24+ Examples for Poetry Examples to Download
In the realm of literary expression, poetry stands as a testament to the boundless creativity of human language. Evoking emotions, painting vivid images, and conveying profound thoughts, poetry encapsulates the beauty of words. In this exploration, we will dive into the essence of poetry, guide you through the process of crafting a poetic masterpiece, and offer insights into the enchanting world of metaphors, tone, and thematic depth.
1. Poetry Journal Template

2. Ordinary Object Poetry Template

3. Concept Poetry Template

4. Student Poetry Template

5. Photographic Poetry Template

6. End-to-End Style Conditioned Poetry

aclanthology.org
7. Analyzing Electronic Poetry

elmcip.net
8. Poetry Warm Up

sausd.us
9. Elements of Poetry

unm.edu
10. Symbolism in Poetry

hunter.cuny.edu
11. Poetry Analysis

dupontmanual.com
12. Poetry Explication

bucks.edu
13. Literary Terms in Poetry

myerberg.org
14. Glossary of Poetry

pbworks.com
15. Poetry Structural Elements

sjsu.edu
16. Poetry Unit
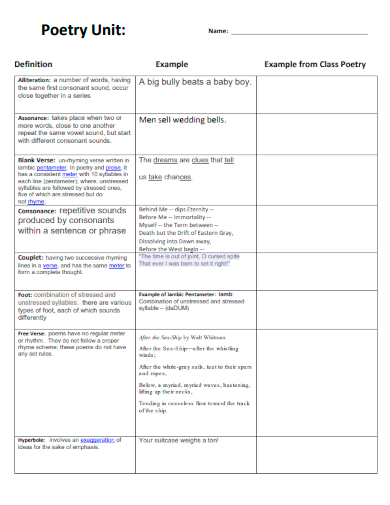
crsd.org
17. Poetry Online Writing

astate.edu
18. Quoting Poetry

monmouth.edu
19. Poetry Square Model

arts.wa.gov
20. Writing about Poetry

hamilton.edu
21. Sample Poetry

mass.edu
22. Examples of Lyrical Poetry

norwellschools.org
23. Poetry in Classroom
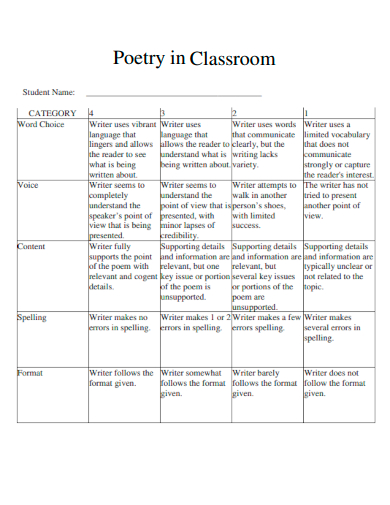
digitalcollections.sit.edu
24. Narrative Poetry

freiburg.de
25. Learning and Teaching of Poetry
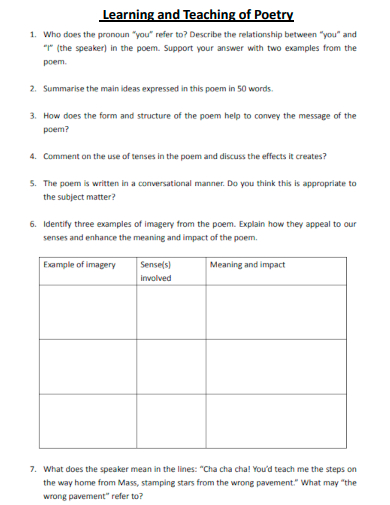
edb.gov.hk
What is Poetry?
Poetry is a form of literary art that defies traditional prose conventions. It is a canvas upon which emotions, thoughts, and experiences are painted with a rhythmic and melodic brush. This art form relies on language’s capacity to evoke emotions through carefully chosen words, rhythm, and structure. Each poem is a tapestry woven with elements such as tone, theme, alliteration, and stanza formation, all coming together to create a rich and evocative reading experience.
How to Write a Poem
Creating a poem is an intimate journey of self-expression, where your emotions and thoughts become art. To embark on this journey, follow these steps to weave your own tapestry of words, one stanza at a time.
Step 1: Selecting a Theme
Begin by selecting a theme that resonates with you. This could be love, nature, freedom, or any topic that stirs your emotions. The theme sets the context for your poem, guiding your words toward a unified message.
Step 2: Setting the Tone
The tone of your poem sets the emotional atmosphere. Decide if your poem will be melancholic, joyful, contemplative, or another tone that aligns with your chosen theme. The tone imbues your verses with the desired emotional impact.
Step 3: Exploring Literary Devices
Introduce literary devices to your poem to add depth and beauty. Metaphors, for instance, offer vivid imagery by comparing unrelated concepts, while alliteration provides a melodic quality by repeating consonant sounds. Experiment with these devices to enhance the sensory experience of your poem.
Step 4: Crafting Stanzaic Structure
The stanza, a group of lines in a poem, serves as a structural element. Determine the number of lines per stanza and the rhyme scheme. For example, a sonnet follows a specific rhyme scheme and structure, while free verse offers flexibility. Your choice depends on the desired rhythm and flow of your poem.
FAQs
Can I use multiple tones in a single poem?
Yes, you can! Mixing tones can create dynamic contrasts, emphasizing different emotions within the same poem. Just ensure that the shifts in tone contribute to the overall theme and flow.
How do I find inspiration for themes?
Inspiration can be found in everyday life, personal experiences, books, nature, and even other poems. Reflect on what moves you and delve into your emotions to find compelling themes.
Are there rules for syllable counts in each line?
While some forms like haiku have strict syllable counts, many modern poems have flexible syllable patterns. The choice depends on the desired rhythm and emphasis of your verses.
As you embark on your poetic journey, remember that every poem is a unique creation, a reflection of your thoughts and emotions woven into the fabric of language. By embracing themes, playing with tones, employing literary devices, and crafting a stanzaic structure, you breathe life into your verses. Let poetry be your canvas, and let your words resonate with the power of metaphors and context, forming a timeless masterpiece that captures the essence of the human experience.

