15+ E-Commerce Examples
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. E-commerce encompasses various business models, including business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), and consumer-to-business (C2B). It enables businesses to reach a global audience, offers convenience to consumers, and often involves electronic payment systems, Ecommerce Chatbot, Ecommerce Marketing, and logistics management to facilitate the entire transaction process. An effective e-commerce marketing strategy is essential for businesses to thrive in the competitive online marketplace. Developing a comprehensive e-commerce marketing plan can help businesses target the right audience, optimize their online presence, and increase sales.
What is E-Commerce?
Ecommerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the practice of conducting business transactions online. This involves selling and buying products or services through digital platforms such as websites and mobile apps. E-commerce allows businesses to operate beyond physical stores, reaching customers worldwide and offering them the convenience of shopping from anywhere at any time.
Examples of E-Commerce
- Amazon
- eBay
- Alibaba
- Etsy
- Walmart
- Shopify
- Target
- Best Buy
- Zappos
- Overstock
- Wayfair
- ASOS
- Rakuten
- Newegg
- Flipkart
Types of E-Commerce
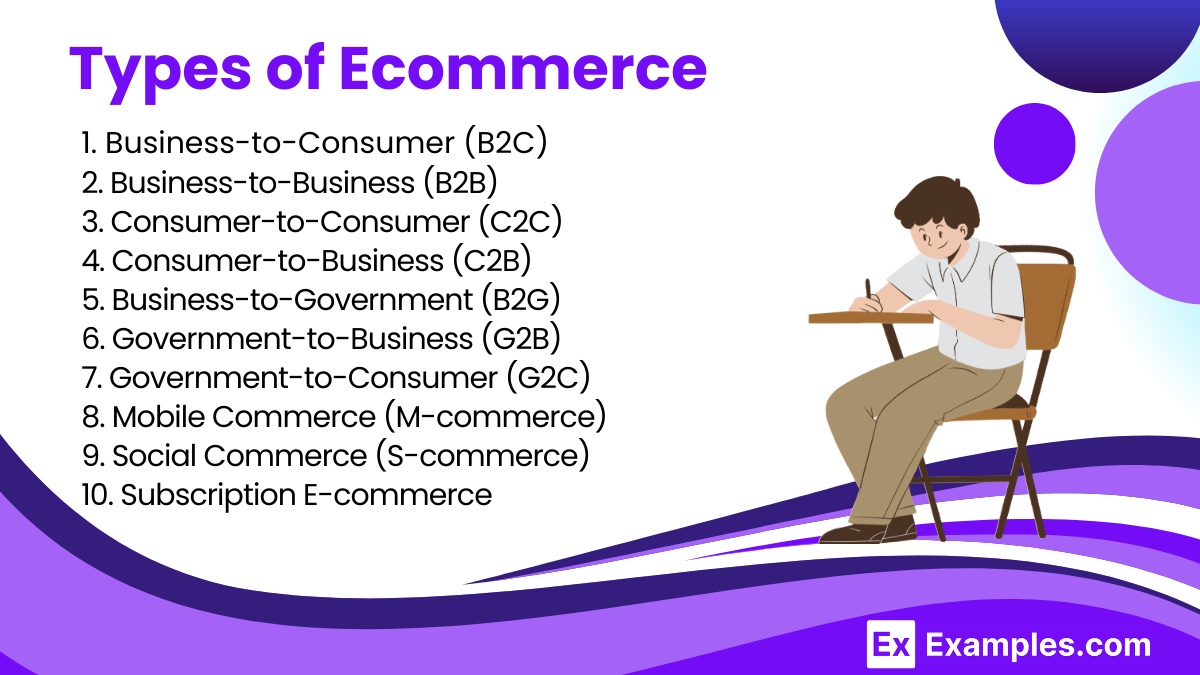
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Description: Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- Examples: Amazon, Walmart, Zappos.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Description: Transactions between businesses.
- Examples: Alibaba, ThomasNet, Costco Wholesale.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- Description: Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third-party platform.
- Examples: eBay, Craigslist, Facebook Marketplace.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
- Description: Transactions where individuals sell products or services to businesses.
- Examples: Shutterstock (selling photos), Upwork (freelance services), influencer marketing.
5. Business-to-Government (B2G)
- Description: Transactions between businesses and government entities.
- Examples: Government procurement sites, defense contractors, public sector software providers.
6. Government-to-Business (G2B)
- Description: Transactions where governments sell products or services to businesses.
- Examples: Licensing services, public records access, government data services.
7. Government-to-Consumer (G2C)
- Description: Transactions between governments and individual consumers.
- Examples: Online tax filing, license renewals, public service portals.
8. Mobile Commerce (M-commerce)
- Description: Transactions conducted through mobile devices.
- Examples: Mobile shopping apps like Amazon, mobile banking, mobile payment services like Apple Pay.
9. Social Commerce (S-commerce)
- Description: Transactions conducted through social media platforms.
- Examples: Shopping features on Instagram, Facebook Shops, Pinterest Buyable Pins.
10. Subscription E-commerce
- Description: Transactions where consumers subscribe to receive products or services on a regular basis.
- Examples: Netflix (streaming services), Dollar Shave Club (subscription boxes), Adobe Creative Cloud (software subscriptions).
Working of E-Commerce
- Website/App Setup: Businesses set up an online store through a website or mobile app, showcasing their products or services with detailed descriptions and prices.
- Customer Browsing: Customers browse the online store, using search functions and categories to find products or services they are interested in.
- Selection and Cart: Customers select items and add them to their virtual shopping cart.
- Checkout Process: Customers proceed to checkout, where they enter shipping and payment information.
- Payment Processing: Payment is processed through secure online payment gateways (e.g., credit cards, PayPal).
- Order Confirmation: Once payment is successful, the customer receives an order confirmation via email or app notification.
- Order Fulfillment: The business processes the order, packing the items and arranging for shipping through logistics partners.
- Shipping and Delivery: The order is shipped and delivered to the customer’s specified address.
- Post-Sale Support: Customers receive post-sale support, including order tracking, handling returns or exchanges, and customer service assistance.
Where does E-Commerce Take Place?
- Online Marketplaces
- Platforms such as Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba where multiple vendors sell products to consumers.
- Company Websites
- Businesses operate their own online stores, like Nike.com or Apple.com, where they sell directly to consumers.
- Social Media Platforms
- Social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest now offer shopping features that allow users to buy products directly.
- Mobile Apps
- Dedicated shopping apps like Etsy, Wish, and retail-specific apps (e.g., Walmart, Target) provide mobile-friendly shopping experiences.
- B2B Platforms
- Websites like Alibaba and ThomasNet facilitate business-to-business transactions.
How does E-Commerce Take Place?
- Product Listing
- Description: Businesses list their products or services online with detailed descriptions, prices, and images.
- Platform: This can be done on their own websites, online marketplaces, or social media shops.
- Customer Browsing and Selection
- Browsing: Customers use search functions, filters, and categories to find products.
- Selection: They select items and add them to their virtual shopping carts.
- Shopping Cart and Checkout
- Cart Management: Customers review their selected items in the shopping cart.
- Checkout Process: Customers proceed to checkout, entering shipping details and selecting payment methods.
- Payment Processing
- Payment Gateways: Payments are processed securely through gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or direct credit card processing.
- Transaction Confirmation: Once payment is successful, customers receive an order confirmation.
- Order Fulfillment
- Processing: The business receives the order, processes it, and prepares it for shipment.
- Packaging and Shipping: Items are packaged and shipped using logistics services (e.g., UPS, FedEx).
- Delivery
- Shipping: Orders are delivered to the customer’s specified address.
- Tracking: Customers can track their shipments through tracking numbers provided by the logistics partner.
- Post-Sale Services
- Customer Support: Handling queries, returns, and exchanges through customer service.
- Feedback: Customers leave reviews and feedback about their purchasing experience.
E-Commerce Website
An e-commerce website is an online platform where businesses sell products or services to consumers over the internet. These websites allow customers to browse products, make purchases, and manage orders from the comfort of their homes or on the go. Effective email marketing strategies can enhance customer engagement and drive sales by sending personalized promotions and updates directly to customers. Additionally, providing a detailed invoice for your e-commerce sales ensures transparency and helps customers keep track of their purchases
Steps to Create an E-Commerce Website
- Choose a Domain Name
- Select a unique and memorable name for your website.
- Select an E-commerce Platform
- Choose a platform like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, or BigCommerce.
- Design Your Website
- Create a user-friendly and visually appealing design. Customize templates or hire a web designer.
- Add Products
- Upload product images, descriptions, prices, and specifications.
- Set Up Payment and Shipping
- Integrate payment gateways and configure shipping options.
- Implement Security Measures
- Ensure your website is secure with SSL certificates and other security protocols.
- Launch Your Website
- Test all features thoroughly and launch your site to the public.
- Market Your Website
- Use digital marketing strategies like SEO, social media marketing, and email campaigns to attract customers.
E-Commerce Business
An e-commerce business is a company that operates primarily over the internet, selling products or services to consumers or other businesses. E-commerce businesses leverage online platforms and digital tools to reach a broader audience, provide convenience, and streamline the buying process.
Steps to Start an E-Commerce Business
- Research and Planning
- Identify a niche market, conduct competitor analysis, and create a business plan.
- Choose a Business Model
- Decide whether to operate as B2C, B2B, C2C, or C2B based on target market and goals.
- Register Your Business
- Choose a business name, register it, and obtain necessary licenses and permits.
- Select an E-commerce Platform
- Choose a platform like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, or BigCommerce based on your needs.
- Set Up Your Online Store
- Design your website, add products, set up payment and shipping options.
- Source Products
- Decide whether to manufacture, wholesale, or dropship your products.
- Launch and Market Your Business
- Launch your online store and implement marketing strategies to attract customers.
- Monitor and Optimize
- Use analytics to track performance, customer behavior, and sales. Continuously optimize your processes and strategies.
Challenges of E-Commerce
- Competition
- Description: High competition from numerous online businesses.
- Impact: Difficult to stand out and attract customers.
- Security Concerns
- Description: Risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Impact: Loss of customer trust and potential financial loss.
- Logistics and Delivery
- Description: Managing efficient order fulfillment and timely delivery.
- Impact: Customer dissatisfaction due to delays or shipping errors.
- Customer Retention
- Description: Keeping customers engaged and loyal.
- Impact: High customer acquisition costs if retention strategies fail.
- Technology Dependence
- Description: Reliance on technology and platform stability.
- Impact: Downtime or technical issues can disrupt sales.
- Payment Processing
- Description: Handling secure and diverse payment options.
- Impact: Transaction failures and customer frustration.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Description: Adhering to international and local laws and regulations.
- Impact: Legal issues and fines for non-compliance.
- Customer Service
- Description: Providing effective and timely support.
- Impact: Negative customer experiences if service is lacking.
- Return and Refund Management
- Description: Handling returns and refunds efficiently.
- Impact: Increased operational costs and potential abuse of return policies.
- Website Traffic and Conversion
- Description: Driving traffic to the website and converting visitors into buyers.
- Impact: Low sales if traffic generation and conversion strategies are ineffective.
Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Commerce
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Global Reach | Allows businesses to reach a worldwide audience. |
| 24/7 Availability | Customers can shop anytime, increasing sales opportunities. |
| Lower Operational Costs | Reduced need for physical stores and staff. |
| Personalization and Customer Targeting | Tailor marketing efforts to individual preferences. |
| Convenience for Customers | Easy access to products and services from home. |
| Data Collection and Analytics | Gather insights on customer behavior and preferences. |
| Scalability | Easier to scale business operations compared to physical stores. |
| Flexibility | Quick to update inventory, prices, and product details. |
| Cost-Effective Marketing | Leverage SEO, social media, and email marketing at lower costs. |
| Reduced Overheads | No need for physical storefronts and associated costs. |
Tips for How to Succeed in E-Commerce

- Understand Your Market: Know your audience and competitors.
- Choose the Right Platform: Select a scalable and user-friendly e-commerce platform.
- Offer Quality Products: Ensure high-quality products to build trust.
- Create an Engaging Website: Focus on UX and visual appeal.
- Optimize for Search Engines: Implement SEO strategies.
- Leverage Social Media: Promote products and engage with customers.
- Offer Excellent Customer Service: Provide responsive support.
- Utilize Data Analytics: Make data-driven decisions.
- Implement Secure Payment Options: Offer secure payment methods.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: Manage inventory and ensure fast shipping.
- Effective Marketing Strategies: Use email marketing and paid advertising.
- Build Customer Loyalty: Implement loyalty programs.
Why is ecommerce important?
Ecommerce is important because it provides convenience, a broader reach, and often lower costs for both businesses and consumers.
What are the benefits of ecommerce for businesses?
Businesses benefit from ecommerce through increased sales, broader market reach, reduced operating costs, and improved customer insights.
How can consumers benefit from ecommerce?
Consumers benefit from ecommerce through convenience, a wider selection of products, competitive pricing, and easy access to reviews and information.
What are some popular ecommerce platforms?
Popular ecommerce platforms include Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, and BigCommerce, offering various features for different business needs.
How do payment gateways work in ecommerce?
Payment gateways securely process online payments, verifying transaction details and transferring funds from the customer to the merchant.
What is drop shipping in ecommerce?
Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store sells products without keeping inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers.
How can businesses improve their ecommerce presence?
Businesses can improve their ecommerce presence by optimizing their website, enhancing user experience, employing SEO, and utilizing social media marketing.
What is mobile commerce (m-commerce)?
Mobile commerce, or m-commerce, refers to buying and selling goods and services through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
How important is customer service in ecommerce?
Customer service is crucial in ecommerce as it builds trust, resolves issues, enhances user experience, and fosters customer loyalty.
What is an online marketplace?
An online marketplace is a platform where multiple sellers offer products or services, like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy.


