Gigabyte – 20 Examples, Uses, Applications, Differences
Gigabyte Technology is a leading manufacturer in the realm of digital communication and communication technology. Renowned for their high-performance motherboards and graphics cards, Gigabyte also ventures into cloud computing solutions, enhancing their product portfolio to meet modern technological demands. Their innovative approach ensures robust and reliable technology, making Gigabyte a trusted name in the industry.
What is Gigabyte?
Gigabyte Technology is a leading manufacturer specializing in high-performance computer hardware, including motherboards and graphics cards, as well as solutions in digital communication and cloud computing.
Examples of Gigabyte
- Gigabyte Z690 AORUS Master Motherboard
- Gigabyte AORUS GeForce RTX 3080 Graphics Card
- Gigabyte B550M DS3H Motherboard
- Gigabyte AERO 15 OLED Laptop
- Gigabyte AORUS 15G Gaming Laptop
- Gigabyte AORUS FI27Q Gaming Monitor
- Gigabyte AORUS NVMe Gen4 SSD
- Gigabyte Radeon RX 6800 XT Graphics Card
- Gigabyte X570 AORUS Elite Motherboard
- Gigabyte AORUS 17X Gaming Laptop
- Gigabyte H410M S2H Motherboard
- Gigabyte AORUS AC300W Gaming Case
- Gigabyte P750GM Power Supply
- Gigabyte AORUS FO48U Gaming Monitor
- Gigabyte M32Q Gaming Monitor
- Gigabyte AORUS K1 Mechanical Keyboard
- Gigabyte AORUS M5 Gaming Mouse
- Gigabyte AORUS CV27Q Gaming Monitor
- Gigabyte B365M DS3H Motherboard
- Gigabyte AORUS Waterforce X 360 AIO Cooler
How big is a Gigabyte?
1 GB = 1,048,576 kilobytes (KB)
1 GB = 1,073,741,824 bytes
What are Gigabyte used for?
1. Storage Devices
- Hard Drives and SSDs: Gigabytes are commonly used to describe the capacity of hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs). For instance, a 500 GB hard drive can store a significant amount of data, including applications, documents, and multimedia files.
- USB Drives and Memory Cards: Portable storage devices like USB flash drives and SD cards are often labeled in Gigabytes, such as a 64 GB flash drive or a 32 GB memory card.
2. Memory (RAM) Measurement
- RAM: Although less common than Gibibytes in technical specifications, Gigabytes are sometimes used to indicate the capacity of computer memory (RAM). For example, a computer might be advertised with 8 GB of RAM.
3. Software and Applications
- Software Size: The size of software applications, including operating systems, is often measured in Gigabytes. For example, an operating system might require 20 GB of disk space.
- Game Files: Modern video games can be very large, often requiring several Gigabytes of storage space. For instance, a game might need 50 GB of space for installation.
4. Multimedia Files
- Videos and Movies: High-definition videos and movies can be large, with sizes often measured in Gigabytes. A high-definition movie might be around 4 to 8 GB in size.
- Music Libraries: Large collections of music files, especially in high-quality formats, can also accumulate into Gigabytes. For example, 1 GB of storage can hold roughly 200-250 high-quality MP3 songs.
5. Data Transfer and Internet Plans
- Data Plans: Internet service providers (ISPs) and mobile carriers use Gigabytes to describe data limits in their plans. For example, a mobile data plan might offer 10 GB of data per month.
- File Transfers: Large file transfers, especially over networks or the internet, are measured in Gigabytes. For instance, downloading a 5 GB file from the internet.
6. Cloud Storage
- Cloud Services: Cloud storage providers use Gigabytes to describe the amount of storage they offer. For instance, a cloud service might provide 100 GB of free storage.
- Backup Solutions: Cloud backup services often advertise their plans in Gigabytes, indicating how much data you can back up. For example, a plan might offer 50 GB of backup space.
7. Digital Media and Content Creation
- Image Files: High-resolution images and professional photography can take up significant storage, often measured in Gigabytes. For instance, a collection of high-resolution photos might require several Gigabytes of storage.
- Video Editing: Video editing projects, especially those involving high-definition footage, can require large amounts of storage space measured in Gigabytes.
Other Units of Gigabyte
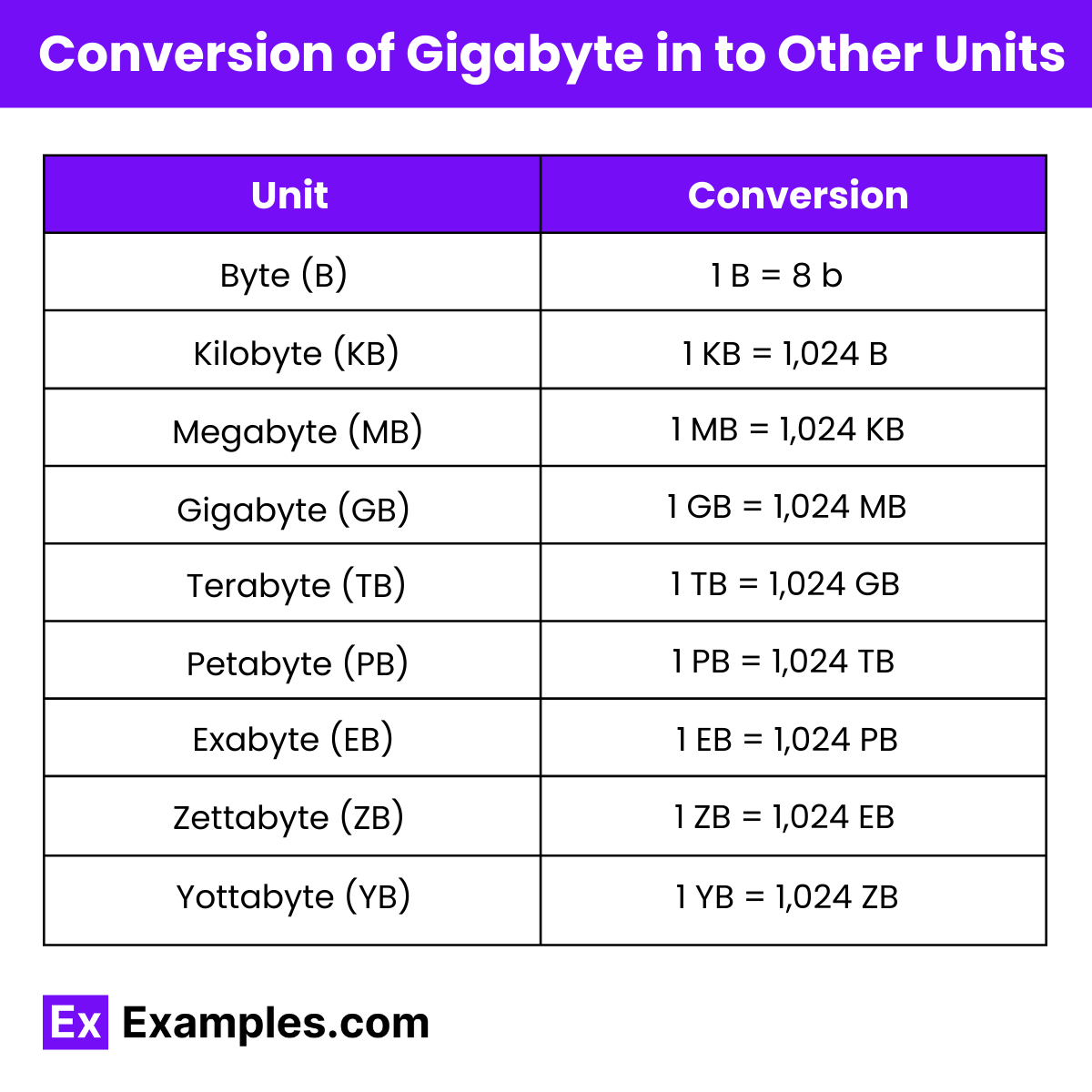
| Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Bytes | 1,073,741,824 bytes |
| Kilobytes (KB) | 1,048,576 kilobytes |
| Megabytes (MB) | 1,024 megabytes |
| Terabytes (TB) | 0.001 terabytes |
| Petabytes (PB) | 0.000001 petabytes |
| Bits | 8,589,934,592 bits |
| Kilobits (Kb) | 8,388,608 kilobits |
| Megabits (Mb) | 8,192 megabits |
| Terabits (Tb) | 0.008 terabits |
Gigabyte (GB) to Byte(B)
A byte is the basic unit of digital information. 1 gigabyte (GB) is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes.
Gigabyte (GB) to Kilobytes (KB)
A kilobyte consists of 1,024 bytes. Therefore, 1 gigabyte equals 1,048,576 kilobytes.
Gigabyte (GB) to Megabytes (MB)
A megabyte is made up of 1,024 kilobytes. Thus, 1 gigabyte is equivalent to 1,024 megabytes.
Gigabyte (GB) to Terabytes (TB)
A terabyte consists of 1,024 gigabytes. Therefore, 1 gigabyte is 0.001 terabytes.
Gigabyte (GB) to Petabytes (PB)
A petabyte is composed of 1,024 terabytes. Thus, 1 gigabyte is 0.000001 petabytes.
Gigabyte (GB) to Bits
A bit is the smallest unit of data, representing a binary value (0 or 1). Since there are 8 bits in a byte, 1 gigabyte equals 8,589,934,592 bits.
Gigabyte (GB) to Kilobits (Kb)
A kilobit consists of 1,024 bits. Therefore, 1 gigabyte equals 8,388,608 kilobits.
Gigabyte (GB) to Megabits (Mb)
A megabit is made up of 1,024 kilobits. Thus, 1 gigabyte is equivalent to 8,192 megabits.
Gigabyte (GB) to Terabits (Tb)
A terabit consists of 1,024 gigabits. Therefore, 1 gigabyte is 0.008 terabits.
Applications of Gigabyte in Data Storage
1. Personal Computing
- Internal Storage: Most computers and laptops come with storage measured in gigabytes, ranging from 128 GB to 1 TB (1,024 GB). This storage is used for the operating system, software applications, and user data.
- USB Flash Drives: Available in sizes ranging from 4 GB to 256 GB, these portable devices are used for transferring files between computers and for backing up important data.
2. Mobile Devices
- Smartphones and Tablets: Devices typically come with storage capacities measured in gigabytes, such as 32 GB, 64 GB, or 128 GB, to store apps, photos, videos, and other user data.
- MicroSD Cards: Used to expand storage in smartphones, cameras, and other portable devices, these cards are available in capacities like 32 GB and 64 GB.
3. Software and Applications
- Operating Systems: Operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux distributions often require several gigabytes of storage for installation. For example, Windows 10 requires around 20 GB of storage space.
- Applications: Software applications, including productivity suites, games, and multimedia programs, often need several gigabytes of storage. For instance, Microsoft Office and Adobe Creative Suite can each occupy multiple gigabytes.
4. Gaming
- Game Storage: Many video games, especially those with high-resolution graphics and extensive content, require several gigabytes of storage. A typical modern game might require anywhere from 10 GB to 100 GB or more.
- Game Consoles: Gaming consoles like the PlayStation 4 and Xbox One offer storage capacities in gigabytes, such as 500 GB or 1 TB (1,024 GB), to store games and downloadable content (DLC).
5. Multimedia Storage
- Photos and Videos: Digital photos and videos, especially those in high resolution, can take up several gigabytes of storage. For example, a collection of 1,000 high-resolution photos might occupy around 4-8 GB.
- Music Libraries: Storing music files, whether they are in MP3, FLAC, or other formats, can require several gigabytes. A music library of 1,000 songs might need around 5-10 GB.
6. Cloud Storage
- Service Plans: Many cloud storage services offer plans with capacities measured in gigabytes, such as 15 GB free on Google Drive or 5 GB free on iCloud. Paid plans often provide more storage, ranging from 100 GB to several terabytes (TB).
- Backup and Sync: Cloud services use gigabyte-level storage for backing up and syncing files across multiple devices.
7. Embedded Systems
- IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart home devices and industrial sensors, often use storage measured in gigabytes for firmware, application data, and logs.
- Automotive Systems: Modern cars use onboard computers with storage capacities in gigabytes to run navigation systems, entertainment systems, and vehicle diagnostics.
8. Educational Tools
- E-books and Courseware: Digital textbooks, e-books, and educational courseware often require several gigabytes of storage, especially when they include multimedia content.
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Coursera, Khan Academy, and others store video lectures, interactive content, and user data, often in gigabyte quantities.
9. Surveillance
- Security Systems: Surveillance cameras and systems generate video footage that is stored in gigabytes. High-resolution video files from multiple cameras can quickly add up to significant storage requirements.
- Data Retention: Businesses and governments use gigabyte storage to comply with data retention policies for surveillance footage.
10. Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: Hospitals and clinics store gigabytes of medical images from X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Electronic Health Records: Patient records and data require gigabyte-level storage to ensure quick access and secure backup.
What is the Difference Between Gigabyte and Gibibyte
| Feature | Gigabyte (GB) | Gibibyte (GiB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A gigabyte is 10^9 bytes. | A gibibyte is 2^30 bytes. |
| Bytes Equivalent | 1,000,000,000 bytes | 1,073,741,824 bytes |
| Measurement System | Decimal (Base-10) | Binary (Base-2) |
| Common Usage | Everyday computing, storage | Computing, precise data storage |
| Application | Hard drives, flash drives | RAM, file systems |
| Standardization Body | International System of Units (SI) | International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) |
| Abbreviation | GB | GiB |
| Comparison to Bytes | 1 GB ≈ 0.931 GiB | 1 GiB ≈ 1.074 GB |
| Example Usage | Advertised storage capacities | Technical specifications |
| Conversion Factor | 1 GB = 1,000,000,000 bytes | 1 GiB = 1,073,741,824 bytes |
| Common Storage Devices | Hard disks, SSDs, USB drives | Memory modules, some software |
| Marketing vs. Technical | Often used in marketing | More precise for technical details |
How many bytes are in a gigabyte?
A gigabyte contains 1,073,741,824 bytes, essential for storing data in various digital formats, including those influenced by electromagnetism.
What can you store in a gigabyte?
A gigabyte can store approximately 250 songs, 300 photos, or 1 hour of HD video, commonly used in PaaS solutions.
How does electromagnetism relate to gigabytes?
Electromagnetism plays a crucial role in the functioning of hard drives and SSDs, where gigabytes of data are stored.
Is gigabyte storage available in cloud services?
Yes, cloud services, including PaaS, offer gigabyte-level storage for scalable and flexible data management.
How many gigabytes do typical smartphones have?
Most smartphones have between 32 GB and 512 GB of storage, influenced by advancements in electromagnetism.
What is the difference between gigabytes and gibibytes?
A gigabyte equals 1,000,000,000 bytes, while a gibibyte equals 1,073,741,824 bytes. Both are essential in PaaS environments.
What devices typically use gigabytes of storage?
Devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets, as well as servers in PaaS, typically use gigabytes of storage.
How do gigabytes impact data transfer?
Gigabytes influence the speed and volume of data transfer, crucial for efficient electromagnetism-based devices and PaaS applications.
What role do gigabytes play in electromagnetism-based storage?
Gigabytes quantify the storage capacity of devices like hard drives and SSDs, which rely on principles of electromagnetism.
What advancements have improved gigabyte storage?
Advances in electromagnetism and technology have significantly increased the capacity and efficiency of gigabyte storage in digital devices and PaaS platforms.