Mile Per US Gallon – 18+ Examples, Types, Formula, Uses, Conversion
Mile per US Gallon (MPG) is a measurement of fuel efficiency in vehicles. It represents the number of miles a vehicle can travel using one US gallon of fuel. This unit is commonly used in the United States to evaluate and compare the fuel economy of different vehicles. Higher MPG values indicate better fuel efficiency, helping consumers make informed decisions about their vehicle purchases and driving habits. Understanding MPG is crucial for both environmental and economic reasons.
What is Mile Per US Gallon?
Mile per US Gallon (MPG) is a measure of fuel efficiency, indicating how many miles a vehicle can travel on one gallon of gasoline. Higher MPG values denote better fuel efficiency, with variations for city, highway, and combined driving conditions.
Mile Per US Gallon Examples
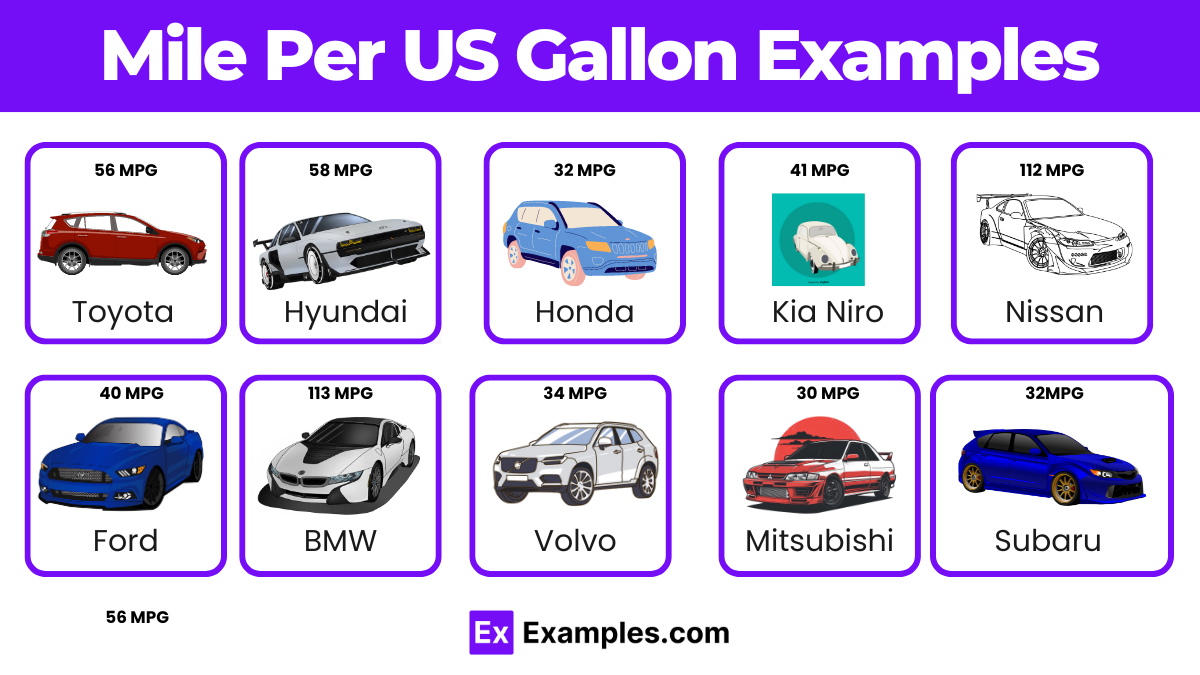
- Toyota Prius – 56 MPG
- Honda Civic – 32 MPG
- Ford Fusion Hybrid – 43 MPG
- Chevrolet Volt – 42 MPG
- Hyundai Ioniq – 58 MPG
- Tesla Model 3 – 120 MPGe (miles per gallon equivalent)
- Toyota Camry Hybrid – 52 MPG
- Kia Optima Hybrid – 41 MPG
- Ford Escape Hybrid – 40 MPG
- Chevrolet Malibu Hybrid – 46 MPG
- Honda Accord Hybrid – 48 MPG
- Nissan Leaf – 112 MPGe
- Hyundai Sonata Hybrid – 52 MPG
- BMW i3 – 113 MPGe
- Volkswagen Jetta – 34 MPG
- Subaru Impreza – 31 MPG
- Mazda 3 – 30 MPG
- Lexus ES 300h – 44 MPG
- Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid – 30 MPG
- Subaru – 32MPG
Types of Mile Per US Gallon
- City MPG – Measurement of fuel efficiency during city driving conditions, characterized by frequent stops, starts, and lower speeds.
- Highway MPG – Measurement of fuel efficiency during highway driving, involving steady speeds and fewer stops.
- Combined MPG – Average of city and highway MPG, providing an overall fuel efficiency rating for mixed driving conditions.
- Curb Weight MPG – MPG calculated considering the vehicle’s curb weight, affecting its fuel efficiency.
- Test Cycle MPG – MPG obtained from standardized test cycles simulating different driving conditions.
- EPA Estimated MPG – MPG figures estimated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) using standardized testing procedures.
- Real-World MPG – Actual MPG observed by drivers under real-world conditions, often different from test cycle results due to various factors like driving style and terrain.
- Adjusted MPG – MPG figures adjusted to reflect real-world driving conditions more accurately, considering factors like air conditioning use and driving habits.
Miles Per Gallon to Km Per Liter
Miles Per Gallon to Km Per Liter – Converting miles per gallon (MPG) to kilometers per liter (km/L) involves changing units of measurement from the US system to the metric system. To convert, multiply MPG by 0.425144. This conversion helps compare fuel efficiency globally.
Miles Per Gallon Formula
MPG = Miles Driven/Gallons of Fuel Used
Miles Per Gallon us to Imperial
To convert miles per US gallon (MPG US) to miles per Imperial gallon (MPG Imperial), you can use the conversion factor: 1 US gallon is approximately 0.832674 Imperial gallons. The formula is:
Imperial MPG = US MPG × 1.20095
Why Does Every Car have Multiple MPG figures?
- Driving Conditions – Different driving conditions, such as city or highway, affect fuel efficiency.
- Test Cycles – Manufacturers test vehicles in various cycles to simulate real-world conditions.
- Load and Weight – Vehicle load impacts MPG; heavier loads reduce fuel efficiency.
- Speed Variations – Speed changes influence fuel consumption rates, as shown in the measurement chart, with higher speeds generally reducing fuel efficiency.
- Terrain – Hilly or flat terrains lead to different MPG results.
- Climate – Extreme temperatures can affect engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Driving Style – Aggressive driving lowers MPG, while smooth driving improves it.
How Is Fuel Economy Calculated?
- Fill the Tank – Start with a full fuel tank.
- Reset the Odometer – Reset the trip odometer to zero.
- Drive Normally – Drive your vehicle as you typically would.
- Record Miles Driven – Note the number of miles driven from the trip odometer.
- Refill the Tank – Refill the tank to full, recording the gallons of fuel added.
- Use the Formula – Calculate fuel economy using the MPG formula
- Compare Values – Compare the calculated MPG with manufacturer ratings or a measurement chart.
- Adjust for Conditions – Consider factors like driving conditions and load, which can affect fuel economy.
Are MPG Figures Realistic?
- Laboratory Testing – MPG figures are often determined under controlled conditions, which may not reflect real-world driving.
- Standardized Procedures – Manufacturers follow standardized testing procedures to ensure consistency, but these may not account for all variables.
- Ideal Conditions – Tests are conducted in ideal conditions, unlike the varying conditions drivers face.
- Driving Habits – Individual driving styles, such as aggressive acceleration, can differ from the testing norms, affecting actual MPG.
- Load and Terrain – Real-world driving involves varying loads and terrains, which aren’t fully replicated in tests.
- Climate Effects – Extreme weather can impact fuel efficiency differently than laboratory conditions.
- Maintenance – Well-maintained vehicles perform closer to rated MPG, whereas poor maintenance can reduce efficiency.
How to Calculate Miles per Gallon for a Trip?
- Initial Fill-Up: Begin with a completely filled fuel tank.
- Note Initial Odometer Reading: Record the odometer reading at the start of your trip.
- Drive Your Trip: Complete your trip as planned.
- Final Fill-Up: At the end of your trip, refill the tank to full capacity.
- Note Final Odometer Reading: Record the odometer reading after refilling.
- Calculate Miles Driven: Subtract the initial odometer reading from the final reading to get the total miles driven.
- Record Gallons Used: Note the number of gallons needed to refill the tank.
- Use the Formula: Compute MPG using the formula:
Miles per gallon to liters per 100km
Miles Per Gallon to Liters Per 100km – Converting miles per gallon (MPG) to liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km) involves changing units of measurement from the US system to the metric system. Use the following steps and formula:
- Start with MPG – Begin with the MPG value you want to convert.
- Convert MPG to km/L – Multiply the MPG value by 0.425144 to convert it to kilometers per liter (km/L).
km/L=MPG×0.425144
- Calculate L/100km – Divide 100 by the km/L value to get liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km).
L/100km=100/km/L
Uses
- Fuel Efficiency Comparison – Helps consumers compare the fuel efficiency of different vehicles.
- Environmental Impact Assessment – Assists in evaluating the environmental impact of vehicles based on fuel consumption.
- Cost Estimation – Aids in estimating fuel costs for trips and long-term vehicle ownership.
- Regulatory Compliance – Ensures vehicles meet government fuel efficiency standards and regulations.
- Vehicle Marketing – Used by manufacturers to market the fuel efficiency of their vehicles to potential buyers.
- Performance Analysis – Helps drivers monitor and optimize their driving habits for better fuel economy.
- Fleet Management – Enables businesses to manage and optimize fuel usage across their fleet of vehicles.
- Resale Value – Influences the resale value of vehicles, as higher MPG ratings can make a vehicle more attractive to buyers.
Mile Per US Gallon Conversion Table
| MPG (US) | km/L | L/100km | MPG (Imperial) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 4.25144 | 23.52 | 12.01 |
| 15 | 6.37716 | 15.68 | 18.02 |
| 20 | 8.50288 | 11.76 | 24.02 |
| 25 | 10.6286 | 9.41 | 30.02 |
| 30 | 12.75432 | 7.84 | 36.03 |
| 35 | 14.88004 | 6.72 | 42.03 |
| 40 | 17.00576 | 5.88 | 48.04 |
| 45 | 19.13148 | 5.24 | 54.04 |
| 50 | 21.2572 | 4.70 | 60.05 |
How is MPG calculated?
MPG is calculated by dividing the number of miles driven by the number of gallons of fuel used.
Why is MPG important?
MPG is important because it helps determine the fuel efficiency and cost-effectiveness of a vehicle, impacting fuel costs and environmental footprint.
What is a good MPG for a car?
A good MPG varies, but generally, 25-30 MPG is considered average for most cars, while 30+ MPG is considered good.
How can I improve my car’s MPG?
Improve MPG by maintaining your car, keeping tires properly inflated, reducing excess weight, and driving smoothly.
Does driving speed affect MPG?
Yes, driving at higher speeds typically reduces MPG due to increased aerodynamic drag and engine load.
How does vehicle weight influence MPG?
Heavier vehicles require more energy to move, leading to lower MPG compared to lighter vehicles.
What role do tire pressures play in MPG?
Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, improving MPG, while underinflated tires decrease fuel efficiency.
Do hybrid cars have better MPG?
Yes, hybrid cars generally have better MPG due to their combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor.
How does air conditioning impact MPG?
Using air conditioning increases engine load, which can reduce MPG, especially during city driving.
Are MPG ratings the same for city and highway driving?
No, city MPG is usually lower due to frequent stops and starts, while highway MPG is higher due to steady speeds.