
10. Annual Church Budget

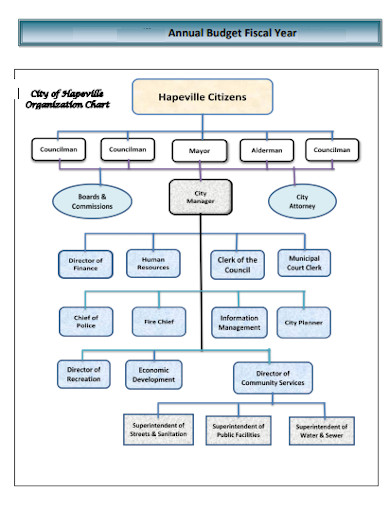
11. Governmental Annual Budgeting
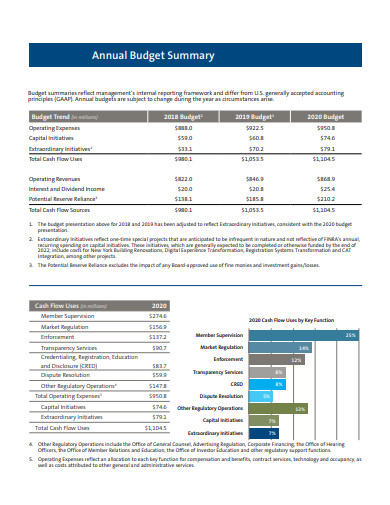
12. Annual Budget Summary
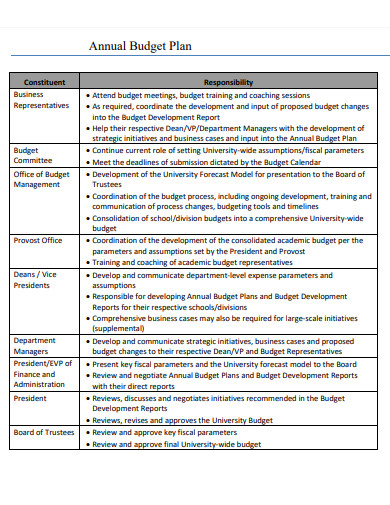
13. Annual Budget Plan
14. Company Annual Budget
15. Annual Operating Budget
16. Nonprofit Annual Budget
What Is an Annual Budget?
An annual budget is a financial strategy that projects a certain company’s incomings and outgoings for a 12-month period. In Will Kenton’s 2019 article for Investopedia, it was stated that the plan of action is mainly used by individuals and organizations to take full control over their respective financial undertakings. The same article expounded that the annual budget also assists these individuals and organizations in devising a financial plan and in maneuvering the plan’s specification to fulfill their financial goals. With those statements presented, we can conclude that such a program is very much helpful both for financial-conscious and ordinary people.
Budgeting Obstacles
When you want to put yourself in a comfortable position in the future, you have to go through a lot of challenges first. And, we all know how beneficial budgeting is with respect to a secured financial future. That is why the road to successful short-term financing and long-term financing is full of obstacles. A few of these obstacles, according to Bob Haegele, include erratic income, unanticipated expenses, FOMO, and urge to spend.
Erratic income – Not all professions have fixed rates. When someone has an inconsistent income, setting a successful budget plan will require great effort in the gathering of records.
Unanticipated Expenses – No matter how careful you are in setting your budget, there are cases when some expenses just slip your mind. This is why it is very important to set aside an emergency fund.
FOMO – FOMO stands for fear of mission out. This problem is very common to millennials. A good analogy of this is when your friends hand you over a concert ticket whose genre is way out of your taste. But, you did go and spend on it, anyway, to avoid passing up on the fun with them.
Urge To Spend – Let’s face it. When you have cash on your hand, there’s a tingling feeling to just squander them right away for things you wanted for a long time. This rash action can be a cause in the imbalance of your budgeting.
How To Make an Annual Budget
A lot can happen in a year’s time. So when you make your annual budget, you should consider setting all the important areas in a way that is easy to adjust and understand. For your convenience, we have set out our thorough outline of the steps you need to take to achieve such attributes for your budget plan.
1. Determine Net Income
Start making your budget by determining your net income. You can get all the details you need in your income statements or income portfolios.
2. Identify Expense Items
With the help of your monthly expense reports or your previous annual expense reports, pick out all the expense items that you think are still applicable for this year’s current budgeting. These items are one of the main drivers of your budget plan.
3. Set Realistic Goals
Another factor that directs your annual budget are your goals. Before setting them, know what a SMART goal is, and browse through various smart goal examples.
4. Allocate Income to Expense Items
This next step requires your knowledge and skills in prioritization and resource distribution. In going through this process, you have to make sure that your expenses do not surpass your net income.
5. Update Every Year
A country’s economy fluctuates almost every second. And, significant changes will be made obvious once it reaches a span of one year. This is why you have to adjust your budget annually.
FAQs:
What is the difference between financial budgeting and financial forecasting?
Financial budgeting is the process of predicting both the income and expenditure of an organization or individual over a period of time. On the other hand, financial forecasting is the projection of organizations or individuals’ future financial standings on a specific time frame. Moreover, it is done in accordance with past data.
What method of budgeting do most companies use?
The budgeting methods that are commonly used by companies consist of zero-based, incremental, value proposition, and activity-based.
1. Zero-based budgeting is an approach where all financial assumptions will be disregarded and have to be made right from scratch.
2. Incremental budgeting refers to the retention of the previous budget figures but with little add-ons on them.
3. Value proposition budgeting is the type of budgeting that ensures that all areas are highly relevant to the budgetary goals and objectives.
4. Activity-based budgeting is the method where the company analyzes the probable activities before giving out predictions on the expenses. Additionally, the expenses need to be related to the activities.
Is a yearly basis good for budgeting?
Yes, it is. In fact, My Money Design cited that one of the many reasons why it is way better than monthly budgeting is because it helps make your budgeting adjustable. Moreover, budgeting annually lets you identify and add expenses and income that you might have forgotten to put into consideration.
George Washington once said, “We must consult our means rather than our wishes.” It implies that individuals or organizations have to act according to their available resources when attempting to meet both personal and corporate goals. A perfect process for them to do so is the annual budgeting. It does not only help in their yearly business goal setting and personal goal setting, but it also assists in identifying the corporate finance essentials, as well as the personal finance essentials. Though the path for its completion is a little bit rough, overcoming it will surely be more than satisfying.