What is a combustion reaction?
A reaction between a metal and a nonmetal
A reaction involving the breakdown of a compound
A reaction between a substance and oxygen producing heat and light
A reaction between acids and bases

A scientist can have many chemical reactions depending on the extraneous contexts, themes, and circumstances that will create a massive shift in the physical properties and chemical properties of the object. One of the most exothermic reactions one can naturally occur in life are combustion reaction. (See endothermic reaction as a juxtaposition of the combustion reaction)
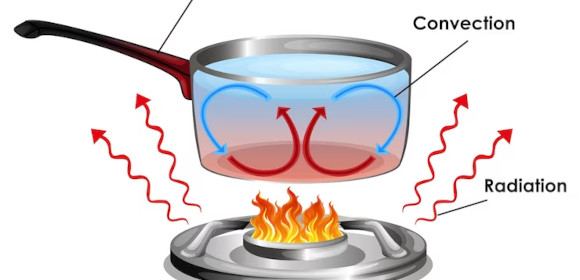
A combustion reaction is a specific chemical reaction where a combustible fuel, heat, and oxygen will react and create heat or thermal energy. The heat of combustion usually ends up creating fire, which will die out as soon as the whole system loses fuel or oxygen.
A combustion reaction happens when specific elements, compounds, commodities, or products produce heat or thermal energy in a closed system. This means that it is very easy to spot a combustion reaction due to the various things a combustion reaction requires.
Begin by determining if the whole reaction uses and reacts to oxygen gas to give off heat. If the reaction does not use or react with oxygen, then it isn’t a combustion reaction.
Heat is one of the most important factors in the combustion reaction. If heat is not present in the input of the whole reaction, then it isn’t a combustion reaction.
The fuel is the reactant that will react with oxygen and heat to create the combustion reaction. You must identify if fuel is present in the input of the whole reaction that causes the combustion reaction. If it is not present in the reaction, then it is not considered a combustion reaction.
A combustion reaction creates a fire or thermal energy as its main output. This means that the whole reaction is exothermic and will produce heat rather than absorb it. If the reaction is not exothermic then it is not a combustion reaction.
A combustion reaction is a type of reaction that will produce fire in the instant the reaction will occur. A common real-life example of a combustion reaction is the creation of fire when a person uses a match or lighter. The match uses friction to create heat, which will react to the tip of the match and use its body as its fuel. The lighter also uses a similar principle, but will instead use the lighter fluid as its fuel source instead of the body.
A combustion reaction has three conditions and components that will facilitate and generate this specific reaction. Heat must be applied to the reaction, which will interact with the fuel source and the oxygen of the reactant. All three conditions or components must be present in the initial stage of the combustion process to induce a combustion reaction.
There are two types of combustion reactions that people can naturally observe in real-life. Flaming combustion is a combustion reaction wherein the release of heat (usually fire) occurs on the surface of a solid object. Smoldering combustion is a combustion reaction wherein the release of heat occurs on the gas that is above the fuel source An example of smoldering combustion is the fire that butane creates when something generates a spark on its vapors.
A lot of our modern tools and comforts rely on combustion reactions to either create a fire or cause heat. It is important to know how a combustion reaction occurs as this said reaction creates fire as its main product.

A scientist can have many chemical reactions depending on the extraneous contexts, themes, and circumstances that will create a massive shift in the physical properties and chemical properties of the object. One of the most exothermic reactions one can naturally occur in life are combustion reaction. (See endothermic reaction as a juxtaposition of the combustion reaction)

intel.com
Details
File Format
Size: 39 KB
chemeng.queensu.ca
Details
File Format
Size: 41 KB

nitsri.ac.in
Details
File Format
Size: 39 KB
jawilliamsschool.ca
Details
File Format
Size: 51 KB
nsta.org
Details
File Format
Size: 21 KB
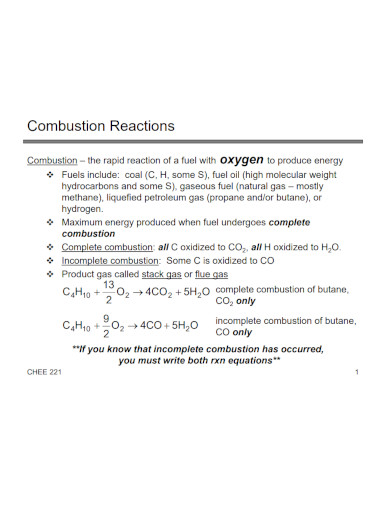
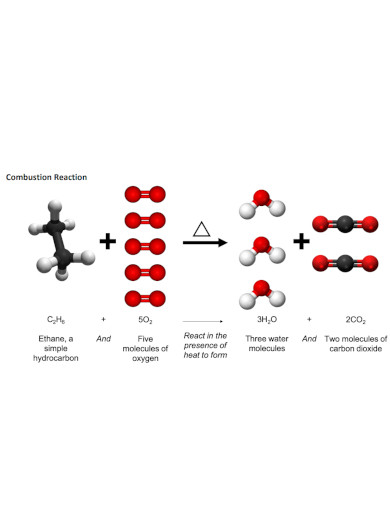
A combustion reaction is a specific chemical reaction where a combustible fuel, heat, and oxygen will react and create heat or thermal energy. The heat of combustion usually ends up creating fire, which will die out as soon as the whole system loses fuel or oxygen.
A combustion reaction happens when specific elements, compounds, commodities, or products produce heat or thermal energy in a closed system. This means that it is very easy to spot a combustion reaction due to the various things a combustion reaction requires.
Begin by determining if the whole reaction uses and reacts to oxygen gas to give off heat. If the reaction does not use or react with oxygen, then it isn’t a combustion reaction.
Heat is one of the most important factors in the combustion reaction. If heat is not present in the input of the whole reaction, then it isn’t a combustion reaction.
The fuel is the reactant that will react with oxygen and heat to create the combustion reaction. You must identify if fuel is present in the input of the whole reaction that causes the combustion reaction. If it is not present in the reaction, then it is not considered a combustion reaction.
A combustion reaction creates a fire or thermal energy as its main output. This means that the whole reaction is exothermic and will produce heat rather than absorb it. If the reaction is not exothermic then it is not a combustion reaction.
A combustion reaction is a type of reaction that will produce fire in the instant the reaction will occur. A common real-life example of a combustion reaction is the creation of fire when a person uses a match or lighter. The match uses friction to create heat, which will react to the tip of the match and use its body as its fuel. The lighter also uses a similar principle, but will instead use the lighter fluid as its fuel source instead of the body.
A combustion reaction has three conditions and components that will facilitate and generate this specific reaction. Heat must be applied to the reaction, which will interact with the fuel source and the oxygen of the reactant. All three conditions or components must be present in the initial stage of the combustion process to induce a combustion reaction.
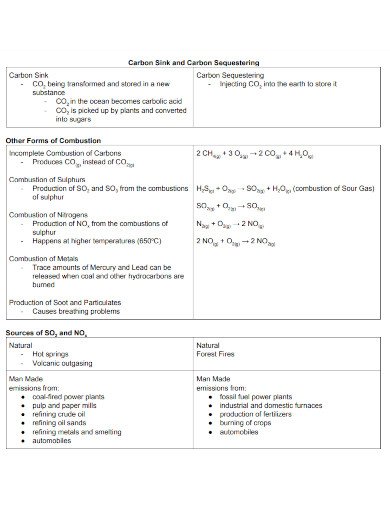
There are two types of combustion reactions that people can naturally observe in real-life. Flaming combustion is a combustion reaction wherein the release of heat (usually fire) occurs on the surface of a solid object. Smoldering combustion is a combustion reaction wherein the release of heat occurs on the gas that is above the fuel source An example of smoldering combustion is the fire that butane creates when something generates a spark on its vapors.
A lot of our modern tools and comforts rely on combustion reactions to either create a fire or cause heat. It is important to know how a combustion reaction occurs as this said reaction creates fire as its main product.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is a combustion reaction?
A reaction between a metal and a nonmetal
A reaction involving the breakdown of a compound
A reaction between a substance and oxygen producing heat and light
A reaction between acids and bases
Which of the following is a common example of a combustion reaction?
Rusting of iron
Melting of ice
Burning of propane
Dissolving salt in water
What are the typical products of a complete combustion reaction involving a hydrocarbon?
Carbon monoxide and water
Carbon dioxide and water
Carbon and oxygen
Methane and oxygen
Which of the following conditions is necessary for a combustion reaction to occur?
Presence of a catalyst
Presence of water
Presence of oxygen
Presence of nitrogen
Incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons can lead to the production of which harmful gas?
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Ozone
What type of reaction is the combustion of magnesium in air?
Exothermic
Endothermic
Neutralization
Decomposition
Which of the following is a sign that a combustion reaction has taken place?
Production of a precipitate
Change in color
Formation of bubbles
Release of heat and light
Which of the following substances is commonly used as a fire extinguisher for small fires?
Water
Alcohol
Sodium chloride
Carbon tetrachloride
What is the role of a spark in initiating a combustion reaction in an internal combustion engine?
It acts as a catalyst
It provides oxygen
It provides the activation energy
It removes impurities
Which of the following is an example of a combustion reaction in everyday life?
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Electrolysis
Fermentation
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

