Email Address Examples to Download
An email address is a unique identifier for an email account that allows users to send and receive electronic messages over the Internet. It is composed of two main parts: a local part and a domain part, separated by the “@” symbol.
What is Email Address?
An Email Address is a unique identifier used to send and receive electronic messages over the Internet. It acts as a digital address for email communications, allowing messages to be directed to the appropriate recipient.
Examples of Email Address
- john.doe@example.com
- jane.smith@company.com
- contact@website.org
- info@business.net
- support@service.com
- admin@university.edu
- sales@shop.co
- manager@department.gov
- hello@startup.io
- careers@enterprise.biz
- marketing@brand.co.uk
- customercare@retail.com
- newsletter@newsportal.com
- ceo@corporation.com
- feedback@nonprofit.org
Types of Email Address
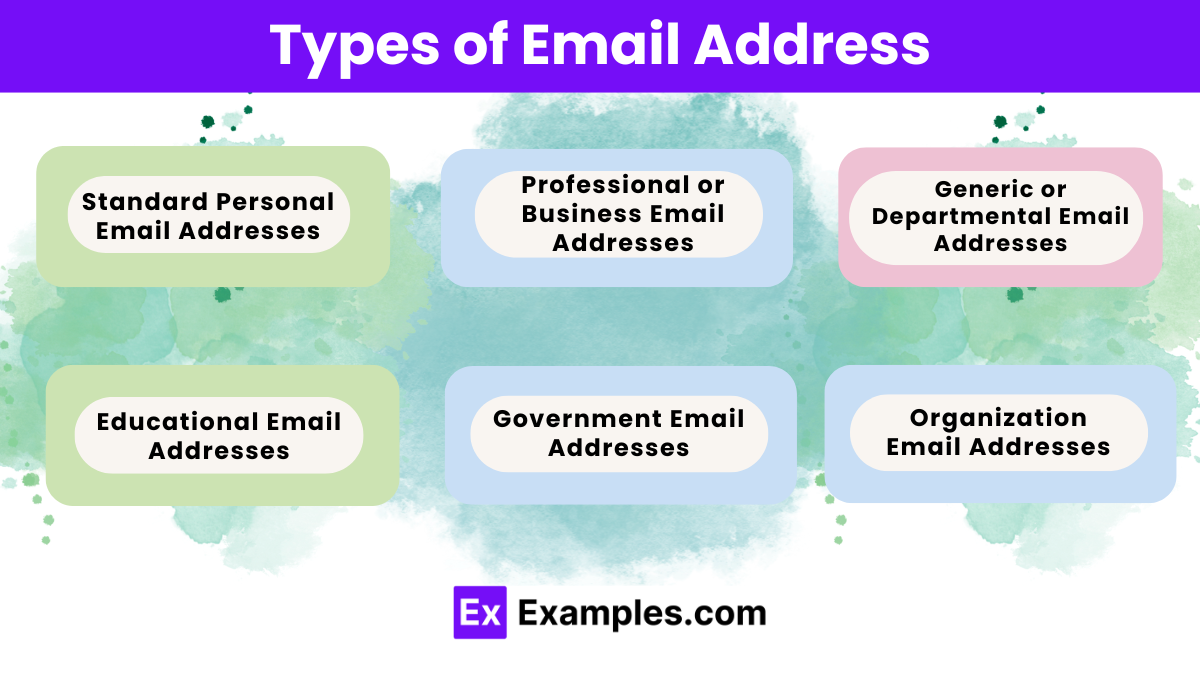
Personal Email Addresses: Typically used for individual, non-business purposes. They often use domains provided by popular email services.
- john.doe@gmail.com: An example of a personal email address using Google’s email service.
- jane_smith@yahoo.com: An example of a personal email address using Yahoo’s email service.
- alex.taylor@hotmail.com: An example of a personal email address using Microsoft’s Hotmail service.
- samantha.brown@outlook.com: An example of a personal email address using Microsoft’s Outlook service.
Professional Email Addresses: Used for business and professional purposes, often using custom domains related to the business or organization.
- john.doe@companyname.com: A professional email address using a custom domain for a company.
- jane.smith@businesscorp.net: A professional email address for a business corporation.
- alex.taylor@nonprofit.org: An email address for a non-profit organization.
- samantha.brown@techstartup.io: A professional email address for a tech startup using a custom domain.
Educational Email Addresses: Assigned to students, faculty, and staff of educational institutions, typically using the institution’s domain.
- johndoe@university.edu: A student or faculty email address using an educational institution’s domain.
- janesmith@school.edu: An example of an email address for a school.
- alex.taylor@college.edu: A college email address for a student or staff member.
- sam.brown@academy.edu: An email address for an academy.
Government Email Addresses: Used by government employees, often with domains that indicate the governmental department or agency.
- john.doe@state.gov: An email address for a government employee in the United States Department of State.
- jane.smith@city.gov: An example of a municipal government email address.
- alex.taylor@county.us: A county government email address in the United States.
- sam.brown@agency.gov: An email address for a specific government agency.
Temporary or Disposable Email Addresses: Used for short-term purposes to avoid spam or for privacy reasons.
- tempuser123@mailinator.com: An example of a disposable email address using Mailinator.
- disposable.email@10minutemail.com: An email address from a service providing temporary email addresses for 10 minutes.
- useonce@tempmail.com: An example of a temporary email address.
- throwaway123@guerrillamail.com: A disposable email address using Guerrilla Mail.
How to Create an Email Address
Creating an email involves setting up an email account with an email service provider and then composing and sending your first email. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
Step 1: Choose an Email Service Provider
First, select an email service provider. Some popular options include:
- Gmail (by Google)
- Outlook (by Microsoft)
- Yahoo Mail (by Yahoo)
- ProtonMail (for encrypted emails)
Step 2: Sign Up for an Email Account
- Visit the Provider’s Website:
- Go to the website of your chosen email service provider (e.g., www.gmail.com, www.outlook.com).
- Click on “Sign Up” or “Create Account”:
- Look for a button or link that says “Sign Up” or “Create Account”.
- Fill Out the Registration Form:
- Name: Enter your first and last name.
- Username: Choose a unique username (this will be your email address, e.g., johndoe@gmail.com).
- Password: Create a strong password. Follow the guidelines for length and complexity.
- Other Information: Fill in any additional information requested, such as your phone number and recovery email address.
- Agree to Terms and Conditions:
- Read and agree to the service provider’s terms and conditions.
- Verify Your Account:
- You may need to verify your account by entering a code sent to your phone number or recovery email.
Step 3: Log In to Your Email Account
- Visit the Email Provider’s Website:
- Go to the login page of your email provider (e.g., www.gmail.com).
- Enter Your Username and Password:
- Enter the username and password you created during the sign-up process.
- Access Your Inbox:
- Once logged in, you’ll be directed to your inbox where you can view, send, and manage your emails.
Step 4: Compose and Send an Email
- Click on “Compose” or “New Email”:
- Look for a button labeled “Compose” or “New Email”.
- Fill In the Email Details:
- To: Enter the recipient’s email address (e.g., friend@example.com).
- Subject: Enter a subject line that summarizes the email content.
- Body: Write your message in the main text area.
- Add Attachments (Optional):
- If you need to attach files (documents, images, etc.), look for an “Attach” button (often represented by a paperclip icon) and select the files you want to attach.
- Send the Email:
- Once your email is ready, click the “Send” button to send your message.
Uses of Email Address
- Communication with Family and Friends: Email addresses are commonly used to keep in touch with family and friends. They allow for the exchange of messages, photos, and updates, making it easy to stay connected regardless of distance.
- Subscriptions and Newsletters: Many people use email addresses to subscribe to newsletters, blogs, and online publications. This ensures they receive regular updates, news, and information directly in their inbox.
- Online Shopping and Receipts: When shopping online, email addresses are used to receive order confirmations, shipping notifications, and electronic receipts. This helps in keeping track of purchases and managing financial records.
- Social Media Accounts: Email addresses are often required to create and manage social media accounts. They are used for account verification, password recovery, and receiving notifications from platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Personal Finance Management: Email addresses are used to manage personal finances through online banking, investment accounts, and budget tracking apps. Notifications for transactions, account balances, and alerts are typically sent via email.
- Business Communication: Email is a primary mode of communication in the professional world. Employees use email addresses to communicate with colleagues, clients, and vendors, facilitating efficient and formal exchanges.
- Job Applications and Recruitment: Email addresses are used in job applications to send resumes, cover letters, and follow-up messages. Recruiters also use email to communicate with candidates, schedule interviews, and provide job offers.
- Project Management and Collaboration: Email is essential for project management and collaboration. Teams use email to share updates, assign tasks, and coordinate efforts, often integrating with project management tools.
- Marketing and Advertising: Businesses use email addresses to send marketing materials, promotional offers, and advertisements to potential and existing customers. Email marketing campaigns are a key component of digital marketing strategies.
- Customer Support: Email addresses are used for customer support, allowing customers to contact businesses with inquiries, complaints, or feedback. Companies can provide timely responses and maintain records of customer interactions.
- Internal Communication: Organizations use email for internal communication among employees, departments, and management. This ensures that information is shared quickly and efficiently within the organization.
- Event Planning and Invitations: Email addresses are used to send invitations and updates for organizational events, such as meetings, conferences, and social gatherings. This helps in coordinating attendance and managing RSVPs.
- Document Sharing and Collaboration: Email allows for the sharing and collaboration of documents, spreadsheets, and presentations. Employees can easily exchange and edit documents, ensuring seamless workflow and productivity.
- Announcements and Bulletins: Organizations use email to distribute announcements, newsletters, and bulletins to employees and stakeholders. This keeps everyone informed about important updates, changes, and news.
- Account Management: Email addresses are essential for managing various online accounts, such as cloud storage, software subscriptions, and service providers. Notifications related to account activity, billing, and updates are sent via email.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Email Address
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Instant Communication: Email allows for fast and immediate exchange of messages across the globe. | Spam and Junk Mail: Users often receive unsolicited emails that can clutter inboxes and pose security risks. |
| Cost-Effective: Sending emails is generally free, making it a cost-efficient communication method. | Security Risks: Emails can be susceptible to hacking, phishing attacks, and malware. |
| Accessibility: Emails can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it convenient for users. | Overload: Users can become overwhelmed with the volume of emails, leading to important messages being missed. |
| Record Keeping: Emails provide a written record of communication that can be referenced later. | Miscommunication: Tone and intent can be misinterpreted in written text, leading to misunderstandings. |
| Attachments: Users can send documents, images, and other files easily through email. | Dependence on Internet: Email requires a stable internet connection, which may not always be available. |
| Organizational Tools: Email platforms often include features like folders, filters, and search functions to help manage messages. | Privacy Concerns: Emails can be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, risking sensitive information. |
| Environmental Benefits: Reduces the need for paper, contributing to environmental conservation. | Technical Issues: Emails can sometimes get lost, delayed, or fail to deliver due to technical problems. |
How is an email address structured?
An email address has a format: username@domain.com, where “username” is the user identifier and “domain.com” is the email service provider.
What is the purpose of an email address?
The purpose of an email address is to facilitate communication by sending and receiving messages, documents, and other files electronically.
How do I create an email address?
You create an email address by signing up with an email service provider like Gmail, Yahoo, or Outlook.
Can I have multiple email addresses?
Yes, you can have multiple email addresses, often for different purposes like personal, professional, and educational use.
What is a domain in an email address?
The domain in an email address identifies the email service provider or the organization hosting the email service.
How do I choose a username for my email address?
Choose a unique and memorable username, avoiding personal information for privacy and security.
What are common email service providers?
Common email service providers include Gmail, Yahoo Mail, Outlook, and ProtonMail.
How do I secure my email address?
Secure your email address by using a strong password, enabling two-factor authentication, and avoiding phishing scams.
What is email forwarding?
Email forwarding automatically sends emails from one address to another, consolidating messages in a single inbox.
Can I change my email address?
You can’t change an existing email address but can create a new one and set up forwarding or notifications.



