10 Medical Coding Examples
Medical coding involves translating healthcare diagnoses, procedures, medical services, and equipment into standardized alphanumeric codes. This process ensures uniform documentation across the medical field, facilitating accurate billing, insurance claims, and patient records. Medical coders use specific code sets, such as ICD (International Classification of Diseases), CPT (Current Procedural Terminology), and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System). Their work is crucial for maintaining efficient healthcare operations and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards. Medical coders also assist in the preparation of medical statements and medical certificates, which are essential for accurate documentation and patient care continuity.
What is Medical Coding?
Medical coding is the process of converting healthcare diagnoses, treatments, services, and equipment into standardized alphanumeric codes. This systematized documentation is essential for accurate billing statements, insurance claims, and maintaining comprehensive patient records, ensuring efficiency and compliance within the healthcare industry.
Medical Coding Examples
ICD-10 Codes (International Classification of Diseases)
- E11.9 – Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications.
- J45.909 – Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated.
- I10 – Essential (primary) hypertension.
CPT Codes (Current Procedural Terminology)
- 99213 – Office or other outpatient visit for an established patient, typically 15 minutes.
- 93000 – Electrocardiogram, routine ECG with at least 12 leads; with interpretation and report.
- 45378 – Colonoscopy, flexible, proximal to splenic flexure; diagnostic.
HCPCS Codes (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
- A9270 – Non-covered item or service.
- J1100 – Injection, dexamethasone sodium phosphate, 1 mg.
- E0114 – Crutches, underarm, other than wood, adjustable or fixed, pair, with pads, tips, and handgrips.
Types of Medical Coding
- ICD Coding: International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes diagnose and classify diseases and health conditions.
- CPT Coding: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic procedures and services.
- HCPCS Coding: Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes include supplies, medications, and non-physician services.
- DRG Coding: Diagnosis-Related Groups (DRG) codes classify hospital cases into groups for payment purposes.
- SNOMED CT: Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT) provides comprehensive, precise clinical healthcare terminology.
Skills Needed for Medical Coding
- Attention to Detail
- Analytical Skills
- Knowledge of Medical Terminology
- Understanding of Anatomy and Physiology
- Proficiency in ICD, CPT, and HCPCS Codes
- Familiarity with EHR Systems
- Communication Skills
- Problem-Solving Abilities
- Time Management
- Compliance Knowledge
- Confidentiality Awareness
- Continuous Learning and Adaptability
Responsibilities of a Medical Coding
- Accurate Coding: Assign correct codes to diagnoses, procedures, and treatments using ICD, CPT, and HCPCS systems.
- Documentation Review: Analyze patient records to ensure accurate and complete documentation of medical data.
- Billing Support: Facilitate accurate billing and claims processing by ensuring proper coding.
- Compliance: Adhere to regulatory requirements and coding guidelines to maintain compliance with healthcare laws.
- Communication: Collaborate with healthcare providers to clarify diagnoses and obtain additional information for accurate coding, ensuring alignment with the healthcare budget.
- Data Entry: Input coded information into healthcare databases and electronic health records (EHR) systems.
- Quality Assurance: Conduct audits to ensure coding accuracy and resolve discrepancies.
- Continuing Education: Stay updated with changes in coding systems and healthcare regulations through ongoing education and training, ensuring your knowledge is current and adaptable, similar to maintaining a Family Emergency Communication Plan.
Why is Medical Coding Needed?
- Standardization: It provides a universal language for documenting medical diagnoses, treatments, and services, ensuring consistency across the healthcare industry.
- Efficient Billing: Accurate coding facilitates precise billing and insurance claims, reducing errors and ensuring timely reimbursement for healthcare providers.
- Data Management: It helps in organizing and managing large volumes of medical data, making it easier to retrieve and analyze patient information.
- Compliance: Medical coding ensures compliance with healthcare regulations and standards, minimizing legal risks and ensuring proper documentation.
- Public Health: It aids in tracking health trends, disease outbreaks, and treatment outcomes, contributing to public health research and policy-making.
- Quality Care: Accurate coding ensures that patients receive appropriate care based on their documented medical history, leading to better healthcare outcomes.
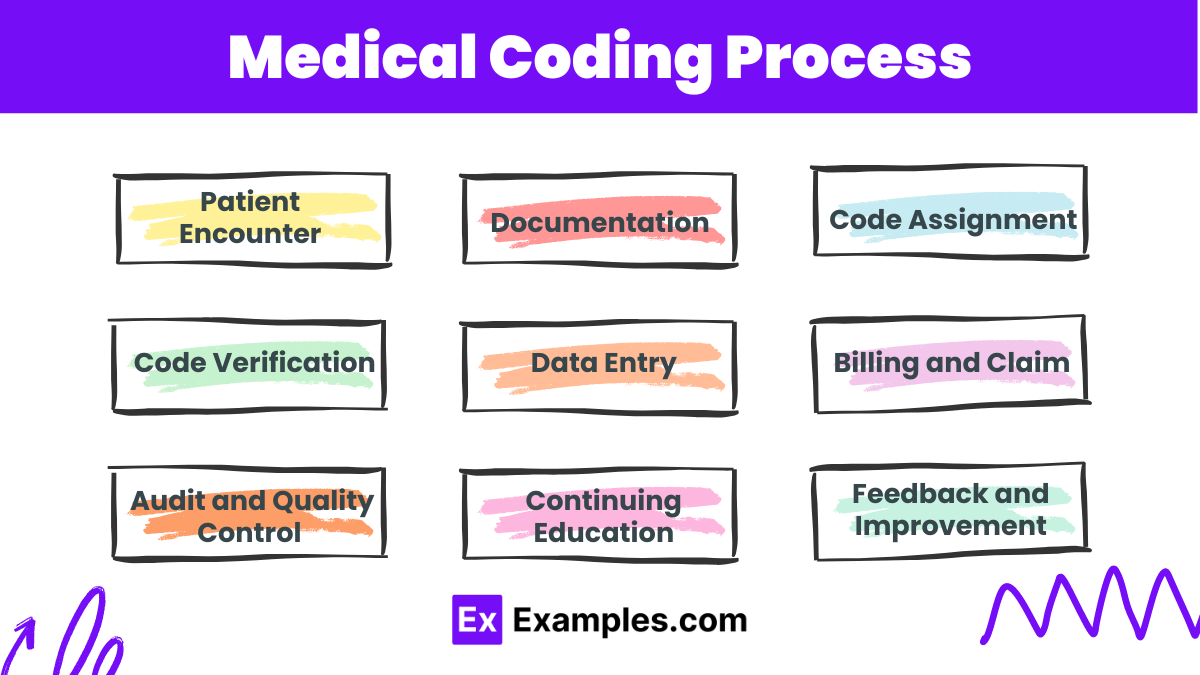
Medical Coding Process
Patient Encounter : A patient visits a healthcare provider for a medical issue or routine check-up.
Documentation : The healthcare provider records the patient’s symptoms, diagnoses, procedures, and treatments in the patient’s medical record.
Code Assignment : The medical coder reviews the documentation and assigns the appropriate codes for diagnoses (ICD), procedures (CPT), and services (HCPCS).
Code Verification : The coder ensures that the assigned codes accurately reflect the documentation and comply with coding guidelines and regulations.
Data Entry : The coded information is entered into the healthcare provider’s billing system or electronic health record (EHR) system.
Billing and Claims : The coded data is used to generate bills for patients and claims for insurance companies to process payments.
Audit and Quality Control : Regular audits are conducted to ensure coding accuracy, compliance with regulations, and identify areas for improvement.
Continuing Education : Medical coders participate in ongoing education to stay updated with changes in coding systems and healthcare regulations.
Feedback and Improvement : Coders receive feedback from audits and adjust practices for ongoing accuracy and compliance.
Medical Coding Salary
- Entry-Level Medical Coders: Typically earn between $35,000 to $45,000 per year.
- Experienced Medical Coders: With several years of experience, salaries can range from $50,000 to $65,000 annually.
- Certified Medical Coders: Those with certifications like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) can earn between $55,000 to $75,000 per year.
- Senior and Specialized Coders: Highly experienced or specialized coders can earn upwards of $80,000 to $100,000 annually.
Medical Coding Jobs
- Medical Coder: Assigns standardized codes to medical diagnoses and procedures.
- Medical Billing Specialist: Manages billing processes and insurance claims.
- Coding Auditor: Reviews medical records for coding accuracy and compliance.
- HIM (Health Information Management) Specialist: Oversees the management of medical records and health information.
- Clinical Documentation Specialist: Ensures accurate documentation of patient records for coding and billing.
- Coding Supervisor: Manages a team of medical coders and ensures adherence to coding standards.
- Compliance Officer: Ensures that coding practices comply with healthcare regulations.
- Revenue Cycle Analyst: Analyzes financial data related to coding and billing processes.
- Freelance Medical Coder: Provides coding services on a contract or freelance basis.
- Coding Trainer/Educator: Teaches coding practices and guidelines to new coders or healthcare staff.
Medical Coding vs. Medical Billing
| Aspect | Medical Coding | Medical Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes. | Processing and submitting insurance claims based on coded information. |
| Primary Codes Used | ICD, CPT, HCPCS | Uses codes provided by medical coders. |
| Main Responsibility | Ensuring accurate and compliant code assignment. | Ensuring timely and accurate insurance claims and patient billing. |
| Focus Area | Medical terminology, anatomy, and coding systems. | Insurance policies, claims process, and payment posting. |
| Skills Required | Attention to detail, analytical skills, knowledge of medical codes. | Organizational skills, communication skills, knowledge of billing software. |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, clinics, coding agencies, remote work. | Healthcare facilities, billing agencies, insurance companies. |
| Certification | CPC, CCS, RHIT, etc. | CPB (Certified Professional Biller), CHRS (Certified Healthcare Reimbursement Specialist), etc. |
| Role in Revenue Cycle | Front-end process, ensures documentation accuracy. | Back-end process, ensures payment collection. |
| Interaction with | Healthcare providers, clinical documentation specialists. | Insurance companies, patients, healthcare providers. |
| Outcome | Accurate medical records and compliance. | Revenue generation and financial stability for healthcare providers. |
What software do medical coders use?
Coders often use electronic health record (EHR) systems, coding software like EncoderPro, and billing software.
Is medical coding a good career?
Yes, it offers stable job opportunities, the potential for remote work, and is in high demand.
What is DRG coding?
DRG (Diagnosis-Related Groups) coding classifies hospital cases to determine how much Medicare pays the hospital.
How do medical coders stay updated with changes?
They participate in continuing education, professional organizations, and regularly review updates from coding manuals and guidelines.
What challenges do medical coders face?
Challenges include keeping up with changing codes, ensuring accuracy, and dealing with incomplete or unclear documentation.
What is the role of a coding auditor?
A coding auditor reviews medical records to ensure coding accuracy and compliance with regulations.
How do medical coders ensure accuracy?
By meticulously reviewing medical records, following coding guidelines, and using auditing tools and techniques.
What is SNOMED CT?
SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms) provides comprehensive clinical healthcare terminology.
How does medical coding impact patient care?
Accurate coding ensures appropriate treatment plans and helps in tracking patient outcomes and health trends.
What industries employ medical coders?
Medical coders work in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, billing agencies, and healthcare consulting firms.