In the realm of academic writing, proper citation is paramount to acknowledging the ideas and work of others while ensuring the credibility and integrity of one’s research. One commonly used citation style is the Chicago Citation, which offers a systematic approach to referencing sources. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Chicago Citation, providing a definition, a step-by-step guide, answers to frequently asked questions, and a creative conclusion that highlights the function and significance of this citation style.
[bb_toc content=”][/bb_toc]
1. Chicago Citation Footnotes

politics.ucsc.edu
2. Chicago Citation Format
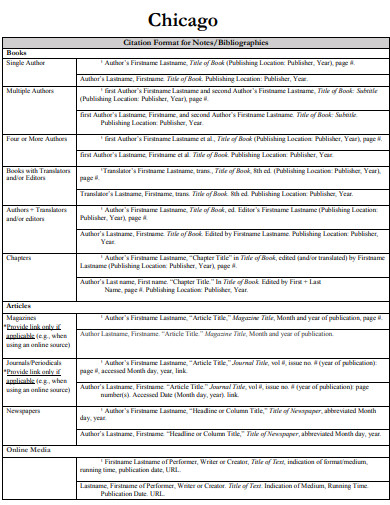
sjsu.edu
3. Chicago Citation Work Cited

writingcenter.mst.edu
4. Chicago Citation Essay

redlands.edu
5. Chicago Citation Bibliography

lboro.ac.uk
6. Chicago Citation Intext

spark.library.yorku.ca
7. Chicago Citation Paper

library.mcmaster.ca
8. Chicago Citation Book

scc.losrios.edu
9. Chicago Citation Text

uwb.edu
10. Chicago Citation Turabian

collin.edu
11. Chicago Citation Journal Article

mvcc.edu
12. Chicago Citation Annotated Bibliography

bmccprodstroac.blob.core.windows.net
13. Chicago Citation Referencing

library.cit.ie
14. MLA Chicago Citation
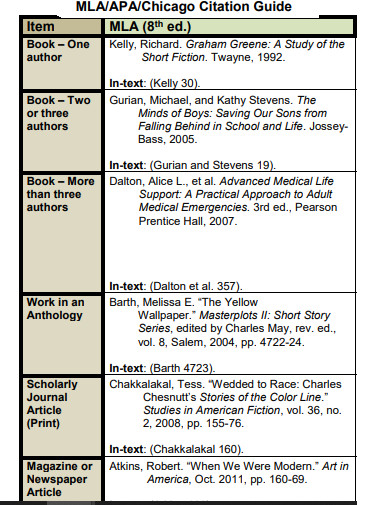
static1.squarespace.com
15. Chicago Citation Quote

cmich.edu
16. Chicago Manual Citation Style

arts.pdn.ac.lk
17. Chicago Citation 17th Edition

qatar.vcu.edu
What is a Chicago Citation?
Chicago Citation is a citation style that originated from the University of Chicago Press and is widely adopted by various disciplines, particularly in the humanities and social sciences. It provides guidelines for referencing sources in a consistent manner, incorporating both in-text citations and a detailed reference page or bibliography at the end of a research paper. The Chicago Citation style offers flexibility in terms of referencing different types of sources, including books, articles, websites, and more, and it emphasizes precision in text structure and punctuation to ensure accurate citation.
How to Write a Chicago Citation Format
Mastering the art of writing Chicago Citations requires an understanding of the prescribed format, text structure, and punctuation rules. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure accurate and consistent citations in your Chicago Style Paper, enhancing the credibility of your research.
Step 1: Book Titles and Authors
When citing a book in Chicago style, start by including the author’s name, followed by the book title in italics or underlined. Place the publication city, publisher, and year of publication in parentheses.
Step 2: Journal Articles and Periodicals
For journal articles, include the author’s name, article title in quotation marks, journal title in italics or underlined, volume number (if available), issue number (if available), year of publication, and page range.
Step 3: Websites and Online Sources
When citing websites or online sources, include the author (if available), the title or description of the page or article, the name of the website in italics, the publication or revision date (if available), and the URL.
FAQs
How does Chicago Citation differ from other citation styles?
Chicago Citation stands out for its emphasis on providing detailed publication information, use of footnotes or endnotes, and flexibility in formatting various sources. It allows for the inclusion of additional explanatory notes, which can enhance the reader’s understanding of the cited material.
Should I include page numbers in my Chicago citations?
Yes, page numbers are crucial in Chicago Citation, particularly in in-text citations. It helps readers locate the specific information you referenced within the source. Be sure to include page numbers whenever applicable, especially when quoting or paraphrasing.
Do I need to create a separate reference page and bibliography in Chicago Citation?
In the Chicago style, a reference page or bibliography is required at the end of the research paper. This comprehensive list includes all the sources cited within the paper. Each entry should be formatted according to the Chicago style guidelines, providing complete and accurate information for each source.
Chicago Citation serves a vital function in academic writing, ensuring the proper acknowledgment of sources and facilitating the credibility of research papers. By following the step-by-step guide and adhering to the specific formatting requirements, writers can seamlessly incorporate citations into their Chicago-style papers. The meticulous attention to detail regarding text structure, punctuation, and referencing different types of sources exemplifies the precision and integrity of this citation style. Embrace the art of Chicago Citation, and you will elevate the quality and professionalism of your academic work.



