Kilobyte – 40 Examples, Uses, Applications, Differences
A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information storage, equivalent to 1,024 bytes. In the realms of cloud computing and digital communication, kilobytes play a crucial role in data transmission and storage efficiency. As communication technology advances, understanding the basic units like kilobytes becomes essential for optimizing data handling and improving system performance. This fundamental knowledge supports the seamless integration and functionality of modern digital systems.
What is Kilobyte?
A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information storage equal to 1,024 bytes. It is commonly used to measure the size of small files and data in computing and digital communication.
Examples of Kilobyte
- A short text document
- An email without attachments
- A small thumbnail image
- A short text message (SMS)
- A simple website HTML file
- An address book contact entry
- A basic spreadsheet file
- A small icon file
- A small log file
- A basic configuration file
- A short poem or essay
- A small JSON file
- A short XML file
- A single entry in a database
- A brief memo or note
- A short list of items
- A minimalistic CSS file
- A tiny vector graphic (SVG)
- A short script or batch file
- A small programming code file
- A basic INI file
- A short piece of music in MIDI format
- A brief journal entry
- A small plaintext file
- A short excerpt from a book
- A minimalistic JSON file
- A small piece of encoded data
- A single line of binary code
- A short excerpt from a log file
- A small system file
- A brief entry in a digital diary
- A simple readme file
- A single function in a code library
- A brief error message log
- A small help documentation file
- A short data packet in networking
- A small configuration script
- A brief API response
- A minimalistic HTML template
- A short term paper draft
How Much is a Kilobyte?
What are Kilobyte used for?
1. File Sizes
Kilobytes are often used to measure the size of small to moderately sized files, such as:
- Text Files: Documents like Word files, text files (.txt), and other small documents.
- Images: Small image files, especially those in formats like GIF or PNG with limited colors.
- Web Pages: Basic HTML web pages and small scripts or style sheets.
2. Memory and Storage
Kilobytes are used to measure the capacity of smaller memory units and storage in older or simpler systems. Examples include:
- Cache Memory: L1 and L2 cache memory in CPUs, often measured in kilobytes.
- Embedded Systems: Memory in microcontrollers and other embedded systems, where storage and memory are limited.
3. Networking
In networking, kilobytes are used to measure data transfer rates and packet sizes, especially in contexts where the amount of data transferred is relatively small. For instance:
- Data Transfer: Measuring small data transfers, such as initial packet exchanges in network communications.
- Email Attachments: Small email attachments, which are often limited to a few kilobytes.
4. Programming and Development
Developers often use kilobytes to define buffer sizes, memory allocation for smaller structures, and other low-level memory management tasks. Examples include:
- Buffer Sizes: Allocating buffer sizes for small data operations in programs.
- Data Structures: Allocating memory for small data structures or arrays.
5. Configuration Files and Settings
Configuration files and settings files, which are typically small in size, are often measured in kilobytes. Examples include:
- INI Files: Configuration files for software applications.
- Log Files: Small log files that track application events or errors.
6. Digital Communications
In digital communications, kilobytes can be used to measure the size of messages, data packets, and other small data units. Examples include:
- SMS Messages: Measuring the size of SMS and MMS messages.
- Protocol Data Units: Size of protocol data units (PDUs) in communication protocols.
Converting Kilobyte in to Other Units of Data
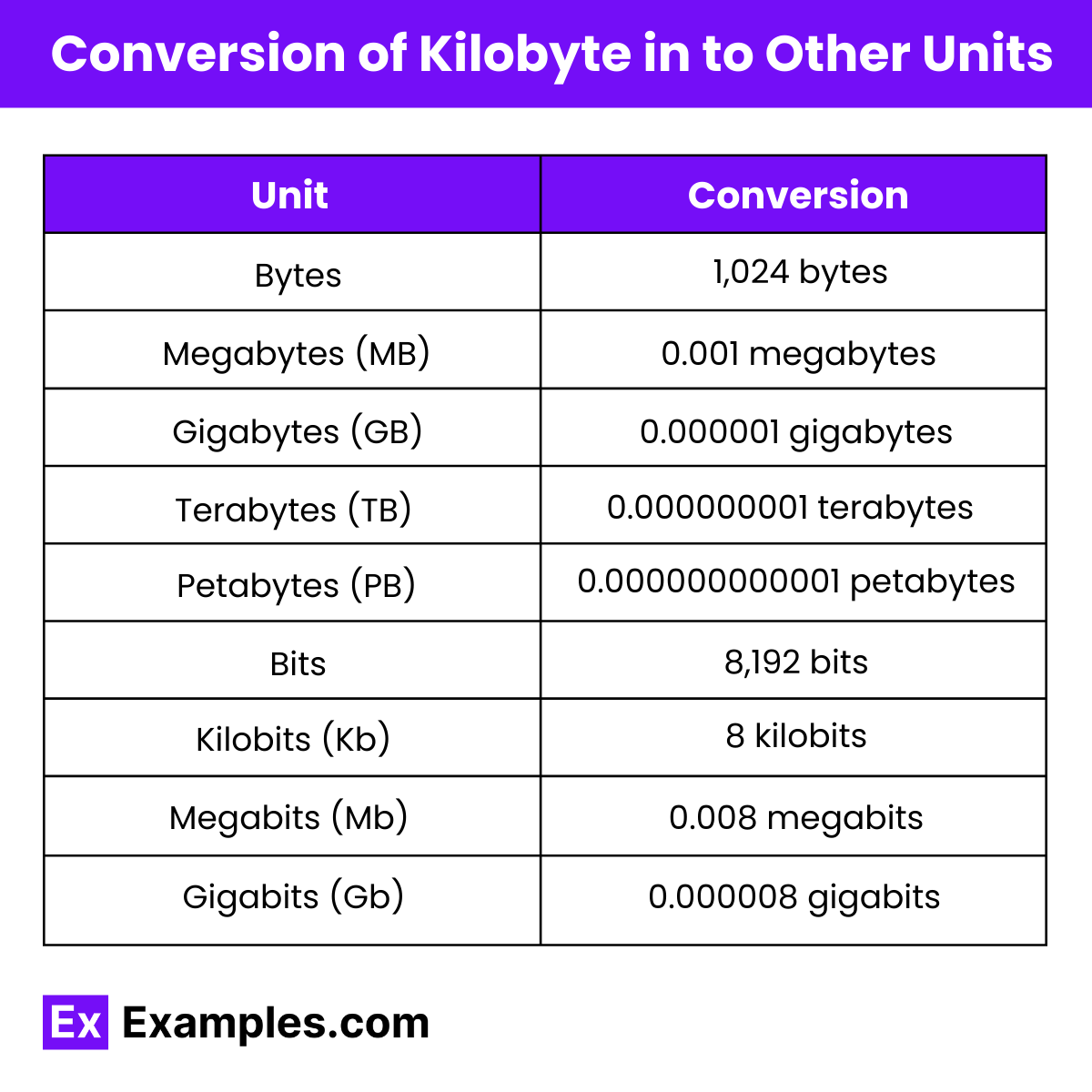
| Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Bytes | 1,024 bytes |
| Megabytes (MB) | 0.001 megabytes |
| Gigabytes (GB) | 0.000001 gigabytes |
| Terabytes (TB) | 0.000000001 terabytes |
| Petabytes (PB) | 0.000000000001 petabytes |
| Bits | 8,192 bits |
| Kilobits (Kb) | 8 kilobits |
| Megabits (Mb) | 0.008 megabits |
| Gigabits (Gb) | 0.000008 gigabits |
Applications of Kilobyte
Text Files
- Documents: Simple text files like
.txtand small word processing files such as.docor.docxoften range from a few kilobytes to several dozen kilobytes. - Emails: Basic emails without attachments or rich formatting usually occupy a few kilobytes.
Images
- Icons: Small icons and graphics, often used in user interfaces, are typically sized in kilobytes.
- Thumbnails: Reduced-size images used as previews in image galleries or online platforms.
Code and Scripts
- Source Code Files: Individual files containing source code for software projects are often in the kilobyte range.
- Scripts: Small scripts written in languages like Python, JavaScript, or Bash are usually measured in kilobytes.
Configuration Files
- Settings Files: Configuration files for applications and operating systems, such as
.inior.cfgfiles, are generally a few kilobytes in size. - Preference Files: User preference files that store settings and customization options.
Web Pages
- HTML Files: Basic HTML files for simple web pages typically range from a few to several kilobytes.
- CSS Files: Stylesheets used for web page formatting are usually in the kilobyte range.
Databases
- Small Database Entries: Individual records or small datasets stored in databases, such as SQLite, can be in the kilobyte range.
- Configuration and Log Files: Logs and configuration files for database management.
Applications
- Mobile Apps: Simple mobile applications or app components, such as configuration files or small data files.
- Game Assets: Small game assets like sprites, sound effects, and configuration files.
Communication
- SMS Messages: Text messages sent via SMS are typically a few kilobytes.
- Chat Logs: Small chat logs from messaging applications.
Miscellaneous
- Metadata: Metadata associated with files, such as EXIF data in images or ID3 tags in a files.
- Compression: Compressed versions of small files, such as zip archives containing a few text documents.
Difference Between Kilobyte and Kibibyte
| Feature | Kilobyte (KB) | Kibibyte (KiB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1 Kilobyte = 1,000 bytes | 1 Kibibyte = 1,024 bytes |
| Symbol | KB | KiB |
| Measurement Base | Decimal (Base 10) | Binary (Base 2) |
| Usage Context | Commonly used in marketing and non-technical contexts for storage devices | Commonly used in computing and technical contexts for precise data measurement |
| Calculation | 1 KB = 10^3 bytes | 1 KiB = 2^10 bytes |
| Size Comparison | Smaller than a kibibyte | Larger than a kilobyte |
| Standard | International System of Units (SI) | International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) |
| Example | 500 KB = 500,000 bytes | 500 KiB = 512,000 bytes |
How many bytes are in a kilobyte?
A kilobyte consists of 1024 bytes. This is a standard unit in computing for data storage.
What can be stored in a kilobyte?
A kilobyte can store a small text file or an icon image, roughly 1000 characters.
Why is a kilobyte 1024 bytes and not 1000?
Kilobyte uses binary system, where 1024 (2^10) bytes is more convenient for computer calculations.
How does electromagnetism relate to kilobytes?
Electromagnetism is fundamental in data storage devices, where data measured in kilobytes is stored and retrieved using magnetic fields.
What is the difference between kilobyte and kibibyte?
A kilobyte is 1024 bytes, while a kibibyte (KiB) strictly denotes 1024 bytes, used to avoid confusion in data measurement.
How many kilobytes are in a megabyte?
There are 1024 kilobytes in one megabyte (MB).
How does PaaS handle data in kilobytes?
PaaS (Platform as a Service) manages data efficiently, often in kilobytes, enabling scalable cloud storage and application hosting.
Why is understanding kilobytes important?
Knowing kilobytes helps in estimating file sizes, storage capacity, and data transfer speeds.
What role does electromagnetism play in PaaS storage solutions?
Electromagnetism enables data storage in PaaS, ensuring efficient retrieval and management of kilobyte-sized files.
How do kilobytes affect software performance?
Smaller kilobyte files load faster and use less memory, improving software performance.