31+ Perfect Competition Examples to Download
In the vast landscape of economic theory, perfect competition stands as a fundamental concept that shapes our understanding of markets, competition, and pricing mechanisms. This article delves into the realm of perfect competition, offering insights into its definition, characteristics, and real-world examples. Whether you’re a student seeking to grasp the basics or an enthusiast eager to explore economic intricacies, this article provides a comprehensive guide to perfect competition.
1. Simple Perfect Competition Example

sfu.ca
2. The Firm and the Industry under Perfect Competition

csun.edu
3. Sample Perfect Competition Example

unf.edu
4. Perfect Competition Questions

users.ssc.wisc.edu
5. Perfect Competition Monopoly

sites.bu.edu
6. Basic Perfect Competition Example

faculty.econ.ucdavis.edu
7. Draft Perfect Competition Example

uir.unisa.ac.za
8. Perfect Competition and Other Market Structures

account.ache.org
9. Highly Competitive Markets Example

manhassetschools.org
10. Perfect Competition and Welfare

econ.ucla.edu
11. Perfect Competition in Markets with Adverse Selection

bfi.uchicago.edu
12. Editable Perfect Competition Example

fimt-ggsipu.org
13. Perfect Competition and Monopoly

dsfepf2015.weebly.com
14. Perfect Competition, Oligopoly and Monopolies
globalyouth.wharton.upenn.edu
15. Note on the History of Perfect Competition

economia.unam.mx
16. Printable Perfect Competition Example

myweb.dmacc.edu
17. Monopoly and Perfect Competition Compared
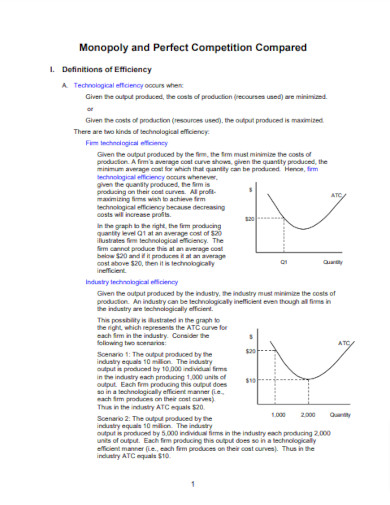
courses.missouristate.edu
18. Perfect Competition Model of Markets

web.mst.edu
19. Producer Theory Perfect Competition

columbia.edu
20. Standard Perfect Competition Example

mlcompton.files.wordpress.com
21. The Perfectly Competitive Market

cambridgescholars.com
22. Price Determination Under Perfect Competition

soghracollege.com
23. Modern Perfect Competition Example

core.ac.uk
24. Creative Perfect Competition Example

magadhmahilacollege.org
25. Perfect Competition and Economic Welfare

dcpopp.expressions.syr.edu
26. Basic Perfect Competition and Monopoly

users.ox.ac.uk
27. Perfect Competition and Profit Maximization

bpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com
28. Perfectly Competitive Markets Example

belkcollegeofbusiness.charlotte.edu
29. Layout Perfect Competition Example

egyankosh.ac.in
30. Outline Perfect Competition Example
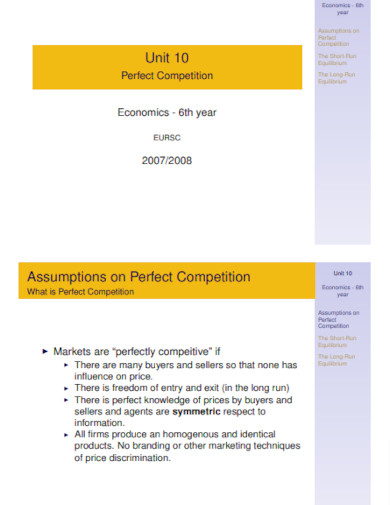
um.es
31. Perfect Competition Multiple Choice Questions
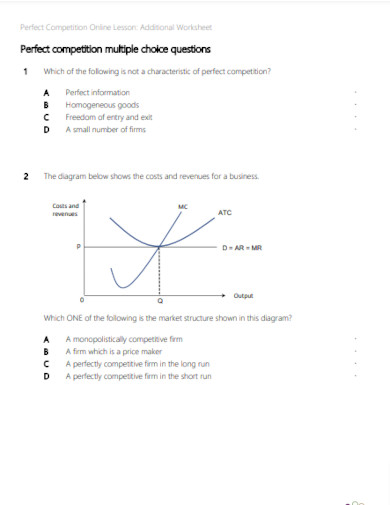
32. Perfect Competition Market Structure

thebusinessguys.ie
What is Perfect Competition?
Perfect competition, within the context of microeconomics, is a theoretical market structure that serves as a foundation for understanding how markets operate under specific conditions. In a perfectly competitive market, numerous buyers and sellers engage in transactions involving identical products. Each participant is a price taker, implying they have no influence on the market price. This context offers a simplified yet insightful way to study market dynamics and their impact on prices and output levels.
How to Understand Perfect Competition?
To gain a holistic understanding of perfect competition, follow this step-by-step guide. Each step sheds light on different aspects of this economic concept, allowing you to grasp its nuances effectively.
Step 1: Grasping the Basic Elements
Begin by understanding the foundational elements of perfect competition. These include a large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, ease of market entry and exit, perfect information availability, and price-taking behavior. These factors collectively create an environment where no single entity can influence the market economy.
Step 2: Observing Cause and Effect
Delve into the cause-and-effect dynamics within a perfectly competitive market. The interaction between supply and demand leads to equilibrium, determining the market-clearing price and quantity. This observation highlights the interplay between buyer and seller decisions and how they impact market outcomes.
Step 3: Exploring Positive Feedback Loop
Explore the concept of positive feedback within perfect competition. As prices rise, more suppliers are incentivized to enter the market, increasing supply and potentially leading to price decreases. Conversely, lower prices may drive some suppliers to exit, potentially causing prices to rise. This positive feedback loop maintains equilibrium.
Step 4: Analyzing Long-Term Goals
Examine the long-term goals of participants in a perfectly competitive market. Since products are homogenous, buyers often choose the lowest-priced option. For sellers, the objective is to maximize profit, driving efficiency and innovation to remain competitive.
FAQs
What is the primary goal of participants in a perfectly competitive market?
In a perfectly competitive market, both buyers and sellers seek to optimize their positions. Buyers aim to acquire goods at the lowest price, while sellers strive to maximize their profits by offering goods efficiently.
Is perfect competition a realistic market scenario?
While perfect competition serves as a theoretical model, real-world markets often deviate from its assumptions. Imperfect information, product differentiation, and other factors can lead to market structures that differ from perfect competition.
How does perfect competition relate to the concept of correlation?
Perfect competition focuses on the relationship between price and quantity supplied/demanded. Correlation, on the other hand, refers to the statistical association between two variables. While not directly linked, both concepts involve understanding relationships within data.
In conclusion, understanding perfect competition is crucial for comprehending the intricate dance of supply and demand within markets. By grasping the essential elements, observing cause-and-effect relationships, exploring feedback loops, and analyzing long-term goals, you can unlock insights into how this model shapes economic landscapes. While perfect competition may be an idealized scenario, it remains a cornerstone of economic thought, providing valuable insights into the broader world of commerce and trade.

