Mebibyte – 30 Examples, Uses, Applications, Differences
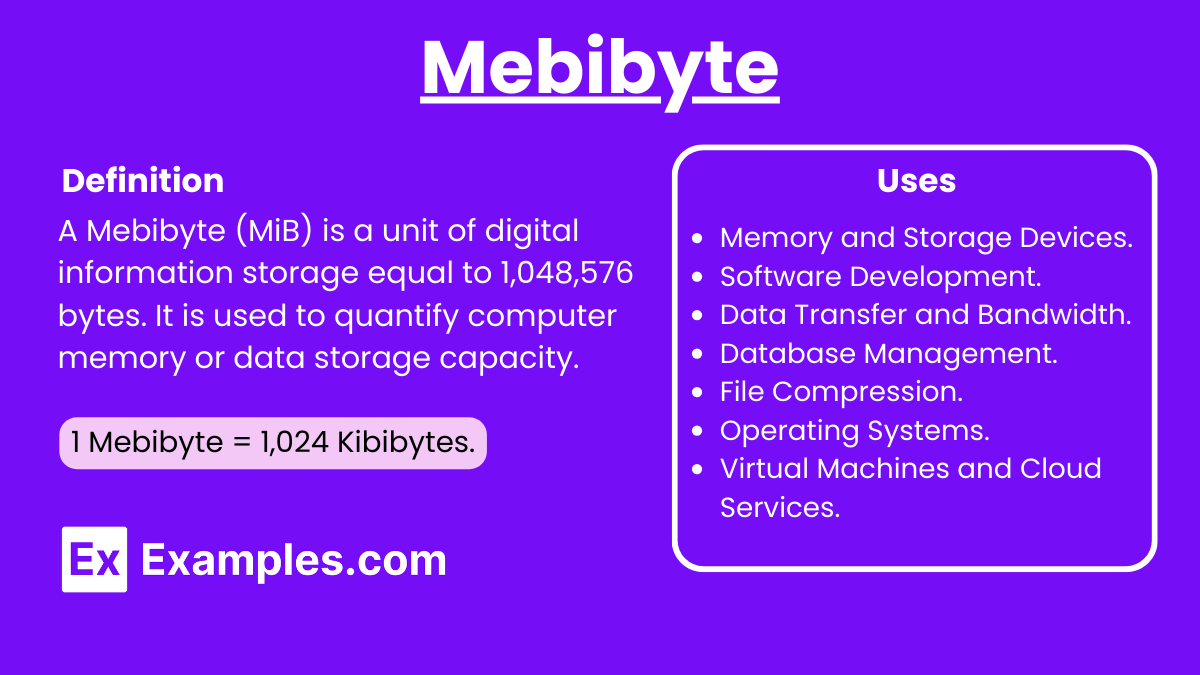
A mebibyte is a unit of digital information storage, equivalent to 2^20 (1,048,576) bytes. It is widely used in fields such as cloud computing, digital communication, and various communication technologies. Unlike the more commonly known megabyte, which is based on the decimal system, the mebibyte is part of the binary system, making it crucial for precise data measurement in technical contexts. Understanding the distinction between these units is essential for professionals working with large-scale data and network systems.
What is Mebibyte?
A mebibyte (MiB) is a unit of digital information storage that equal 1,048,576 bytes. It is part of the binary system used in computing to accurately measure data size.
Examples of Mebibyte
- A typical MP3 song – Approximately 4 MiB.
- A high-quality JPEG image – Around 2-3 MiB.
- A short video clip – About 10 MiB.
- A PDF document – Roughly 1-2 MiB.
- A simple mobile app – Approximately 5 MiB.
- An e-book – Around 1 MiB.
- A PowerPoint presentation – About 5 MiB.
- A web page with images – Around 1-2 MiB.
- An email with attachments – Roughly 1 MiB.
- A compressed ZIP file – About 10 MiB.
- A software update patch – Approximately 8 MiB.
- A short podcast episode – Around 10 MiB.
- A database record – About 2 MiB.
- A firmware update – Roughly 15 MiB.
- A game level file – Approximately 6 MiB.
- A small software program – Around 3 MiB.
- A CAD drawing – About 4 MiB.
- An HTML file with media – Roughly 2 MiB.
- A Linux package file – Approximately 10 MiB.
- A high-resolution PNG image – Around 5 MiB.
- A Python script with libraries – About 2 MiB.
- A system log file – Roughly 1 MiB.
- A small video tutorial – Approximately 12 MiB.
- A multimedia presentation – Around 8 MiB.
- An Excel spreadsheet with data – About 2 MiB.
- A text file with extensive data – Roughly 1 MiB.
- A graphic design file – Approximately 10 MiB.
- A short abook chapter – Around 7 MiB.
- A small database backup – About 10 MiB.
- A medium-resolution GIF – Roughly 2 MiB.
How Much is a Mebibyte?
1 MiB = 1,024 kibibytes (KiB)
1 MiB = 0.001024 gibibytes (GiB)
Comparison to Megabyte
A common point of confusion is the difference between a mebibyte and a megabyte (MB). While they sound similar, they represent different amounts of data:
- 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1,000,000 bytes (10^6 bytes) in the decimal system.
- 1 Mebibyte (MiB) = 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes) in the binary system.
Uses of Mebibyte
1. Memory and Storage Devices
Mebibytes are often used to describe the capacity of computer memory (RAM) and storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. For example:
- RAM: A computer might have 4 GiB (gibibytes) of RAM, where each gibibyte equals 1024 mebibytes.
- SSD/HDD: Storage devices often list capacities in terms of gibibytes or tebibytes, which are based on mebibytes.
2. Operating Systems and File Systems
Operating systems and file systems frequently use binary prefixes to display file sizes and storage capacities. This provides more precise information regarding the actual storage space available and used. For example:
- File Size: When viewing file properties, an operating system may display a file as 5 MiB instead of 5.24 MB, aligning with the binary measurement system.
- Disk Usage: Tools like
dfin Unix-like operating systems use mebibytes to report disk usage.
3. Software Development
Developers often work with memory allocation in terms of mebibytes, especially when dealing with system-level programming, performance tuning, or optimizing applications. This includes:
- Buffer Sizes: Setting buffer sizes in networking applications.
- Data Structures: Allocating memory for large data structures like arrays or caches.
4. Data Transfer and Bandwidth
In networking and data transfer contexts, mebibytes can be used to measure the amount of data transferred or the bandwidth usage. For instance:
- Data Transfer: A download might be 150 MiB, providing a more accurate measure than using megabytes.
- Bandwidth: Network performance tests might report speeds in MiB/s (mebibytes per second).
5. Virtual Machines and Cloud Services
Cloud service providers and virtualization platforms use binary units to specify resource allocation for virtual machines. This includes:
- VM Configuration: Configuring virtual machines with specific amounts of memory (e.g., 512 MiB, 1024 MiB).
- Storage Allocation: Allocating virtual disk sizes in mebibytes for cloud storage solutions.
6. Database Management
Database systems often handle large volumes of data and use mebibytes to manage and optimize storage. Examples include:
- Database Storage: Reporting the size of database files and tablespaces in MiB.
- Backup Files: Measuring the size of backup files for databases.
7. File Compression and Archiving
File compression tools and archiving utilities often display file sizes and compression ratios in mebibytes. This is crucial for understanding storage savings and managing large sets of files. For example:
- Compressed Files: Showing the compressed file size in MiB.
- Archiving Tools: Reporting the total size of files within an archive.
Converting Mebibyte in to Other Units of Data
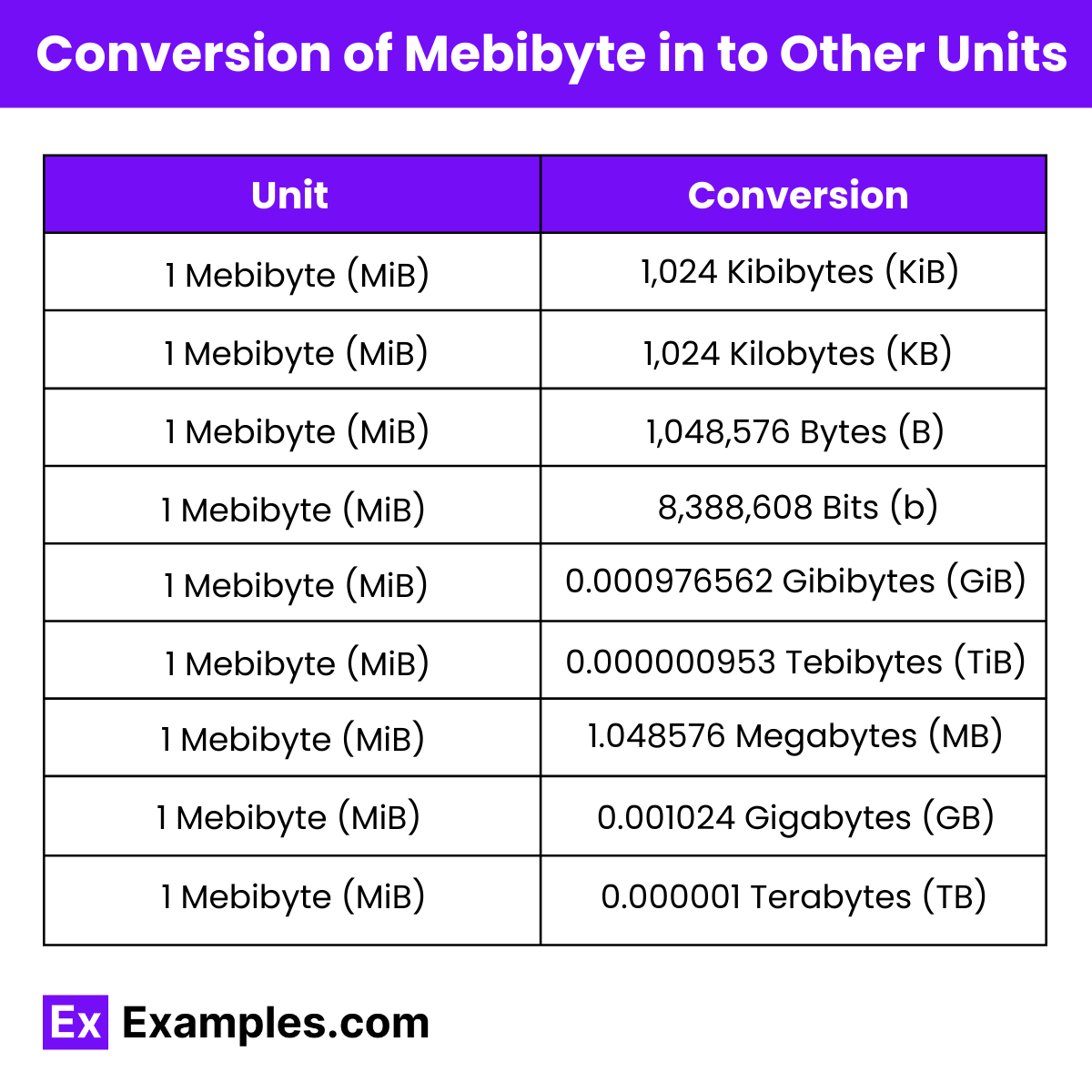
| Unit | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1,024 Kibibytes (KiB) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1,048,576 Bytes (B) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 8,388,608 Bits (b) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.0009765625 Gibibytes (GiB) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.00000095367432 Tebibytes (TiB) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1.048576 Megabytes (MB) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.001024 Gigabytes (GB) |
| 1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.000001 Terabytes (TB) |
Applications of Mebibyte
Memory and Storage Capacity
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Mebibytes are often used to measure the capacity of RAM in computers and other devices.
- Hard Drives and SSDs (Solid State Drives): Storage devices sometimes specify capacities in mebibytes to accurately reflect the binary nature of digital data.
Operating Systems and Software
- System Requirements: Operating systems and software applications specify their memory and storage requirements in mebibytes to ensure precise resource allocation.
- File Systems: Some file systems, such as those used in Unix-like operating systems, might use mebibytes for defining block sizes and partition sizes.
Data Transfer and Bandwidth
- Network Speeds: In contexts where precision is crucial, such as certain network protocols, data transfer rates might be measured in mebibytes per second (MiB/s).
- Bandwidth Allocation: Internet service providers and data centers might use mebibytes to allocate and monitor bandwidth usage accurately.
Virtual Machines and Containers
- Resource Allocation: When configuring virtual machines or containerized applications, system administrators often specify resource limits (e.g., RAM) in mebibytes for precision.
- Snapshots and Backups: The size of virtual machine snapshots and backups may be measured in mebibytes to reflect exact data usage.
Programming and Development
- Memory Management: Developers often use mebibytes to define memory limits and buffers within applications, particularly for systems programming.
- Data Processing: Applications that handle large datasets, such as scientific computing or big data analytics, may measure data in mebibytes for clarity and accuracy.
Embedded Systems
- Firmware and ROM: The size of firmware or read-only memory (ROM) in embedded systems is sometimes specified in mebibytes.
- Resource-Constrained Devices: Devices with limited resources, such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices, use mebibytes to measure and manage memory and storage precisely.
Difference Between Mebibyte and Megabyte
| Characteristic | Mebibyte (MiB) | Megabyte (MB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A unit of data equal to 2^20 (1,048,576) bytes | A unit of data equal to 10^6 (1,000,000) bytes |
| Binary or Decimal | Binary (base 2) | Decimal (base 10) |
| Usage | Primarily used in computing for memory size | Commonly used in storage media and networking speeds |
| Prefix Origin | Derived from “mebi,” a binary prefix | Derived from “mega,” a decimal prefix |
| Symbol | MiB | MB |
| Equivalence | 1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes | 1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes |
| Typical Use Cases | Memory (RAM) specifications | Hard drive capacities, file sizes, data transfer rates |
| Standardization Body | Defined by IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) | Commonly used but not standardized by a specific body |
How does a Mebibyte relate to a Megabyte?
A Mebibyte is slightly larger than a Megabyte, which is 1,000,000 bytes, often used in PaaS applications for precise data measurement.
Why use Mebibyte instead of Megabyte?
Mebibyte provides more accuracy, important for technical fields like electromagnetism and precise PaaS data computations.
How many bytes are in a Mebibyte?
A Mebibyte contains 1,048,576 bytes, commonly used in electromagnetism data analysis and PaaS data storage solutions.
What fields utilize Mebibytes?
Mebibytes are essential in computing, electromagnetism research, and PaaS platforms for accurate data representation.
Is Mebibyte part of the binary system?
Yes, Mebibyte follows the binary system (2^20 bytes), useful in electromagnetism studies and PaaS storage solutions.
How does Mebibyte benefit electromagnetism studies?
In electromagnetism, Mebibytes provide precise data storage and transfer, critical for accurate scientific analysis.
Can Mebibytes be used in PaaS platforms?
Yes, Mebibytes are used in PaaS for efficient data storage and management, ensuring precise digital information handling.
What is the symbol for Mebibyte?
The symbol for Mebibyte is MiB, often seen in electromagnetism data reports and PaaS storage documentation.
How do Mebibytes improve data accuracy?
Mebibytes enhance data accuracy by using a binary measurement system, vital for electromagnetism research and PaaS efficiency.
Are Mebibytes relevant in modern computing?
Absolutely, Mebibytes remain relevant in computing, especially in electromagnetism data analysis and PaaS solutions.
Mebibyte – 30 Examples, Uses, Applications, Differences
A mebibyte is a unit of digital information storage, equivalent to 2^20 (1,048,576) bytes. It is widely used in fields such as cloud computing, digital communication, and various communication technologies. Unlike the more commonly known megabyte, which is based on the decimal system, the mebibyte is part of the binary system, making it crucial for precise data measurement in technical contexts. Understanding the distinction between these units is essential for professionals working with large-scale data and network systems.
What is Mebibyte?
A mebibyte (MiB) is a unit of digital information storage that equal 1,048,576 bytes. It is part of the binary system used in computing to accurately measure data size.
Examples of Mebibyte
A typical MP3 song – Approximately 4 MiB.
A high-quality JPEG image – Around 2-3 MiB.
A short video clip – About 10 MiB.
A PDF document – Roughly 1-2 MiB.
A simple mobile app – Approximately 5 MiB.
An e-book – Around 1 MiB.
A PowerPoint presentation – About 5 MiB.
A web page with images – Around 1-2 MiB.
An email with attachments – Roughly 1 MiB.
A compressed ZIP file – About 10 MiB.
A software update patch – Approximately 8 MiB.
A short podcast episode – Around 10 MiB.
A database record – About 2 MiB.
A firmware update – Roughly 15 MiB.
A game level file – Approximately 6 MiB.
A small software program – Around 3 MiB.
A CAD drawing – About 4 MiB.
An HTML file with media – Roughly 2 MiB.
A Linux package file – Approximately 10 MiB.
A high-resolution PNG image – Around 5 MiB.
A Python script with libraries – About 2 MiB.
A system log file – Roughly 1 MiB.
A small video tutorial – Approximately 12 MiB.
A multimedia presentation – Around 8 MiB.
An Excel spreadsheet with data – About 2 MiB.
A text file with extensive data – Roughly 1 MiB.
A graphic design file – Approximately 10 MiB.
A short abook chapter – Around 7 MiB.
A small database backup – About 10 MiB.
A medium-resolution GIF – Roughly 2 MiB.
How Much is a Mebibyte?
1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes)
1 MiB = 1,024 kibibytes (KiB)
1 MiB = 0.001024 gibibytes (GiB)
Comparison to Megabyte
A common point of confusion is the difference between a mebibyte and a megabyte (MB). While they sound similar, they represent different amounts of data:
1 Megabyte (MB) = 1,000,000 bytes (10^6 bytes) in the decimal system.
1 Mebibyte (MiB) = 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes) in the binary system.
Uses of Mebibyte
1. Memory and Storage Devices
Mebibytes are often used to describe the capacity of computer memory (RAM) and storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. For example:
RAM: A computer might have 4 GiB (gibibytes) of RAM, where each gibibyte equals 1024 mebibytes.
SSD/HDD: Storage devices often list capacities in terms of gibibytes or tebibytes, which are based on mebibytes.
2. Operating Systems and File Systems
Operating systems and file systems frequently use binary prefixes to display file sizes and storage capacities. This provides more precise information regarding the actual storage space available and used. For example:
File Size: When viewing file properties, an operating system may display a file as 5 MiB instead of 5.24 MB, aligning with the binary measurement system.
Disk Usage: Tools like
dfin Unix-like operating systems use mebibytes to report disk usage.
3. Software Development
Developers often work with memory allocation in terms of mebibytes, especially when dealing with system-level programming, performance tuning, or optimizing applications. This includes:
Buffer Sizes: Setting buffer sizes in networking applications.
Data Structures: Allocating memory for large data structures like arrays or caches.
4. Data Transfer and Bandwidth
In networking and data transfer contexts, mebibytes can be used to measure the amount of data transferred or the bandwidth usage. For instance:
Data Transfer: A download might be 150 MiB, providing a more accurate measure than using megabytes.
Bandwidth: Network performance tests might report speeds in MiB/s (mebibytes per second).
5. Virtual Machines and Cloud Services
Cloud service providers and virtualization platforms use binary units to specify resource allocation for virtual machines. This includes:
VM Configuration: Configuring virtual machines with specific amounts of memory (e.g., 512 MiB, 1024 MiB).
Storage Allocation: Allocating virtual disk sizes in mebibytes for cloud storage solutions.
6. Database Management
Database systems often handle large volumes of data and use mebibytes to manage and optimize storage. Examples include:
Database Storage: Reporting the size of database files and tablespaces in MiB.
Backup Files: Measuring the size of backup files for databases.
7. File Compression and Archiving
File compression tools and archiving utilities often display file sizes and compression ratios in mebibytes. This is crucial for understanding storage savings and managing large sets of files. For example:
Compressed Files: Showing the compressed file size in MiB.
Archiving Tools: Reporting the total size of files within an archive.
Converting Mebibyte in to Other Units of Data
Unit | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1,024 Kibibytes (KiB) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1,048,576 Bytes (B) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 8,388,608 Bits (b) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.0009765625 Gibibytes (GiB) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.00000095367432 Tebibytes (TiB) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 1.048576 Megabytes (MB) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.001024 Gigabytes (GB) |
1 Mebibyte (MiB) | 0.000001 Terabytes (TB) |
Applications of Mebibyte
Memory and Storage Capacity
RAM (Random Access Memory): Mebibytes are often used to measure the capacity of RAM in computers and other devices.
Hard Drives and SSDs (Solid State Drives): Storage devices sometimes specify capacities in mebibytes to accurately reflect the binary nature of digital data.
Operating Systems and Software
System Requirements: Operating systems and software applications specify their memory and storage requirements in mebibytes to ensure precise resource allocation.
File Systems: Some file systems, such as those used in Unix-like operating systems, might use mebibytes for defining block sizes and partition sizes.
Data Transfer and Bandwidth
Network Speeds: In contexts where precision is crucial, such as certain network protocols, data transfer rates might be measured in mebibytes per second (MiB/s).
Bandwidth Allocation: Internet service providers and data centers might use mebibytes to allocate and monitor bandwidth usage accurately.
Virtual Machines and Containers
Resource Allocation: When configuring virtual machines or containerized applications, system administrators often specify resource limits (e.g., RAM) in mebibytes for precision.
Snapshots and Backups: The size of virtual machine snapshots and backups may be measured in mebibytes to reflect exact data usage.
Programming and Development
Memory Management: Developers often use mebibytes to define memory limits and buffers within applications, particularly for systems programming.
Data Processing: Applications that handle large datasets, such as scientific computing or big data analytics, may measure data in mebibytes for clarity and accuracy.
Embedded Systems
Firmware and ROM: The size of firmware or read-only memory (ROM) in embedded systems is sometimes specified in mebibytes.
Resource-Constrained Devices: Devices with limited resources, such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices, use mebibytes to measure and manage memory and storage precisely.
Difference Between Mebibyte and Megabyte
Characteristic | Mebibyte (MiB) | Megabyte (MB) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | A unit of data equal to 2^20 (1,048,576) bytes | A unit of data equal to 10^6 (1,000,000) bytes |
Binary or Decimal | Binary (base 2) | Decimal (base 10) |
Usage | Primarily used in computing for memory size | Commonly used in storage media and networking speeds |
Prefix Origin | Derived from “mebi,” a binary prefix | Derived from “mega,” a decimal prefix |
Symbol | MiB | MB |
Equivalence | 1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes | 1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes |
Typical Use Cases | Memory (RAM) specifications | Hard drive capacities, file sizes, data transfer rates |
Standardization Body | Defined by IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) | Commonly used but not standardized by a specific body |
How does a Mebibyte relate to a Megabyte?
A Mebibyte is slightly larger than a Megabyte, which is 1,000,000 bytes, often used in PaaS applications for precise data measurement.
Why use Mebibyte instead of Megabyte?
Mebibyte provides more accuracy, important for technical fields like electromagnetism and precise PaaS data computations.
How many bytes are in a Mebibyte?
A Mebibyte contains 1,048,576 bytes, commonly used in electromagnetism data analysis and PaaS data storage solutions.
What fields utilize Mebibytes?
Mebibytes are essential in computing, electromagnetism research, and PaaS platforms for accurate data representation.
Is Mebibyte part of the binary system?
Yes, Mebibyte follows the binary system (2^20 bytes), useful in electromagnetism studies and PaaS storage solutions.
How does Mebibyte benefit electromagnetism studies?
In electromagnetism, Mebibytes provide precise data storage and transfer, critical for accurate scientific analysis.
Can Mebibytes be used in PaaS platforms?
Yes, Mebibytes are used in PaaS for efficient data storage and management, ensuring precise digital information handling.
What is the symbol for Mebibyte?
The symbol for Mebibyte is MiB, often seen in electromagnetism data reports and PaaS storage documentation.
How do Mebibytes improve data accuracy?
Mebibytes enhance data accuracy by using a binary measurement system, vital for electromagnetism research and PaaS efficiency.
Are Mebibytes relevant in modern computing?
Absolutely, Mebibytes remain relevant in computing, especially in electromagnetism data analysis and PaaS solutions.

