Gibibit – 20 Examples, Conversion Chart, Uses
A Gibibit (Gib) is a unit of digital information storage, equivalent to 1,073,741,824 bits or 2^30 bits. This binary-based measurement is often used in cloud computing, where precise data quantification is essential. In the realm of digital communication, understanding gibibits is crucial for managing data transmission and storage effectively. As communication technology evolves, the accurate measurement of data in gibibits ensures efficient and reliable information exchange.
What is Gibibit?
A terabit is a unit of digital information storage equivalent to one trillion bits. It is commonly used to measure data transfer speeds in high-capacity communication technology networks.
Examples of Gibibit
- High-Speed Internet: Residential internet plans offering gigabit speeds for faster browsing and streaming.
- Cloud Computing: Enhanced performance in cloud-based applications and services with gigabit connectivity.
- Online Gaming: Reduced latency and smoother gameplay experiences in multiplayer games.
- Video Conferencing: Improved quality and stability in HD video calls and virtual meetings.
- Data Centers: Faster data transfer and backup processes in enterprise data centers.
- Streaming Services: Seamless streaming of 4K and 8K videos on platforms like Netflix and YouTube.
- Smart Homes: Efficient operation of multiple smart devices and IoT gadgets simultaneously.
- Telemedicine: Reliable and high-quality video consultations in healthcare services.
- Remote Work: Enhanced productivity with quick access to cloud-based tools and resources.
- Digital Communication: Faster email and messaging services for businesses and individuals.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Improved VR experiences with reduced lag and higher resolution.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhanced AR applications with real-time data processing.
- Software Updates: Swift download and installation of software updates and patches.
- File Sharing: Quick upload and download of large files in collaborative work environments.
- E-commerce: Faster loading times for online stores, improving user experience.
- Education: Access to high-quality online courses and interactive learning platforms.
- Smart Cities: Efficient management of city infrastructure through connected devices.
- Surveillance Systems: High-definition video surveillance with real-time monitoring.
- Public Wi-Fi: Faster and more reliable internet access in public spaces like airports and libraries.
- Television Broadcasts: High-quality live broadcasts and streaming of sports and events.
Conversion of Gibibit
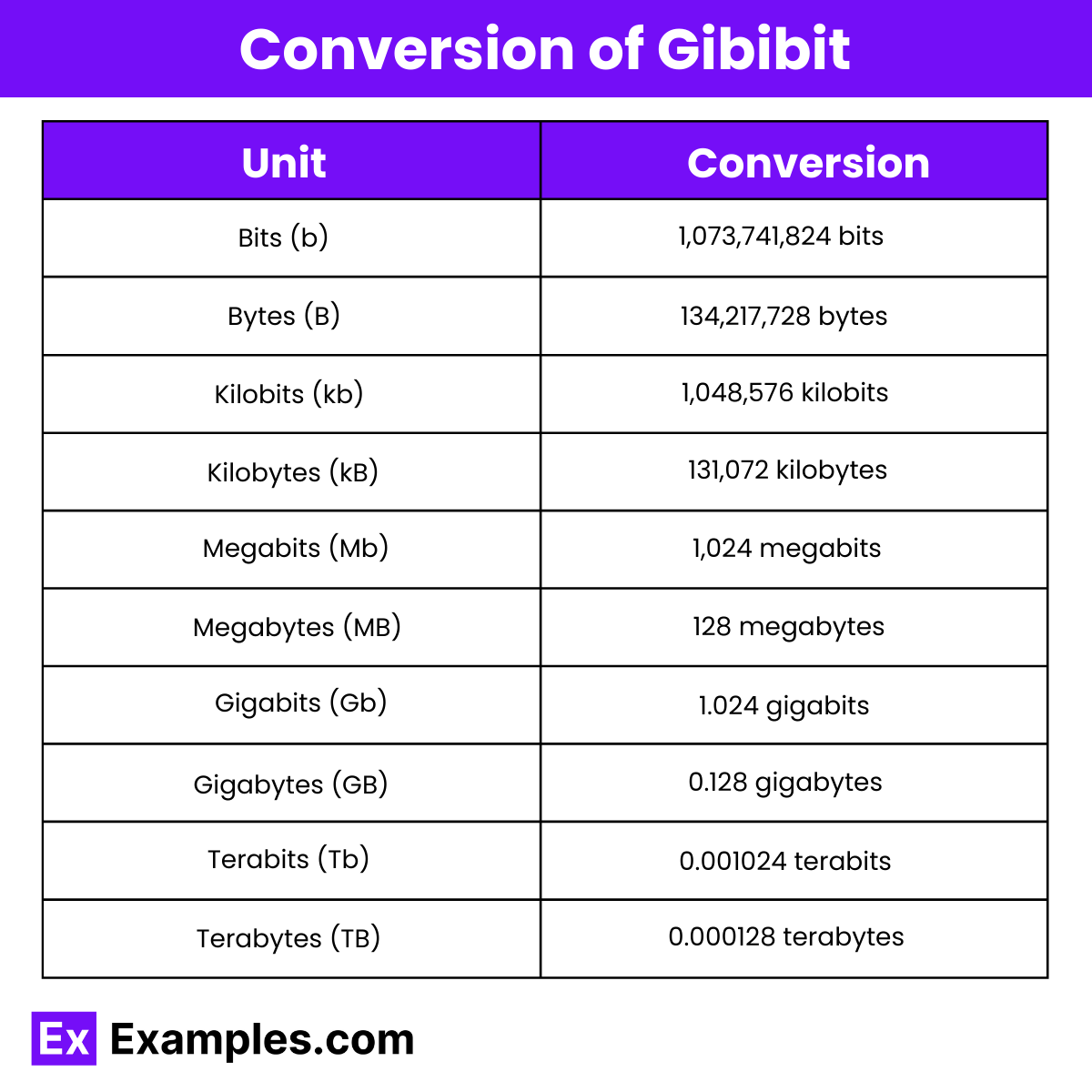
| Unit (Symbol) | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
| Bits (b) | 1 Gibibit = 1,073,741,824 bits |
| Bytes (B) | 1 Gibibit = 134,217,728 bytes |
| Kilobits (kb) | 1 Gibibit = 1,048,576 kilobits |
| Kilobytes (kB) | 1 Gibibit = 131,072 kilobytes |
| Megabits (Mb) | 1 Gibibit = 1,024 megabits |
| Megabytes (MB) | 1 Gibibit = 128 megabytes |
| Gigabits (Gb) | 1 Gibibit = 1.024 gigabits |
| Gigabytes (GB) | 1 Gibibit = 0.128 gigabytes |
| Terabits (Tb) | 1 Gibibit = 0.001024 terabits |
| Terabytes (TB) | 1 Gibibit = 0.000128 terabytes |
Gibibit to Bits (b)
The smallest unit of digital information. One gibibit equals 1,073,741,824 bits. Bits are often used to measure data transfer speeds.
Gibibit to Bytes (B)
There are 8 bits in a byte. One gibibit equals 134,217,728 bytes. Bytes are commonly used to measure file sizes and storage capacity.
Gibibit to Kilobits (kb)
A kilobit is 1,000 bits. One gibibit equals 1,048,576 kilobits. Kilobits are used to measure data transfer rates, such as internet speeds.
Gibibit to Kilobytes (kB)
A kilobyte is 1,000 bytes. One gibibit equals 131,072 kilobytes. Kilobytes are used to describe smaller file sizes.
Gibibit to Megabits (Mb)
A megabit is 1,000,000 bits. One gibibit equals 1,024 megabits. Megabits are used for higher-speed internet connections.
Gibibit to Megabytes (MB)
A megabyte is 1,000,000 bytes. One gibibit equals 128 megabytes. Megabytes are used for medium-sized files, such as images and music files.
Gibibit to Gigabits (Gb)
A gigabit is 1,000,000,000 bits. One gibibit equals approximately 1.024 gigabits. Gigabits are used for high-speed data transfer rates.
Gibibit to Gigabytes (GB)
A gigabyte is 1,000,000,000 bytes. One gibibit equals 0.128 gigabytes. Gigabytes are used for larger files, such as HD videos and software applications.
Gibibit to Terabits (Tb)
A terabit is 1,000,000,000,000 bits. One gibibit equals 0.001024 terabits. Terabits are used for very large data quantities and high-speed network capacities.
Gibibit to Terabytes (TB)
A terabyte is 1,000,000,000,000 bytes. One gibibit equals 0.000128 terabytes. Terabytes are used for massive storage capacities, such as those in data centers.
Importance of Gibibit
Standardized Measurement
- Consistency: Gibibits provide a consistent measurement unit across different platforms and devices. This helps in avoiding confusion that arises from the use of multiple units like megabits (Mb) or gigabits (Gb).
- Precision: Using gibibits ensures precision in measuring large data volumes, critical for technical specifications and engineering applications.
Data Storage and Transmission
- Data Storage: Gibibits are essential in quantifying storage capacity for hard drives, SSDs, and other storage devices. For example, a hard drive’s capacity might be specified as 500 gibibits.
- Data Transmission: In networking, gibibits measure data transfer rates. This is important for evaluating the speed of internet connections and network performance.
Industry Standards
- IEC Standard: Gibibits are part of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards. Adopting these standards ensures interoperability between different systems and manufacturers.
- Avoiding Ambiguity: Gibibits help avoid ambiguity between binary and decimal systems. Unlike gigabits, which can mean 1,000,000,000 bits or 1,073,741,824 bits, gibibits are always binary-based.
Practical Applications
- Software and System Design: Software developers and system architects use gibibits to design systems with precise memory and storage requirements.
- Data Analysis: In fields like data science and big data analytics, accurately measuring data in gibibits ensures the correctness of data processing and storage operations.
Where do you use of Gibibit
Data Storage
- Memory and Storage Devices: Gibibits are used to quantify the capacity of memory modules (RAM) and storage devices (such as SSDs and HDDs). For example, a memory module might be described as having a capacity of 8 Gib.
- File Systems: When configuring file systems, gibibits help in defining partition sizes and managing storage allocations accurately.
Networking
- Data Transfer Rates: In networking, gibibits measure data transfer rates, particularly in contexts where binary measurements are preferred for precision. For example, certain network protocols and configurations may specify transfer rates in Gibps (gibibits per second).
- Bandwidth Measurement: Network bandwidth for certain applications, especially in data centers and high-performance computing environments, might be specified in gibibits.
Operating Systems and Software
- System Specifications: Operating systems and software applications may use gibibits to specify memory requirements and storage needs, ensuring clarity in binary-based measurements.
- Virtual Machines: When configuring virtual machines, gibibits are used to allocate memory and storage resources accurately.
Cloud Computing
- Cloud Storage: Cloud service providers may use gibibits to describe storage capacities and data transfer limits, ensuring precision in billing and resource allocation.
- Data Transfer: In cloud environments, gibibits help in defining data transfer rates between servers and storage systems, facilitating efficient data management.
Technical Documentation
- Technical Specifications: Technical documents and product specifications often use gibibits to describe capacities and speeds in binary terms, providing clear and unambiguous information.
- Engineering Standards: Standards and protocols in computing and networking may adopt gibibits to ensure consistency and accuracy in measurements.
Data Management
- Big Data and Analytics: In big data environments, gibibits are used to measure and manage large datasets, ensuring precise storage and processing capacities.
- Backup and Recovery: Gibibits help in defining backup sizes and recovery data volumes, crucial for data integrity and disaster recovery planning.
Educational Purposes
- Teaching and Learning: In educational settings, gibibits are used to teach students about binary measurements, data storage, and networking concepts, providing a clear understanding of digital information.
- Research and Development: Researchers use gibibits in studies and experiments that require precise data measurement and management.
Embedded Systems
- Firmware and Embedded Applications: In embedded systems, gibibits help define memory and storage requirements for firmware and other embedded applications, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
- IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices may use gibibits to specify data storage and transfer capabilities, supporting accurate and reliable operation.
What is the difference between Gibibit and Gibibyte
| Aspect | Gibibit (Gib) | Gibibyte (GiB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1 Gibibit = 2^30 bits | 1 Gibibyte = 2^30 bytes |
| Units | Bits | Bytes |
| Binary Equivalent | 1 Gibibit = 1,024 Mebibits (Mib) | 1 Gibibyte = 1,024 Mebibytes (MiB) |
| Decimal Equivalent | 1 Gibibit ≈ 1.0737 billion (10^9) bits | 1 Gibibyte ≈ 1.0737 billion (10^9) bytes |
| Usage | Network bandwidth, data transfer rates | Data storage capacities |
| Measurement Context | Typically used for measuring data transfer speed or network capacity | Typically used for measuring data storage and capacity |
| Volume Comparison | 1 Gibibit = 0.125 Gibibytes (GiB) | 1 Gibibyte = 8 Gibibits (Gib) |
| Symbol | Gib | GiB |
| Common Applications | High-speed data transfer, network engineering | Storage devices, memory modules, file systems |
How does a gibibit compare to a gigabit?
A gibibit is 1,073,741,824 bits, while a gigabit is 1,000,000,000 bits.
Why use gibibits instead of gigabits?
Gibibits provide precise binary measurements, avoiding confusion with decimal-based gigabits.
Are gibibits used in memory specifications?
Yes, gibibits are commonly used to specify RAM capacities in computing.
How do gibibits benefit networking?
Gibibits measure data transfer rates in high-speed networks, ensuring accuracy.
What is the symbol for gibibit?
The symbol for gibibit is Gib.
How many bits are in a gibibit?
There are 1,073,741,824 bits in one gibibit.
Can gibibits measure storage device capacity?
Yes, storage devices like SSDs and HDDs often use gibibits for capacity measurement.
How many gibibits are in a tebibit?
There are 1,024 gibibits in a tebibit.
How do gibibits relate to data transfer rates?
High-speed data transfer rates in networking can be measured in gibibits per second (Gibps).
How do gibibits help in file systems?
File systems use gibibits to define partition sizes and manage storage accurately.


