20+ Company Culture Examples to Download
Company Culture is the foundation of any successful organization, reflecting its values, internal communication, and shared interests among employees. It shapes the workplace environment and influences job satisfaction, career growth, and overall productivity. A strong company culture fosters clear and open internal communication in company, ensuring that everyone is aligned with the company’s mission and goals. It also emphasizes company values, guiding employees’ actions and decisions to create a cohesive and motivated workforce.
What is Company Culture?
Company Culture is the collective values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape the interactions and internal communication within a workplace, influencing job satisfaction and career growth. It also encompasses practices like corporate greeting cards that reflect the organization’s spirit and community.
8 Types of Company Culture
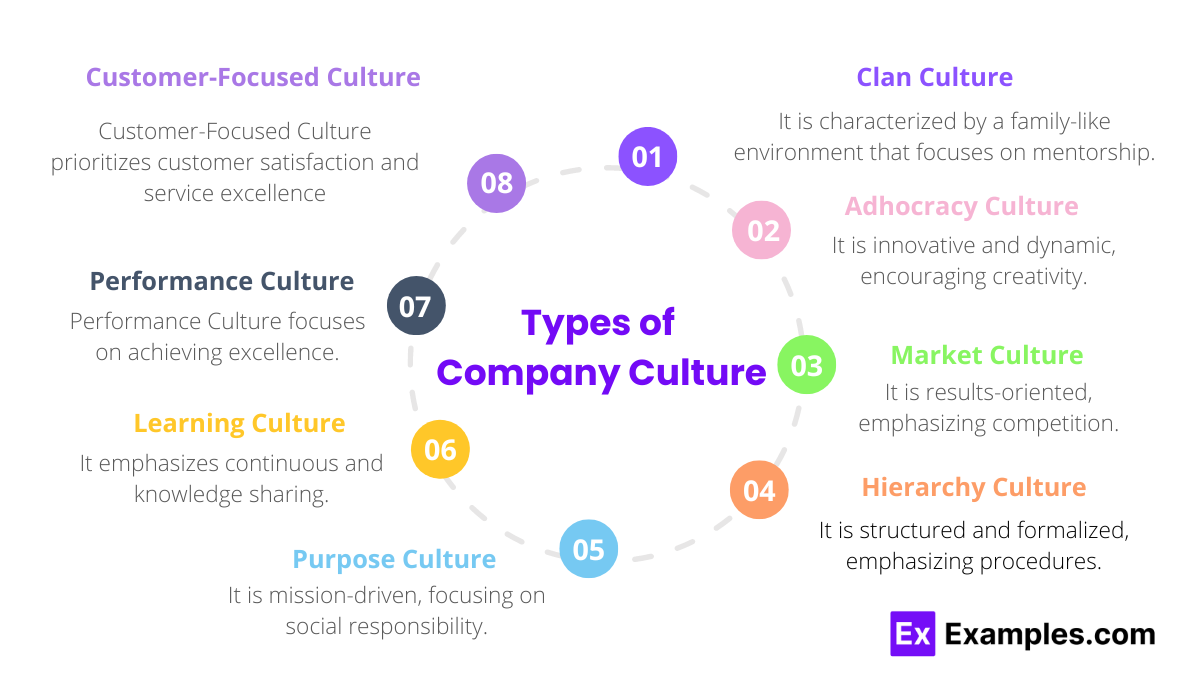
1. Clan Culture
Clan Culture is characterized by a family-like environment that focuses on mentorship and teamwork. This type of culture values collaboration, employee engagement, and personal development. Internal communication is open and informal, promoting feedback and team discussions. Internal storytelling is a key element, with success stories and shared experiences fostering a sense of community. Even during unhappy resignation letters, the tone remains respectful and supportive, reflecting the deep interpersonal relationships within the organization.
2. Adhocracy Culture
Adhocracy Culture is innovative and dynamic, encouraging creativity and risk-taking. This culture thrives on flexibility, an entrepreneurial spirit, and a focus on new ideas. Internal communication often includes brainstorming sessions and platforms for innovative thinking. Internal storytelling highlights groundbreaking projects and creative achievements. In the event of an unhappy resignation letter, the organization views it as a learning opportunity to refine its innovative processes and environment.
3. Market Culture
Market Culture is results-oriented, emphasizing competition and achieving targets. It is defined by high-performance standards, a goal-driven approach, and a strong customer focus. Internal communication is clear, direct, and centered around performance metrics. Internal storytelling celebrates sales achievements and successful project completions. When handling unhappy resignation letters, the focus is on constructive feedback and maintaining professional relationships to uphold the performance-driven ethos.
4. Hierarchy Culture
Hierarchy Culture is structured and formalized, emphasizing procedures and stability. This culture thrives on a clear organizational structure, well-defined roles, and control mechanisms. Internal communication follows formal channels and protocols, ensuring consistency and order. Internal storytelling often includes narratives about adherence to procedures and the benefits of a stable work environment. Unhappy resignation letters are managed through formal HR processes, with a focus on maintaining organizational stability and learning from the feedback.
5. Purpose Culture
Purpose Culture is mission-driven, focusing on social responsibility and community impact. It is values-driven and committed to a cause, guiding employees’ actions and decisions. Internal communication is inspirational, aligning employees with the organization’s mission and values. Internal storytelling highlights impactful projects and community involvement. When dealing with unhappy resignation letters, the organization seeks to understand and address concerns while reinforcing its commitment to the greater good.
6. Learning Culture
Learning Culture emphasizes continuous improvement and knowledge sharing. It encourages ongoing learning, training, and professional development for all employees. Internal communication includes knowledge-sharing platforms and regular training sessions. Internal storytelling showcases educational achievements and innovative solutions discovered through continuous learning. Unhappy resignation letters are used as a feedback mechanism to identify areas for further growth and development.
7. Performance Culture
Performance Culture focuses on achieving excellence and rewarding high performance. It is merit-based, competitive, and driven by high standards. Internal communication jobs revolves around performance reviews and constructive feedback, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Internal storytelling celebrates top performers and significant milestones. Unhappy resignation letters are addressed with a focus on understanding performance-related concerns and enhancing the support for high achievers.
8. Customer-Focused Culture
Customer-Focused Culture prioritizes customer satisfaction and service excellence. This culture is defined by customer-centric policies, proactive service, and responsiveness to customer needs. Internal communication includes customer feedback loops and service training to ensure exceptional service. Internal storytelling highlights success stories related to outstanding customer service and loyalty. When handling unhappy resignation letters, the organization seeks to understand if customer-related pressures contributed and works to improve the support systems for its
Examples of Company Culture
Collaborative Culture: Collaborative Culture emphasizes teamwork and open communication, fostering a cooperative work environment
Innovative Culture: Innovative Culture prioritizes creativity and encourages employees to take risks and think outside the box.
Customer-Centric Culture: Customer-Centric Culture focuses on providing exceptional customer service and satisfaction.
Result-Oriented Culture: Result-Oriented Culture emphasizes achieving targets and high performance. Internal communication is clear and goal-oriented, ensuring employees are aligned with the company’s objectives.
Adaptive Culture; Adaptive Culture is flexible and responsive to change, encouraging employees to be agile and innovative.
Community-Oriented Culture: Community-Oriented Culture values social responsibility and community involvement. Internal communication is motivational, aligning employees with the organization’s mission.
Learning Culture: Learning Culture focuses on continuous development and knowledge sharing. Internal communication includes training sessions and knowledge-sharing platforms, promoting employee engagement.
Formal Culture: Formal Culture values structure, clear roles, and established procedures. Internal communication follows formal channels and protocols, ensuring consistency.
Inclusive Culture: Inclusive Culture ensures diversity and equality in the workplace, fostering a sense of belonging.
Empowerment Culture: Empowerment Culture encourages employees to take ownership and make decisions. Internal communication supports autonomy and provides the resources needed for decision-making, enhancing employee engagement.
Sustainable Culture: Sustainable Culture prioritizes environmental responsibility and sustainable practices. Internal communication includes updates on sustainability initiatives and employee engagement activities.
Intercultural Culture: Intercultural Culture values diversity and effective intercultural communication, enhancing global business operations.
Health-Focused Culture: Health-Focused Culture prioritizes employee well-being and work-life balance. Internal communication includes wellness programs and mental health support, fostering employee engagement.
Tech-Driven Culture: Tech-Driven Culture embraces technological innovation and efficiency. Internal communication supports tech adoption and provides training for new tools, increasing employee engagement.
Creative Culture: Creative Culture encourages artistic expression and out-of-the-box thinking. Internal communication includes platforms for sharing creative ideas and projects, promoting employee engagement.
Employee-Centric Culture: Employee-Centric Culture prioritizes employee satisfaction and development. Internal communication includes feedback mechanisms and professional growth opportunities, increasing employee engagement
Transparent Culture: Transparent Culture values openness and honesty in all operations. Internal Communication for Employee Engagement is clear and open, encouraging transparency and trust, enhancing employee engagement.
Fun Culture: Fun Culture emphasizes a relaxed and enjoyable work environment. Internal communication includes fun activities and events, fostering employee engagement and team bonding.
Safety Culture: Safety Culture prioritizes the health and safety of employees in the workplace. Internal communication includes regular safety training and updates, promoting employee engagement and well-being.
Value-Driven Culture: Value-Driven Culture is guided by core principles and ethical standards. Internal communication reinforces the organization’s values.
Elements of great Company Culture
1. Clear Vision and Mission
- Purpose: A well-defined vision and mission provide direction and purpose, aligning the team with the company’s goals.
- Example: Companies like Google have clear missions that inspire employees to innovate.
2. Core Values
- Integrity: Values such as integrity, honesty, and respect foster a positive environment.
- Example: Patagonia emphasizes environmental responsibility, attracting employees passionate about sustainability.
3. Leadership
- Inspiring Leaders: Effective leaders who lead by example and communicate openly.
- Example: Richard Branson of Virgin Group is known for his approachable leadership style.
4. Open Communication
- Transparency: Regular, honest communication at all levels builds trust.
- Example: Buffer shares its financials and decision-making processes with all employees.
5. Employee Engagement
- Involvement: Engaged employees are more productive and committed.
- Example: Zappos encourages employees to take ownership of their work, leading to high engagement levels.
6. Work-Life Balance
- Flexibility: Encouraging a healthy balance between work and personal life prevents burnout.
- Example: Netflix offers unlimited vacation days, trusting employees to manage their time effectively.
7. Diversity and Inclusion
- Inclusivity: A diverse and inclusive environment fosters creativity and innovation.
- Example: Salesforce has strong diversity and inclusion programs, promoting a wide range of perspectives.
8. Recognition and Rewards
- Appreciation: Regularly recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions.
- Example: Google provides bonuses and awards to recognize outstanding work.
9. Professional Development
- Growth Opportunities: Providing continuous learning and career advancement opportunities.
- Example: Amazon offers tuition assistance programs to help employees pursue further education.
10. Positive Work Environment
- Atmosphere: A pleasant and supportive workplace enhances employee satisfaction.
- Example: HubSpot’s vibrant office spaces and collaborative culture create a positive work atmosphere.
11. Autonomy
- Empowerment: Giving employees the freedom to make decisions and take initiative.
- Example: Spotify allows team autonomy, encouraging innovation and personal responsibility.
12. Team Collaboration
- Cooperation: Encouraging teamwork and collaboration across departments.
- Example: Atlassian fosters a collaborative culture with tools like Jira and Confluence to facilitate teamwork.
13. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Community Involvement: Engaging in CSR activities builds a sense of purpose and community.
- Example: Ben & Jerry’s actively participates in social justice causes, reflecting its commitment to social responsibility.
14. Health and Wellbeing
- Support: Promoting physical and mental health through various programs.
- Example: Microsoft offers wellness programs, including gym memberships and mental health support.
15. Feedback Culture
- Constructive Feedback: Regular, constructive feedback helps employees grow and improve.
- Example: Adobe’s “Check-In” system replaces annual reviews with ongoing feedback and development conversations.
16. Innovation Encouragement
- Creativity: Encouraging innovative thinking and allowing space for creative ideas.
- Example: 3M’s “15% rule” allows employees to spend 15% of their time on projects of their choosing, fostering innovation.
17. Transparency in Decision-Making
- Inclusiveness: Involving employees in decision-making processes builds trust and ownership.
- Example: Whole Foods involves employees in decisions about store operations, enhancing transparency.
18. Strong Company Identity
- Brand: A strong, positive company identity that employees are proud to be associated with.
- Example: Nike’s brand identity focuses on empowerment and innovation, inspiring both employees and customers.
19. Adaptability
- Flexibility: Being open to change and encouraging employees to adapt to new challenges.
- Example: Facebook’s agile work culture enables it to rapidly respond to technological advancements and market changes.
20. Fun and Engagement
- Enjoyment: Creating a fun work environment to enhance employee engagement and satisfaction.
- Example: Pixar’s playful office environment and creative spaces foster a fun and engaging workplace.
What is company culture?
Company culture is the set of shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape interactions and define the work environment within an organization.
How does company culture impact employee engagement?
A positive company culture fosters open communication, collaboration, and recognition, significantly enhancing employee engagement and satisfaction.
Why is internal communication important in company culture?
Internal communication ensures alignment with the company’s mission and goals, promotes transparency, and enhances employee engagement and productivity.
What role does leadership play in shaping company culture?
Leadership sets the tone for company culture by modeling desired behaviors, establishing values, and creating an environment that supports those principles.
How can storytelling be used to strengthen company culture?
Storytelling highlights success stories, reinforces company values, and connects employees, fostering a sense of community and shared purpose.
What are some signs of a negative company culture?
High turnover, poor communication, lack of trust, and low employee morale are indicators of a negative company culture.
How can a company improve its culture?
Improving company culture involves promoting transparency, recognizing achievements, fostering collaboration, and aligning values with organizational practices.
What is the impact of intercultural business communication on company culture?
Effective intercultural communication promotes inclusivity, understanding, and respect for diverse perspectives, enhancing overall company culture.
How do company values influence daily operations?
Company values guide decision-making, shape employee behavior, and create a consistent and cohesive work environment.
Why is employee feedback important in shaping company culture?
Employee feedback provides insights into areas needing improvement, fosters a sense of involvement, and helps tailor the culture to better meet employees’ needs.


