16+ Cloud Computing Examples to Download
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and store data and applications over the internet instead of on local servers or personal computers. It provides scalable resources, enabling businesses and individuals to manage information efficiently and cost-effectively. Key benefits include flexibility, disaster recovery, and remote accessibility. Cloud services are offered in various models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, catering to different needs and enhancing overall productivity and innovation.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that delivers computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software—over the internet. It enables on-demand access to shared resources, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost savings, transforming how businesses manage and utilize their IT infrastructure.
Cloud Computing Examples
- Google Drive: A cloud storage service for files and documents, accessible from any device.
- Dropbox: Cloud-based file storage and sharing platform for personal and professional use.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Integrates with Office 365 for seamless file storage and collaboration.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of cloud services, including computing power and storage.
- Microsoft Azure: Cloud platform providing various services like virtual machines, databases, and AI.
- IBM Cloud: Delivers cloud computing services, including AI, blockchain, and IoT.
- Salesforce: Cloud-based CRM platform for managing customer relationships and sales data.
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Subscription service offering access to Adobe’s creative software applications.
- iCloud: Apple’s cloud service for storing photos, documents, and backups across devices.
- Slack: Collaboration platform that uses cloud technology for messaging and file sharing.
- Zoom: Video conferencing service hosted on the cloud for virtual meetings.
- Netflix: Streaming service that delivers video content over the cloud.
- Spotify: Music streaming service using cloud technology for content delivery.
- Google Workspace: Suite of productivity tools like Gmail, Docs, and Sheets, powered by the cloud.
- Box: Enterprise cloud storage solution for secure file sharing and collaboration.
- Oracle Cloud: Offers cloud services, including database management, analytics, and applications.
- GitHub: Cloud-based platform for version control and collaboration on software development.
Types of Cloud Computing
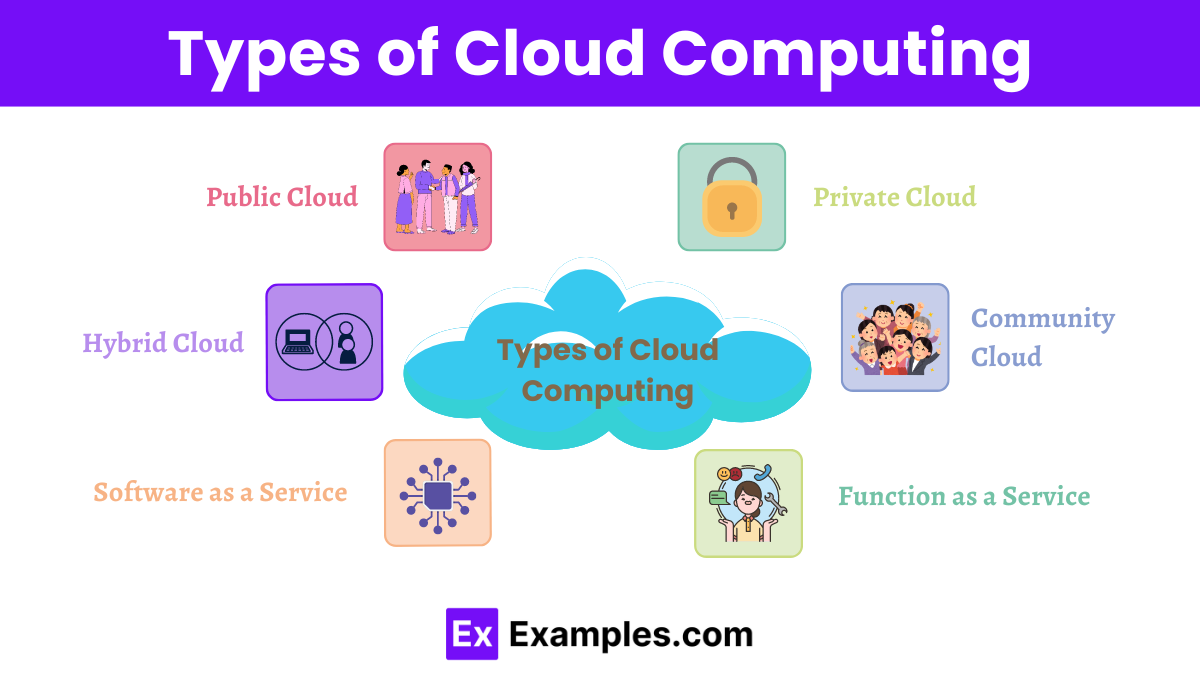
- Public Cloud: Services provided over the internet by third-party providers, accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated cloud infrastructure for a single organization, offering enhanced security and control.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
- Community Cloud: Shared infrastructure for specific communities with common concerns, managed internally or by a third party.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, like virtual machines and storage.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, primarily for application development.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, accessible via web browsers.
- Function as a Service (FaaS): Serverless computing model where developers run code in response to events without managing servers.
- Storage as a Service: Provides scalable and flexible storage solutions over the internet for backup and archiving.
- 10. Database as a Service (DBaaS): Manages databases in the cloud, offering scalability and simplified administration.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Provides cloud-based backup and recovery solutions for business continuity.
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS): Delivers virtual desktops to end-users over the internet, accessible from any device.
- Backup as a Service (BaaS): Cloud-based service for backing up data remotely, ensuring data security and recovery.
- Communication as a Service (CaaS): Provides communication solutions like VoIP, messaging, and video conferencing over the cloud.
- Network as a Service (NaaS): Offers virtualized network services over the internet, enabling flexible and scalable connectivity.
- Security as a Service (SECaaS): Delivers security solutions like antivirus, authentication, and intrusion detection over the cloud.
- Monitoring as a Service (MaaS): Provides real-time monitoring of IT infrastructure and applications through the cloud.
- Analytics as a Service (AaaS): Offers data analytics tools and services over the cloud for business intelligence.
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS): Enables users to develop, host, and manage blockchain applications using cloud infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS): Provides AI tools and frameworks over the cloud for developing AI applications.
Origins of Cloud Computing
1960s: John McCarthy proposed the idea of utility computing. This concept laid the groundwork for cloud computing by envisioning a future where computing power could be shared and accessed on demand.
1970s: The development of virtual machines (VMs) by IBM allowed multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine, creating the foundation for resource sharing and virtualization.
1990s: The rise of the internet and advancements in networking technologies enabled the delivery of applications and services over the web, leading to the first generation of cloud services.
1999: Salesforce launched its customer relationship management (CRM) platform, marking one of the first successful implementations of Software as a Service (SaaS).
2002: Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced its first cloud services, providing storage and computing resources over the internet, which paved the way for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
2006: Google launched Google Docs, offering real-time document collaboration and cloud storage, further popularizing SaaS and cloud-based productivity tools.
2008: Microsoft entered the cloud market with the introduction of Microsoft Azure, expanding the range of cloud services available to businesses and developers.
2010s: The rapid growth of cloud service providers and the widespread adoption of cloud computing transformed how businesses operate, with hybrid and multi-cloud environments becoming common.
Cloud computing components
- Virtualization: Enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, optimizing resource use and flexibility.
- Storage: Provides scalable and secure data storage solutions, ensuring data availability and reliability.
- Networking: Facilitates digital communication between cloud resources, ensuring efficient data transfer and connectivity.
- Servers: Powerful machines that host applications and store data, forming the backbone of cloud infrastructure.
- Software: Includes operating systems, middleware, and applications delivered over the cloud, enabling various services.
- Databases: Manage and store large amounts of structured and unstructured data, accessible through cloud services.
- Security: Protects data and applications with measures like encryption, firewalls, and identity management.
- Management Tools: Provide monitoring, automation, and orchestration software to efficiently manage cloud resources and operations.
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud computing environments. It encompasses a variety of measures to safeguard IT inventory, ensuring that all cloud-based assets are secure from unauthorized access, breaches, and other cyber threats. Effective cloud security requires a combination of technical skills and advanced security protocols, including encryption, firewalls, and identity management. These measures help maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of resources in the cloud, providing peace of mind for businesses and individuals relying on cloud services.
Cloud Sustainability
Cloud sustainability focuses on creating environmentally friendly and resource-efficient cloud computing practices. By leveraging advanced communication technology, cloud providers can optimize data centers for energy efficiency, reducing the carbon footprint. Implementing a robust disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity and data protection, further contributing to sustainable operations. These efforts not only help protect the environment but also enhance the resilience and reliability of cloud services, making them a critical component of modern, sustainable IT infrastructure.
Uses of Cloud Computing
- Data Storage and Backup: Provides scalable solutions for storing large amounts of data, ensuring data is safe and easily recoverable.
- Software Development: Facilitates collaboration and deployment in software development through tools and platforms that require advanced technical skills.
- Web Hosting: Enables reliable and flexible hosting services for websites, eliminating the need for physical servers.
- Disaster Recovery: Ensures business continuity with efficient disaster recovery plans that utilize cloud resources.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzes vast datasets to extract valuable insights, requiring significant technical skills for data manipulation and interpretation.
- Remote Work: Supports remote work environments by providing access to applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Communication Tools: Enhances digital communication through cloud-based tools like video conferencing, email, and messaging services.
- IoT Integration: Manages and processes data from Internet of Things (IoT) devices, supporting innovative applications in various industries.
- Artificial Intelligence: Provides platforms for developing AI and machine learning models, requiring specialized technical skills for implementation.
- E-commerce: Powers e-commerce platforms by offering scalable resources to handle varying levels of traffic and transactions.
Top Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for physical hardware and maintenance, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
- Scalability: Easily scales resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost management.
- Flexibility: Offers the ability to access applications and data from anywhere, supporting remote work and collaboration.
- Disaster Recovery: Provides robust disaster recovery plans that ensure data protection and business continuity.
- Security: Enhances security measures with advanced encryption, firewalls, and identity management, protecting sensitive information.
- Performance: Delivers high performance with the latest hardware and software, ensuring efficient and reliable operations.
- Automatic Updates: Ensures that systems and applications are always up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.
- Collaboration: Facilitates better collaboration by allowing multiple users to work on the same documents and projects in real-time.
- Technical Skills Development: Encourages the development of advanced technical skills and the formulation of experimental hypotheses as users interact with cutting-edge technologies.
- Environmental Sustainability: Promotes eco-friendly practices by optimizing resource use and reducing the carbon footprint of data centers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces hardware and maintenance costs, pay-as-you-go pricing models | Potential for hidden costs and over-provisioning |
| Scalability | Easily scales resources up or down based on demand | Scalability can lead to complexity in managing resources |
| Accessibility | Access data and applications from anywhere, supporting remote work | Dependence on internet connectivity |
| Disaster Recovery | Provides robust disaster recovery plans ensuring data protection and business continuity | Initial setup and configuration can be complex and time-consuming |
| Security | Advanced security measures such as encryption and identity management | Security risks including data breaches and cyber-attacks |
| Performance | High performance with latest hardware and software, ensures efficient operations | Performance can be affected by network latency and bandwidth limitations |
| Automatic Updates | Systems and applications are always up-to-date with latest features and security patches | Limited control over update schedules and potential compatibility issues |
| Collaboration | Real-time collaboration tools for multiple users to work on documents and projects simultaneously | Potential issues with data ownership and control |
| Technical Skills Development | Encourages development of advanced technical skills by interacting with cutting-edge technologies | Requires ongoing learning and adaptation to new tools and platforms |
| Environmental Sustainability | Promotes eco-friendly practices by optimizing resource use and reducing the carbon footprint of data centers | Environmental benefits depend on the energy sources used by cloud providers |
What are the main types of cloud computing?
The main types are public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
What is PaaS?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers hardware and software tools over the internet, primarily for application development.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet, accessible via web browsers.
How does cloud computing save costs?
Cloud computing reduces the need for physical hardware and maintenance, offering pay-as-you-go pricing.
What is cloud scalability?
Cloud scalability is the ability to easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
How does cloud computing support remote work?
Cloud computing enables access to applications and data from any location with an internet connection.
What are common cloud security measures?
Common measures include encryption, firewalls, and identity management.
What is a disaster recovery plan in cloud computing?
A disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity and data protection using cloud resources.
What is a hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.