In every project that you work in, it is of utmost importance for your to provide what the client needs. This is why proper communication channels must be established between your business and your clients. In most cases, project briefs and client briefs are made available.
Client briefs are the documents given by clients to the businesses, establishments and organizations that they would like to work with. If you happen to receive a client brief, it is essential for you to make sure that you will review the entire document and that you will take note of all the important details specified by the client. If you will be observant and careful when looking into a client brief, it will be easier for you to deliver the specifications and expectations of the clients. You may also see summary writing examples and samples.
Client Brief Template
Basic Client Brief Example
Standard Client Brief Example
Why Do You Need to Create a Client Brief
Just as how marketing brief examples make marketing activities more successful in terms of the achievement of set objectives, client briefs also do the same when it is already time for businesses to know what the clients demand from them.
If you are a client, you need to be responsible with how you transact with businesses. Even if quotations and proposals will come from their end, the way you present your needs can also be one of the factors that can affect the entire transaction. Here are some of the reasons why we suggest you to create a client brief:
1. Having a client brief can help you ensure the effectiveness of the time and effort that the business will allot to identify the specifications of the project. Through a client brief, you are giving businesses an idea on how work processes are measured and how you can be satisfied with the deliverable that they can potentially provide you with. You may also see movie summary examples.
2. Developing a client brief can make it easier for you to review the items that are related to project planning and development. With the help of a client brief, you can browse through all the initial materials and other things that you have listed for quality control, project phase assessment and remuneration purposes. You may also like how to write a summary.
3. Creating a client brief can save you a lot of time, effort and even money. Being direct to the point with how you envision the project can narrow down all the procedures, processes and activities that will be implemented by the project team. Hence, resources can be used efficiently and less unexpected spending can be observed. You may also check out client email examples & samples.
Keep in mind that creating client briefs are not limited to clients. There are transactions where agencies that handle clients provide client briefs to their suppliers and other providers so that the latter can have more idea of what is expected from them both by the agency and the client.
Client Brief for Sustainable Landscape Garden Design Example
Client Brief Template Example
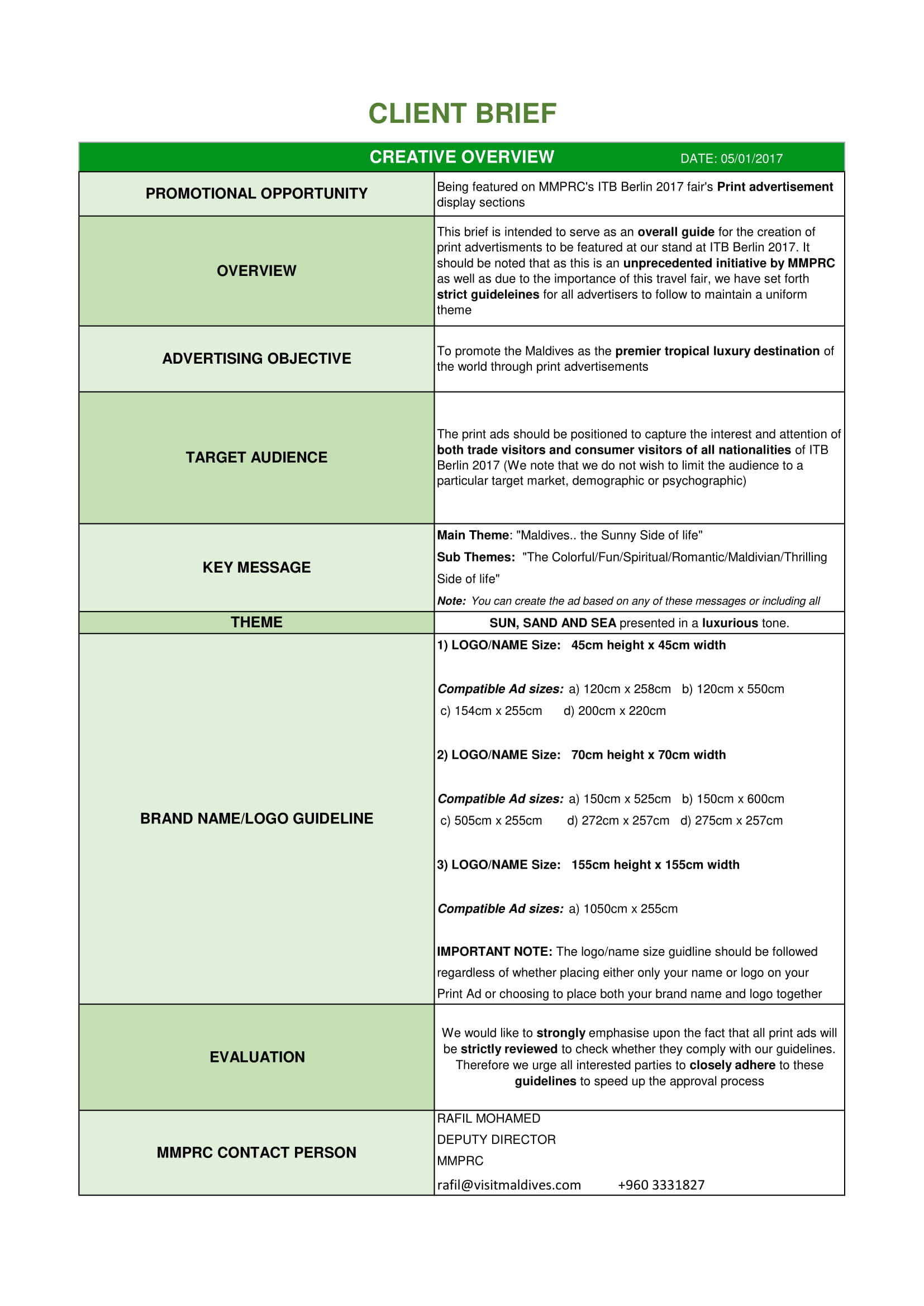
Detailed Client Brief Example
Importance of a Client Brief
A client brief, like an income verification letter and an advertising brief, may be regarded as a simple document. However, you should not overlook the usage of this material as there are a lot of advantages that you can experience by using it. If you can come up with a comprehensive and understandable client brief, then you can have higher chances of getting the final product or output that you would like to have at the end of the transaction. Listed below are some of the reasons why it is essential for a client brief to be created.
1. A client brief is one of the most essential documents that clients need to provide the businesses that they would like to work with. If there is a client brief at hand, it will be faster and easier for establishments to know how to satisfy the needs and demands of both the clients and the projects. You may also see resume summary examples.
2. A client brief can be used as an effective reference. Particular call to actions and proposals can be presented and established if all entities within a project can be aware of the expected output as well as the processes that can make these expectations be realized.
3. A client brief can list down all the specifications of the project or any undertaking the involves businesses and clients. With this document, parties can have a platform where measurable and attainable deliverable can be aligned with project expectations. You may also like interview summary examples.
Client Brief Key Points and Example
Initial Client Brief Example
Client Brief Example
Elements of a Comprehensive Client Brief
Just like any other business document, the completion of all the information found in a client brief can make it more usable and highly relevant. The content of client briefs from one project to another. Hence, it is important for you to know the project idea first before you proceed in the development of a client brief. The most important parts of a basic client brief include the following:
1. List down all the stakeholders of the project, or even the potential ones if you have not fully decided about this matter. Your client brief must showcase a clear view of how you would like the business-to-client transaction to go and materialize. You may also see summary examples.
2. Provide a general plan on how you would like the project to be managed. A structure when it comes to project management, update, and reporting must be specified.
3. Be particular with the current situation of the transaction. The condition of a particular situation where the project will be used is essential to be written down so that the foundation of the transaction can be laid out accordingly.
4. Specifically write the output that you want businesses to achieve. You can be more specific in this discussion especially if the project is big and scopes different areas. You may also like client information sheet examples.
5. Present your initial plan on how you would like the project to be developed. This can help businesses adjust based on the processes that you would like to execute, unless they can provide a better alternative.
6. Present the non-negotiable of the project, more so, be open to suggestions. Have a defined list of the deliverable that you expect from the business. A project requirement checklist will be very helpful for this instance.
7. Quality measures must be discussed. There are different practicalities that you must look into when creating the project brief depending on your project goals.
Again, we would like to reiterate the fact that client briefs differ from one another. You have to create a client brief that is fit for the project that you are working on, the kind of suppliers that you are working with, the demands of the project and other factors that can affect the entire project execution. You may also check out meeting summary examples.
Client Guide/Brief Example
Client Brief Summary Example
Client Design Brief Example
Interior Design Client Brief Example
Client Conversations: Strategic Brief Example
Summarized Client Brief Example
Simple Client Brief Example
Tips in Creating a Client Brief
A client brief is easy to make. However, this does not mean that you can do it in a way that it will be deemed effective and helpful. You still have to be aware of certain tips and guidelines that will allow you to create a well-formulated and presentable client brief. Some tips that you can use when making your own client brief include the following:
1. Make sure that you will clarify all the information that you will include in the client brief. If you can achieve this, there will be better chances of getting the results that you would like to have. Precisely giving an idea of what you expect can result to more accurate and concise results. You may also see thesis summary examples.
2. Develop a client brief accordingly. You must take your time when making this document so you can ensure that all the items placed in the content of the client brief can be very helpful with regards the smooth flow of client and business discussion. You may also like project summary examples.
3. Use to do checklists and other organizational tools that can help you list down your priorities. Having guides when making a client brief can help you be reminded of all the important information that you need to place in the document.
Before sending it to other parties, browse through the entire client brief and look for errors, irrelevant information, and other details that you may want to change or remove. For better final outputs,make use of our downloadable examples for your advantage.