Gigabit – 20 Examples, Conversion Chart, Uses
Gigabit technology is revolutionizing digital communication by offering incredibly fast data transfer speeds, making it essential for modern communication technology. This advancement supports the growing demands of cloud computing, allowing for more efficient and seamless access to cloud-based services. With gigabit speeds, users can experience unprecedented efficiency in both personal and professional digital interactions. As a cornerstone of the future of connectivity, gigabit technology enhances the overall infrastructure of communication technology.
What is Gigabit?
A gigabit is a unit of data transfer rate equal to one billion bits per second (Gbps), used in digital communication to measure high-speed network performance. It is commonly used in communication technology to describe the capacity of internet and network connections.
Examples of Gigabit
- Gigabit Ethernet – Network connections in homes and offices offering speeds up to 1 Gbps.
- Fiber Optic Internet – High-speed internet services providing gigabit speeds.
- 5G Networks – Mobile networks capable of reaching gigabit speeds.
- Data Centers – Facilities using gigabit connections for fast data transfer and storage.
- Streaming Services – Platforms like Netflix and YouTube that require gigabit speeds for 4K streaming.
- Cloud Computing – Services that rely on gigabit connections for efficient data access and processing.
- Smart Cities – Urban areas using gigabit networks for smart infrastructure and services.
- Gaming Consoles – Devices that use gigabit speeds for seamless online gaming experiences.
- Virtual Reality (VR) – Applications that require high-speed gigabit connections for immersive experiences.
- Remote Work – Businesses using gigabit connections for efficient telecommuting and video conferencing.
- Telemedicine – Healthcare services utilizing gigabit speeds for real-time patient consultations.
- IoT Devices – Internet of Things devices that depend on gigabit speeds for rapid data exchange.
- Cloud Storage – Services like Google Drive and Dropbox using gigabit speeds for fast uploads and downloads.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) – Systems that leverage gigabit networks for intensive computational tasks.
- Smart Home Systems – Home automation systems relying on gigabit speeds for smooth operation.
- Educational Platforms – Online learning environments that use gigabit connections for live classes and content delivery.
- Financial Transactions – Stock exchanges and banking services using gigabit speeds for fast, secure transactions.
- Business Networks – Corporate networks employing gigabit technology for efficient internal and external communication.
- Media Production – Studios and production houses using gigabit speeds for high-quality media creation and distribution.
- E-commerce Websites – Online shopping platforms that benefit from gigabit speeds for quick data processing and customer interactions.
Conversion of Gigabit
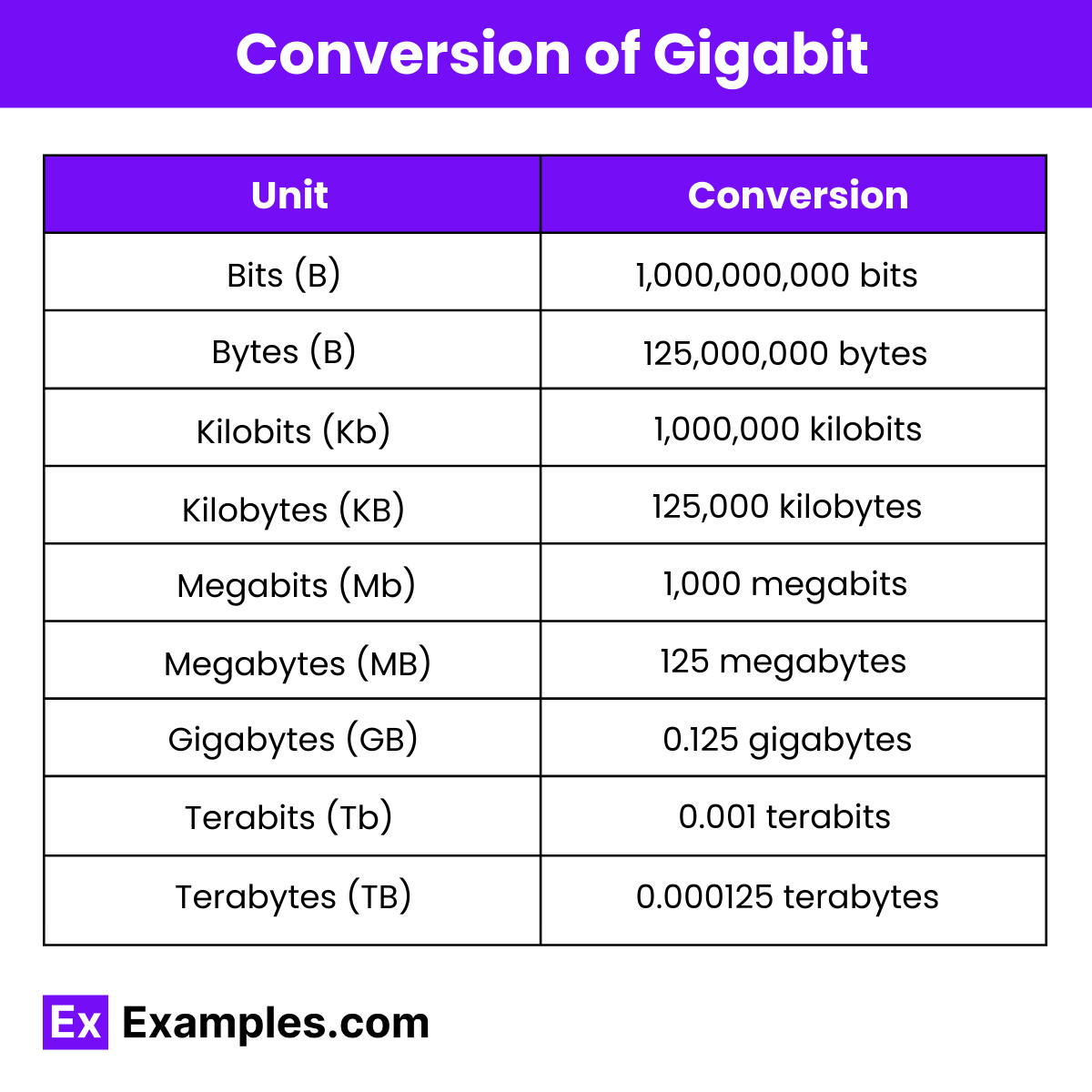
| Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Bits | 1,000,000,000 bits |
| Bytes | 125,000,000 bytes |
| Kilobits (Kb) | 1,000,000 kilobits |
| Kilobytes (KB) | 125,000 kilobytes |
| Megabits (Mb) | 1,000 megabits |
| Megabytes (MB) | 125 megabytes |
| Gigabytes (GB) | 0.125 gigabytes |
| Terabits (Tb) | 0.001 terabits |
| Terabytes (TB) | 0.000125 terabytes |
Gigabit to Bits
A gigabit is equal to one billion bits. Bits are the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a binary value of either 0 or 1.
Gigabit to Bytes
There are 8 bits in a byte. Therefore, 1 gigabit is equal to 1,000,000,000 bits divided by 8, which equals 125,000,000 bytes.
Gigabit to Kilobits (Kb)
One kilobit is equal to 1,000 bits. Thus, 1 gigabit, which is 1,000,000,000 bits, equals 1,000,000 kilobits.
Gigabit to Kilobytes (KB)
Since there are 1,024 bytes in a kilobyte, and 1 gigabit is 125,000,000 bytes, dividing 125,000,000 bytes by 1,024 gives approximately 125,000 kilobytes.
Gigabit to Megabits (Mb)
One megabit is equal to 1,000,000 bits. Therefore, 1 gigabit equals 1,000 megabits.
Gigabit to Megabits (Mb)
Since there are 8 bits in a byte and 1,000,000 bytes in a megabyte, 1 gigabit, which is 1,000 megabits, equals 125 megabytes (1,000 megabits divided by 8).
Gigabit to Gigabytes (GB)
There are 8 gigabits in a gigabyte. Thus, 1 gigabit is equal to 1/8 or 0.125 gigabytes.
Gigabit to Terabits (Tb)
One terabit is equal to 1,000 gigabits. Therefore, 1 gigabit equals 0.001 terabits.
Gigabit to Terabytes (TB)
Since there are 1,000 gigabits in a terabit and 8 terabits in a terabyte, 1 gigabit equals 0.000125 terabytes (1 divided by 8,000).
Importance of Gigabit
Standardized Measurement
- Consistency: Gigabits provide a standardized unit of measurement across various platforms and devices. This uniformity helps avoid confusion when dealing with data sizes and transmission rates.
- Precision: Using gigabits ensures precise measurements of large data volumes, critical for technical specifications and engineering applications.
Data Transmission
- High-Speed Internet: Gigabit speeds are often associated with high-speed internet connections. Internet service providers (ISPs) use gigabit measurements to advertise their fastest service tiers, promising speeds up to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second).
- Networking: In networking, gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is a common standard for local area networks (LANs). It offers faster data transfer rates compared to older standards like Fast Ethernet, significantly improving network performance.
Data Storage
- Capacity Measurement: Although gigabits are less commonly used than gigabytes (GB) for storage, they still serve as a useful measure for certain data quantities, particularly in contexts where transmission speed and network bandwidth are more relevant.
Industry Standards
- IEEE Standard: Gigabits are part of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards, particularly in networking (e.g., IEEE 802.3ab for Gigabit Ethernet). Adopting these standards ensures compatibility and interoperability between devices from different manufacturers.
- Widely Recognized: The term gigabit is widely recognized and used in industry, making it a convenient reference point for consumers and professionals alike.
Practical Applications
- Streaming and Downloading: High-definition video streaming services and large file downloads benefit from gigabit speeds, reducing buffering times and download durations.
- Cloud Computing: Gigabit speeds are essential for efficient cloud computing and data center operations, enabling quick data transfers between servers and clients.
Where do you use of Gigabit
Networking and Internet
- Internet Speeds: Internet service providers (ISPs) advertise their high-speed internet plans using gigabits per second (Gbps). For example, a 1 Gbps connection can download large files and stream high-definition video content with minimal buffering.
- Gigabit Ethernet (GbE): This is a standard for Ethernet networks that provides data transfer rates of up to 1 Gbps. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) to ensure fast and reliable communication between devices.
- Data Centers: Gigabit connections are essential for data centers that require high-speed data transfers between servers, storage devices, and networks.
Data Transmission
- Fiber Optic Networks: Many fiber optic networks use gigabit speeds to provide fast and reliable internet connections to homes and businesses. Fiber optic technology supports high data transfer rates and is crucial for modern telecommunications.
- Wireless Networks: Advanced wireless standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, support gigabit speeds, enabling faster data transmission and improved connectivity for mobile devices.
Media and Entertainment
- Streaming Services: High-definition and ultra-high-definition video streaming services, like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and YouTube, require gigabit speeds to deliver smooth and uninterrupted viewing experiences.
- Online Gaming: Gigabit internet speeds reduce latency and improve the overall gaming experience by allowing faster data exchanges between gaming servers and players.
Cloud Computing
- Cloud Storage: Gigabit speeds facilitate quick uploads and downloads of large files to and from cloud storage services, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive.
- Virtual Machines: In cloud computing environments, gigabit speeds enable efficient data transfers between virtual machines and servers, enhancing the performance of cloud-based applications.
Business and Enterprise
- Corporate Networks: Businesses use gigabit Ethernet to connect computers, printers, and other devices within their offices, ensuring fast and efficient communication and data sharing.
- Video Conferencing: Gigabit speeds support high-quality video conferencing by providing the necessary bandwidth for smooth and clear video and a transmission.
Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: Gigabit speeds are essential for transferring large medical imaging files, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, between healthcare providers and specialists for timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Telemedicine: High-speed internet connections enable remote consultations and real-time communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Education
- Online Learning: Educational institutions use gigabit internet to support online learning platforms, enabling students to access high-quality video lectures, interactive content, and online resources without interruptions.
- Research Collaboration: Researchers and academics use gigabit connections to share large datasets, collaborate on projects, and access remote computing resources.
Home and Personal Use
- Smart Homes: Gigabit speeds are beneficial for smart home systems that require high bandwidth to connect and control multiple devices, such as security cameras, smart thermostats, and home automation systems.
- File Sharing: Gigabit internet makes it easier and faster to share large files, such as photos, videos, and documents, with friends and family.
What is the difference between Gigabit and Gigabyte
| Aspect | Gigabit (Gb) | Gigabyte (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1 Gigabit = 1 billion (10^9) bits | 1 Gigabyte = 1 billion (10^9) bytes |
| Units | Bits | Bytes |
| Binary Equivalent | 1 Gigabit = 1,024 Megabits (Mb) | 1 Gigabyte = 1,024 Megabytes (MB) |
| Decimal Equivalent | 1 Gigabit = 1,000 Megabits | 1 Gigabyte = 1,000 Megabytes |
| Usage | Network bandwidth, data transfer rates | Data storage capacities |
| Measurement Context | Typically used for measuring data transfer speed or network capacity | Typically used for measuring data storage and capacity |
| Volume Comparison | 1 Gigabit = 0.125 Gigabytes (GB) | 1 Gigabyte = 8 Gigabits (Gb) |
| Symbol | Gb | GB |
| Common Applications | Internet speeds, network connections | Storage devices, file sizes |
How do gigabits benefit internet speeds?
Gigabits provide high-speed internet, enabling fast downloads and smooth streaming.
What is gigabit Ethernet?
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is a standard for network connections with speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Why are gigabits important in networking?
They ensure fast and efficient data transmission in local and wide area networks.
How are gigabits used in data centers?
They facilitate high-speed data transfer between servers and storage systems.
Can gigabits be used for wireless networks?
Yes, advanced Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6 support gigabit speeds.
How do gigabits improve cloud services?
They enhance data transfer rates, ensuring quick uploads and downloads.
Are gigabits used in streaming services?
Yes, they enable high-definition and 4K video streaming with minimal buffering.
How do gigabits help in online gaming?
Gigabit speeds reduce latency and improve gaming performance.
Why are gigabits important for businesses?
They support fast network communication, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
What role do gigabits play in smart homes?
They connect multiple devices, ensuring seamless operation and control.
Gigabit – 20 Examples, Conversion Chart, Uses
Gigabit technology is revolutionizing digital communication by offering incredibly fast data transfer speeds, making it essential for modern communication technology. This advancement supports the growing demands of cloud computing, allowing for more efficient and seamless access to cloud-based services. With gigabit speeds, users can experience unprecedented efficiency in both personal and professional digital interactions. As a cornerstone of the future of connectivity, gigabit technology enhances the overall infrastructure of communication technology.
What is Gigabit?
A gigabit is a unit of data transfer rate equal to one billion bits per second (Gbps), used in digital communication to measure high-speed network performance. It is commonly used in communication technology to describe the capacity of internet and network connections.
Examples of Gigabit
Gigabit Ethernet – Network connections in homes and offices offering speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Fiber Optic Internet – High-speed internet services providing gigabit speeds.
5G Networks – Mobile networks capable of reaching gigabit speeds.
Data Centers – Facilities using gigabit connections for fast data transfer and storage.
Streaming Services – Platforms like Netflix and YouTube that require gigabit speeds for 4K streaming.
Cloud Computing – Services that rely on gigabit connections for efficient data access and processing.
Smart Cities – Urban areas using gigabit networks for smart infrastructure and services.
Gaming Consoles – Devices that use gigabit speeds for seamless online gaming experiences.
Virtual Reality (VR) – Applications that require high-speed gigabit connections for immersive experiences.
Remote Work – Businesses using gigabit connections for efficient telecommuting and video conferencing.
Telemedicine – Healthcare services utilizing gigabit speeds for real-time patient consultations.
IoT Devices – Internet of Things devices that depend on gigabit speeds for rapid data exchange.
Cloud Storage – Services like Google Drive and Dropbox using gigabit speeds for fast uploads and downloads.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) – Systems that leverage gigabit networks for intensive computational tasks.
Smart Home Systems – Home automation systems relying on gigabit speeds for smooth operation.
Educational Platforms – Online learning environments that use gigabit connections for live classes and content delivery.
Financial Transactions – Stock exchanges and banking services using gigabit speeds for fast, secure transactions.
Business Networks – Corporate networks employing gigabit technology for efficient internal and external communication.
Media Production – Studios and production houses using gigabit speeds for high-quality media creation and distribution.
E-commerce Websites – Online shopping platforms that benefit from gigabit speeds for quick data processing and customer interactions.
Conversion of Gigabit
Unit | Value |
|---|---|
Bits | 1,000,000,000 bits |
Bytes | 125,000,000 bytes |
Kilobits (Kb) | 1,000,000 kilobits |
Kilobytes (KB) | 125,000 kilobytes |
Megabits (Mb) | 1,000 megabits |
Megabytes (MB) | 125 megabytes |
Gigabytes (GB) | 0.125 gigabytes |
Terabits (Tb) | 0.001 terabits |
Terabytes (TB) | 0.000125 terabytes |
Gigabit to Bits
1 Gb = 1,000,000,000 bits
A gigabit is equal to one billion bits. Bits are the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a binary value of either 0 or 1.
Gigabit to Bytes
]1 Gb = 125,000,000 bytes
There are 8 bits in a byte. Therefore, 1 gigabit is equal to 1,000,000,000 bits divided by 8, which equals 125,000,000 bytes.
Gigabit to Kilobits (Kb)
1 Gb = 1,000,000 kilobits
One kilobit is equal to 1,000 bits. Thus, 1 gigabit, which is 1,000,000,000 bits, equals 1,000,000 kilobits.
Gigabit to Kilobytes (KB)
1 Gb = 125,000 kilobytes
Since there are 1,024 bytes in a kilobyte, and 1 gigabit is 125,000,000 bytes, dividing 125,000,000 bytes by 1,024 gives approximately 125,000 kilobytes.
Gigabit to Megabits (Mb)
1 Gb = 1,000 megabits
One megabit is equal to 1,000,000 bits. Therefore, 1 gigabit equals 1,000 megabits.
Gigabit to Megabits (Mb)
1 Gb = 125 megabytes
Since there are 8 bits in a byte and 1,000,000 bytes in a megabyte, 1 gigabit, which is 1,000 megabits, equals 125 megabytes (1,000 megabits divided by 8).
Gigabit to Gigabytes (GB)
1 Gb = 0.125 gigabytes
There are 8 gigabits in a gigabyte. Thus, 1 gigabit is equal to 1/8 or 0.125 gigabytes.
Gigabit to Terabits (Tb)
1 Gb = 0.001 terabits
One terabit is equal to 1,000 gigabits. Therefore, 1 gigabit equals 0.001 terabits.
Gigabit to Terabytes (TB)
1 Gb = 0.000125 terabytes
Since there are 1,000 gigabits in a terabit and 8 terabits in a terabyte, 1 gigabit equals 0.000125 terabytes (1 divided by 8,000).
Importance of Gigabit
Standardized Measurement
Consistency: Gigabits provide a standardized unit of measurement across various platforms and devices. This uniformity helps avoid confusion when dealing with data sizes and transmission rates.
Precision: Using gigabits ensures precise measurements of large data volumes, critical for technical specifications and engineering applications.
Data Transmission
High-Speed Internet: Gigabit speeds are often associated with high-speed internet connections. Internet service providers (ISPs) use gigabit measurements to advertise their fastest service tiers, promising speeds up to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second).
Networking: In networking, gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is a common standard for local area networks (LANs). It offers faster data transfer rates compared to older standards like Fast Ethernet, significantly improving network performance.
Data Storage
Capacity Measurement: Although gigabits are less commonly used than gigabytes (GB) for storage, they still serve as a useful measure for certain data quantities, particularly in contexts where transmission speed and network bandwidth are more relevant.
Industry Standards
IEEE Standard: Gigabits are part of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards, particularly in networking (e.g., IEEE 802.3ab for Gigabit Ethernet). Adopting these standards ensures compatibility and interoperability between devices from different manufacturers.
Widely Recognized: The term gigabit is widely recognized and used in industry, making it a convenient reference point for consumers and professionals alike.
Practical Applications
Streaming and Downloading: High-definition video streaming services and large file downloads benefit from gigabit speeds, reducing buffering times and download durations.
Cloud Computing: Gigabit speeds are essential for efficient cloud computing and data center operations, enabling quick data transfers between servers and clients.
Where do you use of Gigabit
Networking and Internet
Internet Speeds: Internet service providers (ISPs) advertise their high-speed internet plans using gigabits per second (Gbps). For example, a 1 Gbps connection can download large files and stream high-definition video content with minimal buffering.
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE): This is a standard for Ethernet networks that provides data transfer rates of up to 1 Gbps. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) to ensure fast and reliable communication between devices.
Data Centers: Gigabit connections are essential for data centers that require high-speed data transfers between servers, storage devices, and networks.
Data Transmission
Fiber Optic Networks: Many fiber optic networks use gigabit speeds to provide fast and reliable internet connections to homes and businesses. Fiber optic technology supports high data transfer rates and is crucial for modern telecommunications.
Wireless Networks: Advanced wireless standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 and 5G, support gigabit speeds, enabling faster data transmission and improved connectivity for mobile devices.
Media and Entertainment
Streaming Services: High-definition and ultra-high-definition video streaming services, like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and YouTube, require gigabit speeds to deliver smooth and uninterrupted viewing experiences.
Online Gaming: Gigabit internet speeds reduce latency and improve the overall gaming experience by allowing faster data exchanges between gaming servers and players.
Cloud Computing
Cloud Storage: Gigabit speeds facilitate quick uploads and downloads of large files to and from cloud storage services, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive.
Virtual Machines: In cloud computing environments, gigabit speeds enable efficient data transfers between virtual machines and servers, enhancing the performance of cloud-based applications.
Business and Enterprise
Corporate Networks: Businesses use gigabit Ethernet to connect computers, printers, and other devices within their offices, ensuring fast and efficient communication and data sharing.
Video Conferencing: Gigabit speeds support high-quality video conferencing by providing the necessary bandwidth for smooth and clear video and a transmission.
Healthcare
Medical Imaging: Gigabit speeds are essential for transferring large medical imaging files, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, between healthcare providers and specialists for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Telemedicine: High-speed internet connections enable remote consultations and real-time communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Education
Online Learning: Educational institutions use gigabit internet to support online learning platforms, enabling students to access high-quality video lectures, interactive content, and online resources without interruptions.
Research Collaboration: Researchers and academics use gigabit connections to share large datasets, collaborate on projects, and access remote computing resources.
Home and Personal Use
Smart Homes: Gigabit speeds are beneficial for smart home systems that require high bandwidth to connect and control multiple devices, such as security cameras, smart thermostats, and home automation systems.
File Sharing: Gigabit internet makes it easier and faster to share large files, such as photos, videos, and documents, with friends and family.
What is the difference between Gigabit and Gigabyte
Aspect | Gigabit (Gb) | Gigabyte (GB) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | 1 Gigabit = 1 billion (10^9) bits | 1 Gigabyte = 1 billion (10^9) bytes |
Units | Bits | Bytes |
Binary Equivalent | 1 Gigabit = 1,024 Megabits (Mb) | 1 Gigabyte = 1,024 Megabytes (MB) |
Decimal Equivalent | 1 Gigabit = 1,000 Megabits | 1 Gigabyte = 1,000 Megabytes |
Usage | Network bandwidth, data transfer rates | Data storage capacities |
Measurement Context | Typically used for measuring data transfer speed or network capacity | Typically used for measuring data storage and capacity |
Volume Comparison | 1 Gigabit = 0.125 Gigabytes (GB) | 1 Gigabyte = 8 Gigabits (Gb) |
Symbol | Gb | GB |
Common Applications | Internet speeds, network connections | Storage devices, file sizes |
How do gigabits benefit internet speeds?
Gigabits provide high-speed internet, enabling fast downloads and smooth streaming.
What is gigabit Ethernet?
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is a standard for network connections with speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Why are gigabits important in networking?
They ensure fast and efficient data transmission in local and wide area networks.
How are gigabits used in data centers?
They facilitate high-speed data transfer between servers and storage systems.
Can gigabits be used for wireless networks?
Yes, advanced Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6 support gigabit speeds.
How do gigabits improve cloud services?
They enhance data transfer rates, ensuring quick uploads and downloads.
Are gigabits used in streaming services?
Yes, they enable high-definition and 4K video streaming with minimal buffering.
How do gigabits help in online gaming?
Gigabit speeds reduce latency and improve gaming performance.
Why are gigabits important for businesses?
They support fast network communication, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
What role do gigabits play in smart homes?
They connect multiple devices, ensuring seamless operation and control.

