69+ HTML Examples to Download
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the basic language used to structure and create webpages. It uses tags to define elements like text, images, and links, forming the foundation of web design and development. Simple and essential, HTML powers the content and layout of every website online.
What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to structure and display content on the web, utilizing tags to define elements like text, images, and links.
HTML Format
The basic format of an HTML document is structured as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>: Declares the document as HTML5.<html>: This is the root element that wraps all content in the HTML document.<head>: Contains meta information about the document, such as the<title>tag which sets the title of the webpage.<body>: Contains all the content visible to the users, such as headings (<h1>), paragraphs (<p>), links (<a>), and other elements.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<a href=”https://examples.com”>Examples</a>
</body>
</html>
1. Basic HTML Document

2. HTML Cheatsheet

3. HTML Sample
4. HTML and XHTML

5. HTML and CSS

6. HTML <form> Tag

7. Introduction to HTML

8. HTML Course Syllabus

9. HTML Specification

10. Create HTML File
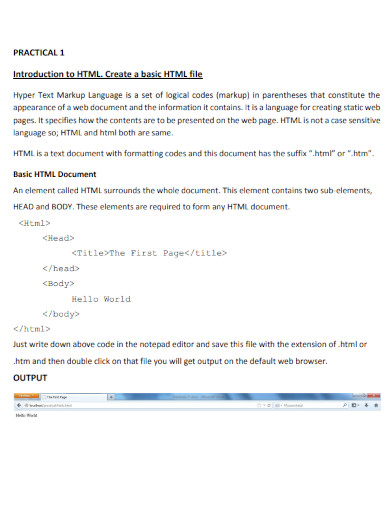
11. HTML Document Format

12. HTML Tags

13. Web Designing Using HTML

14. HTML Code

15. Oracle HTML

16. Differences between HTML and HTML5

17. Creating a Web Page Using HTML

18. HTML Tables
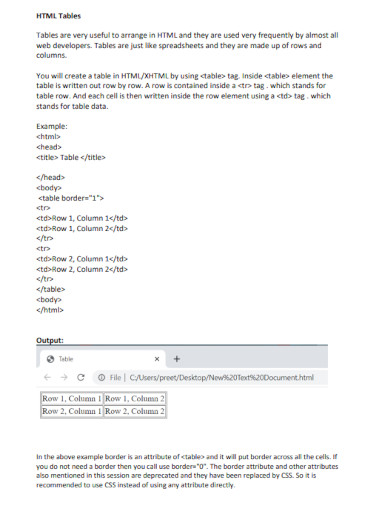
19. HTML PDF

20. HTML Tag Sheet

21. HTML Example

22. HTML Syllabus

23. HTML Sample PDF

24. The Basics of HTML

25. Hello HTML
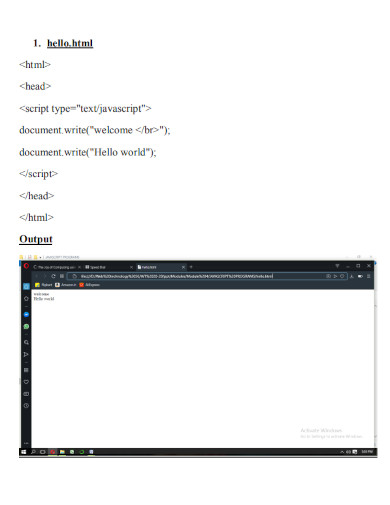
26. Simple HTML Editor

27. HTML Elements

28. Printable HTML

29. HTML for MCA

30. HTML, CSS, Javascript

31. HTML Outline

32. HTML Cheat Sheet Example

33. HTML Format

34. HTML Access
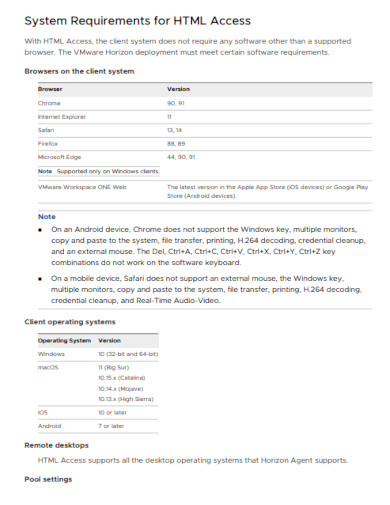
35. HTML Builder

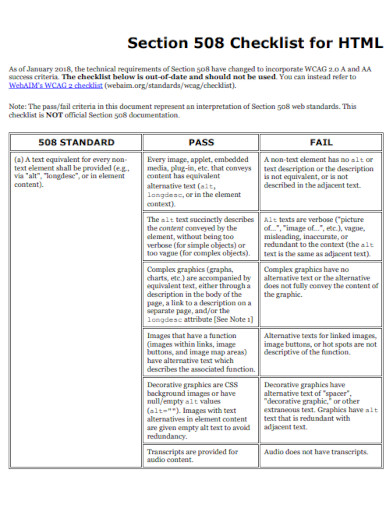
36. Checklist for HTML
37. HTML
38. Creating HTML Forms

39. HTML Example PDF

40. HTML DHTML
41. HTML Chapter

42. Preparing an HTML Document

43. HTML Tags Example

44. HTML Tutorial

45. HTML Computer Science

46. Standard HTML

47. Html Web Page

48. HTML and Java Script

49. Web Developer and HTML

50. HTML Programming

51. HTML Style Sheet

52. Formal HTML

53. Embedding HTML

54. Osnove HTML

55. Sample HTML Template

56. Primer HTML

57. Le Language HTML

58. HTML Sheet

59. HTML5 Semantic Elements
60. HTML Evolution

61. Sample HTML Form

62. Basic HTML Tags

63. Tables and Hyperlinks in HTML

64. HTML 3rd Term Worksheet

65. Basic HTML Template in PDF

66. HTML5 Multimedia

67. HTML Handout
68. HTML Developer
 69. HTML Code Example
69. HTML Code Example
70. Automated HTML
History of HTML
The history of HTML dates back to 1991 when Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, created the first version of HTML. Initially, it was a simple language designed to structure documents and link them together using hyperlinks. The first formal specification, HTML 2.0, was published in 1995, setting the standard for basic web development. Over time, HTML evolved to meet the growing demands of the internet, introducing new features with HTML 3.2 and 4.0, which added support for multimedia and scripting.
In 2014, HTML5 became the latest standard, bringing significant advancements, including support for a, video, and interactive content without the need for plugins. It also improved cross-platform compatibility, making it ideal for modern web and mobile applications. Today, HTML continues to be the backbone of the web, powering billions of websites worldwide.
How to Build HTML

To build HTML, follow these steps:
- Choose a Text Editor: Use a simple editor like Notepad or advanced tools like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text.
- Create a New File: Start a new file and save it with a
.htmlextension. - Write the Structure: Add the basic structure:
- Save the File: Save it as
filename.html. - Open in a Browser: Double-click the file or open it in a browser to view your webpage.
- Enhance the Page: Add more elements like images, links, or lists to expand functionality.
How to Use HTML

- Set Up a Text Editor: Use a plain text editor like Notepad (Windows), TextEdit (Mac), or a code editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom.
- Create a New File: Open your editor and create a new file with a
.htmlextension (e.g.,index.html). - Start with Basic Structure:
- Begin with the
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration. - Add
<html>,<head>, and<body>tags for structure.
- Begin with the
- Add Content: Write HTML tags inside the
<body>section to include headings (<h1>), paragraphs (<p>), links (<a>), images (<img>), and more. - Save the File: Save the file with the
.htmlextension. - Open in a Browser: Double-click the saved file or open it in any web browser to view the webpage.
- Style and Enhance: Use CSS for styling and JavaScript for interactivity to make your HTML document more dynamic.
- Test and Validate: Check for errors and validate your HTML code using online tools like the W3C Validator to ensure compatibility.
FAQs
What is an HTML file used for?
An HTML file is used to create and structure content for webpages, defining elements like headings, paragraphs, images, and links.
What is the purpose of HTML?
The purpose of HTML is to provide the structure and layout of web content, enabling browsers to display it as intended.
Does HTML stand for Hotmail?
No, HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.
How to convert HTML to Word?
Open the HTML file in a browser, copy the content, and paste it into a Word document. Alternatively, use online converters or save as a Word-compatible format.
What are tags in HTML?
Tags in HTML are the basic building blocks used to define elements like headings, links, and images. They usually come in pairs, with opening and closing tags (e.g., <p> and </p> for paragraphs).