Megabyte – 40 Examples, Uses, Differences
A megabyte (MB) is a unit of digital information storage commonly used in communication technology. It equals 1,024 kilobytes (KB) and is crucial for measuring data in cloud computing and other digital platforms. In the realm of digital communication, megabytes help quantify the size of files and the capacity of storage devices, facilitating efficient data transfer and storage management. Understanding megabytes is essential for navigating modern communication technology and leveraging the benefits of cloud computing.
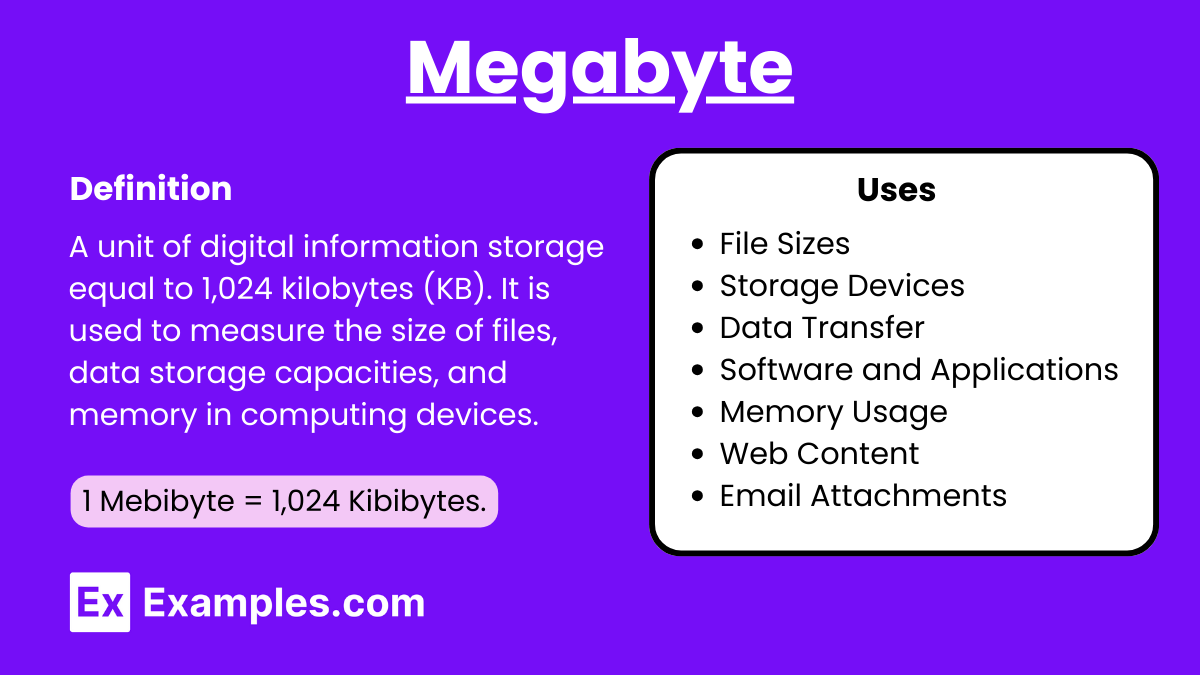
What is Megabyte?
A megabyte (MB) is a unit of digital information storage equal to 1,024 kilobytes (KB) or approximately one million bytes. It is commonly used to measure file sizes and storage capacity in computing and digital communication.
Examples of Megabyte
- A 1-minute MP3 a file
- A medium-quality digital photograph
- A 1-minute video clip in standard definition
- A short eBook
- A PDF document with images
- An average smartphone app
- A small software update
- A short PowerPoint presentation
- A simple game app
- A webpage with images and text
- A scanned document in high resolution
- A MIDI file with multiple tracks
- An email with attachments
- A short voice memo recording
- A small database file
- A compressed ZIP file containing documents
- A 5-minute podcast episode
- A firmware update for a small device
- A single page of a comic book
- A small 3D model file
How Much is a Megabyte?
1 megabyte (MB) = 1,000,000 bytes (B)
Storage Devices and Megabytes
Storage devices like hard drives, USB flash drives, and memory cards use megabytes (or gigabytes) to indicate their capacity. Here’s a brief overview:
- 1 GB (gigabyte) = 1,024 MB in the binary system.
- 1 TB (terabyte) = 1,024 GB = 1,048,576 MB in the binary system.
What are Megabyte used for?
1. File Sizes
Megabytes are often used to describe the size of files, such as documents, images, a files, and videos. For example:
- Documents: A typical PDF document or word processing file might be a few megabytes in size.
- Images: High-resolution images can range from several hundred kilobytes to a few megabytes.
- Audio Files: An MP3 a file of a song is often between 3 MB and 10 MB.
- Videos: Short video clips can range from a few megabytes to several hundred megabytes.
2. Storage Devices
Megabytes are used to measure the capacity of storage devices, although larger units like gigabytes and terabytes are more common today. Examples include:
- USB Flash Drives: Smaller capacity USB drives, often used for quick file transfers, might be measured in megabytes (e.g., 512 MB).
- Older Hard Drives: Earlier generations of hard drives were measured in megabytes before larger capacities became standard.
3. Data Transfer
Megabytes are commonly used to measure data transfer amounts and speeds, particularly in contexts like:
- Download/Upload Sizes: Internet downloads and uploads are often measured in megabytes.
- Network Speeds: Network bandwidth might be described in MB/s (megabytes per second) for certain applications.
4. Software and Applications
Software sizes, both for installation and updates, are frequently measured in megabytes. This includes:
- Applications: Many applications have download sizes ranging from a few megabytes to several hundred megabytes.
- Updates: Software updates and patches are often measured in megabytes.
5. Memory Usage
Megabytes are used to quantify memory usage by applications and processes within a computer system. For instance:
- RAM Usage: The memory consumed by running applications is often measured in megabytes.
- Cache Sizes: Browser caches and other temporary storage areas are often measured in megabytes.
6. Web Content
Web content, including images, videos, and downloadable files, is often described in terms of megabytes. Examples include:
- Webpages: The total size of a webpage, including all its elements, might be a few megabytes.
- Streaming Media: The size of streamed media content, such as video clips or a tracks, is measured in megabytes.
7. Email Attachments
Email services commonly use megabytes to describe the size of attachments and the limits on attachment sizes. For example:
- Attachment Sizes: A typical email attachment might be a few megabytes.
- Email Limits: Many email providers have limits on attachment sizes, often around 25 MB.
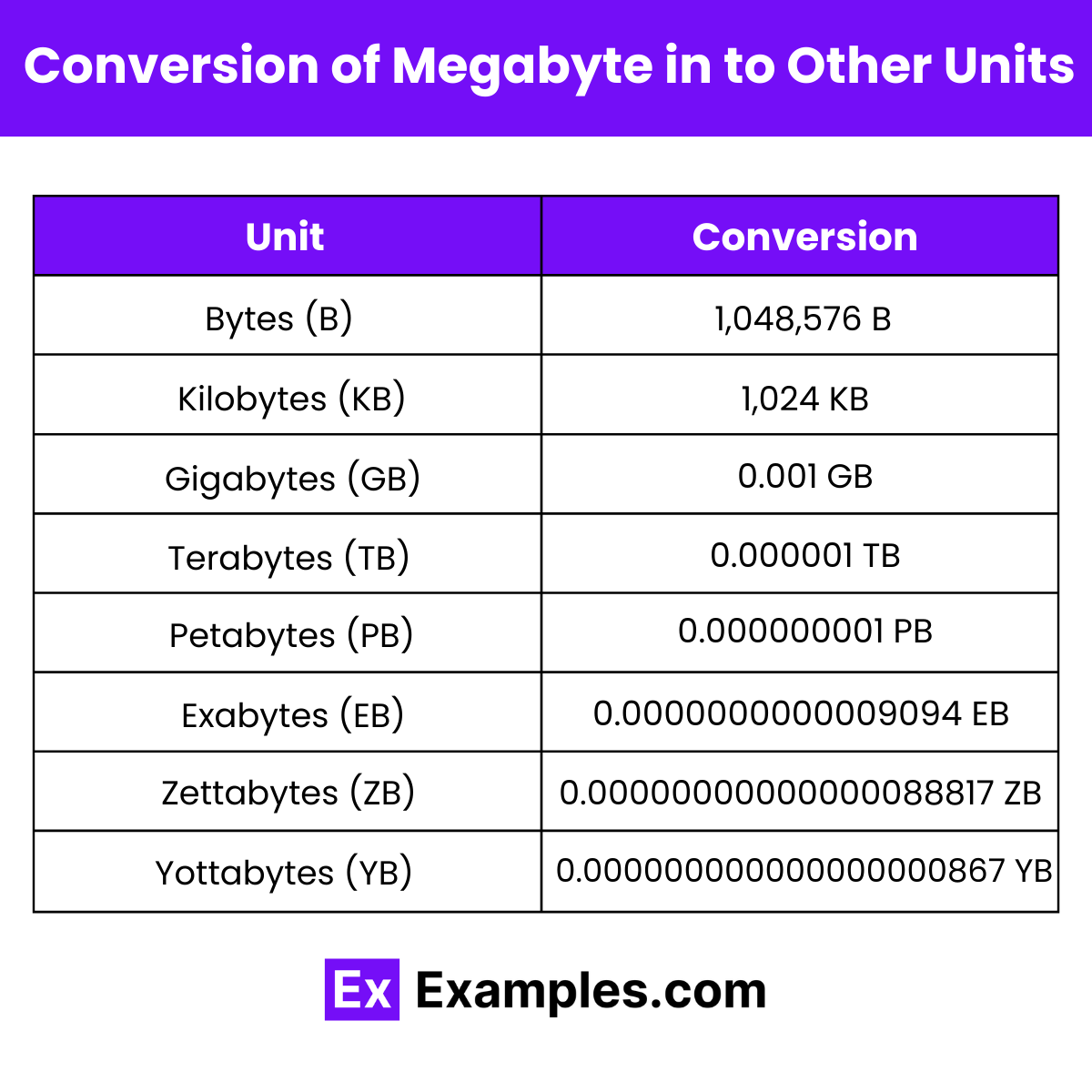
Converting Megabyte in to Other Units of Data
| Unit | Equivalent in Megabytes (MB) |
|---|---|
| Bytes (B) | 1 MB = 1,048,576 B |
| Kilobytes (KB) | 1 MB = 1,024 KB |
| Gigabytes (GB) | 1 MB = 0.0009765625 GB |
| Terabytes (TB) | 1 MB = 0.000000953674316 TB |
| Petabytes (PB) | 1 MB = 0.000000000931322575 PB |
| Exabytes (EB) | 1 MB = 0.000000000000909494702 EB |
| Zettabytes (ZB) | 1 MB = 0.000000000000000888178 ZB |
| Yottabytes (YB) | 1 MB = 0.000000000000000000867362 YB |
Importance of Megabyte
1. Data Storage
Megabytes are crucial for quantifying storage capacity in various digital devices such as:
- Hard Drives: Modern hard drives are often measured in gigabytes (GB) and terabytes (TB), but understanding megabytes helps comprehend smaller data quantities and file sizes.
- USB Drives: These portable storage devices often range from a few megabytes to several gigabytes.
- Memory Cards: Commonly used in cameras, smartphones, and other gadgets, their capacity is often described in megabytes and gigabytes.
2. File Sizes
Megabytes help in understanding and managing file sizes:
- Documents: Text documents, PDFs, and spreadsheets are typically measured in kilobytes or megabytes.
- Images: High-resolution photos often range from a few megabytes to several dozen megabytes.
- Audio Files: MP3 files and other a formats are commonly sized in megabytes, with typical songs ranging from 3-10 MB.
- Software Applications: Installation files for software programs are frequently measured in megabytes.
3. Data Transfer
Megabytes are a standard unit for measuring data transfer:
- Internet Speeds: Data transfer rates are often expressed in megabits per second (Mbps), but the data volume transferred is measured in megabytes.
- Download and Upload: Understanding file sizes in megabytes helps in estimating download and upload times.
4. Memory Usage
Understanding megabytes is essential for managing computer memory:
- RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM is measured in megabytes or gigabytes, and knowing how much memory applications require helps optimize system performance.
- Cache: Memory caches in processors and browsers are often measured in megabytes, impacting speed and efficiency.
5. Media Consumption
Megabytes are critical for quantifying digital media:
- Videos: Short video clips and low-resolution videos are measured in megabytes, while longer and higher resolution videos are in gigabytes.
- Streaming: Streaming services often display data usage in megabytes or gigabytes, helping users manage their data plans.
Difference Between Megabyte and Mebibyte
| Feature | Megabyte (MB) | Mebibyte (MiB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A unit of digital information storage. | A unit of digital information storage. |
| Binary/Decimal Base | Decimal (Base 10) | Binary (Base 2) |
| Size | 1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes (10^6 bytes) | 1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes) |
| Usage | Commonly used in networking, storage devices | Used in computer memory (RAM) and software |
| Prefix Origin | From SI (International System of Units) | From IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) |
| Symbol | MB | MiB |
| Conversion | 1 MB ≈ 0.9537 MiB | 1 MiB ≈ 1.0486 MB |
| Common Contexts | Internet speeds, storage capacities | Operating systems, memory sizes |
| Example | 500 MB Hard Drive | 512 MiB RAM |
How many bytes are in a Megabyte?
There are 1,048,576 bytes in a Megabyte, often used in PaaS environments.
What does MB stand for?
MB stands for Megabyte, commonly used in computing and PaaS services.
How is a Megabyte related to Electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism enables data transmission, including Megabyte-sized files, in digital devices.
What is the difference between a Megabyte and a Gigabyte?
A Gigabyte is 1,024 Megabytes, essential in both Electromagnetism and PaaS platforms.
How is Megabyte used in PaaS?
PaaS providers allocate storage in Megabytes for efficient resource management.
Why is the term Megabyte important?
The term Megabyte is crucial for understanding data storage in PaaS and Electromagnetism applications.
How does Electromagnetism affect data transfer in Megabytes?
Electromagnetism facilitates the wireless transfer of Megabyte-sized data files.
What role does a Megabyte play in cloud services?
Cloud services, including PaaS, measure storage and data transfer in Megabytes.
Can Megabytes be used to describe internet speed?
Yes, internet speeds can be measured in Megabytes per second, influenced by Electromagnetism.
How many Megabytes are in a Terabyte?
There are 1,048,576 Megabytes in a Terabyte, crucial for large-scale PaaS storage solutions.