Non Renewable Resources
There are two types of natural resources a person can observe in the natural world, which are non-renewable and renewable resources. People often use these resources to help create products and services that will improve the person’s quality of life or will enable them to commit specific actions and feats.
What Are Non-Renewable Resources?
Non- Renewable Energy Sources
Non-renewable energy sources are those that do not replenish or do so very slowly in human time scales, making them finite and susceptible to depletion. They have been the primary sources of energy for centuries due to their high energy content and reliability. Here are the main types of non-renewable energy sources:
Fossil Fuels
- Coal: One of the oldest and most abundant fossil fuels, coal is used primarily for electricity generation and industrial processes due to its high energy content.
- Oil: A liquid fossil fuel that is refined into gasoline, diesel, and other petroleum products. It is crucial for transportation, heating, and as a feed stock for chemicals.
- Natural Gas: Composed mainly of methane, natural gas is used for heating, electricity generation, and as a fuel for vehicles. It burns cleaner than coal and oil but still emits carbon dioxide.
Nuclear Energy
- Uranium: Uranium is a heavy metal used as fuel in nuclear power plants. Through a process called nuclear fission, uranium atoms are split to release a large amount of heat, which is then used to generate electricity. While it does not emit greenhouse gases during energy production, the waste it produces is radioactive and requires careful long-term management.
Other Non-Renewable Resources
- Peat: Often considered a precursor to coal, peat is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation matter. It can be used as fuel but is less efficient and more polluting than coal, oil, or natural gas.
Non-renewable energy sources are known for their high energy densities and stability in providing base-load power. However, their extraction, processing, and use have significant environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction. The global shift towards renewable energy aims to reduce these impacts while meeting the world’s growing energy needs sustainably.
Types of non Non Renewable Resources
Fossil Fuels
- Coal: A solid fossil fuel used primarily for electricity generation and steel production.
- Petroleum (Crude Oil): A liquid fossil fuel refined into gasoline, diesel, and other petrochemical products.
- Natural Gas: Composed mostly of methane, it’s used for heating, electricity generation, and as a chemical feedstock.
Nuclear Fuels
- Uranium: A heavy metal used in nuclear reactors for electricity generation through the process of nuclear fission.
Other Non-Renewable Minerals and Metals
- Precious Metals (like gold, silver, and platinum): Valuable for their rarity and used in electronics, jewelry, and various industrial applications.
- Industrial Minerals (like diamonds, phosphate, and sand): Essential for construction, agriculture, and manufacturing.
- Rare Earth Elements: Critical for manufacturing high-tech devices, including smartphones, wind turbines, and electric vehicles
1. Non-Renewable Energy Resources Example

envirsc.uok.edu.in
2. Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources

aagasc.edu.in
3. Nonrenewable Resources Environment and Ecology Standards

gcwgandhinagar.com
4. Nonrenewable Resources Sources of Energy

nios.ac.in
5. Simple Non-Renewable Energy Example

ei.lehigh.edu
6. Sample Non-Renewable Energy Sources

mycvec.com
7. The Issue of Renewable Energy Example

aps.edu
8. Nonrenewable Energy Sources and Their Impacts

eeintennessee.org
9. Mass Flux of Non-renewable Energy for Humanity

scholarworks.uark.edu
10. Basic Natural Resources Example

mmmut.ac.in
11. Africa Non-Renewable Natural Resources
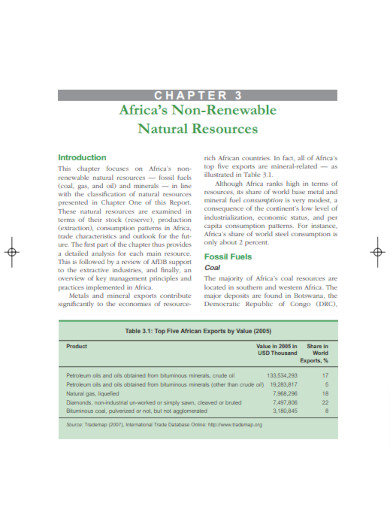
afdb.org
12. Non Renewable Natural Resources Example

eagri.org
13. Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy

generationgenius.com
14. Standard Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy

littlesun.org
15. Modern Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy
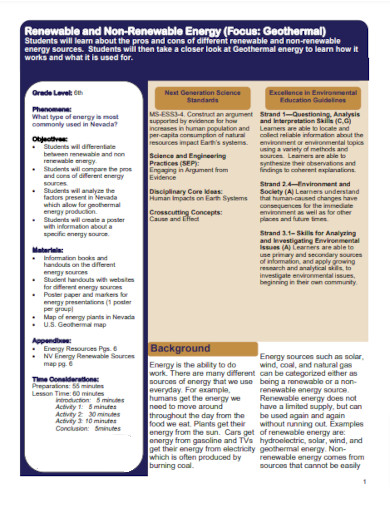
nevadaoutdoorschool.org
16. Editable Non-Renewable Resources Example

cushman.host.dartmouth.edu
17. Economics of Non-Renewable Resources

jncollegeonline.co.in
18. Sustainable Development and Nonrenewable Resources

pubs.usgs.gov
19. Mathematics of Nonrenewable Resources

sigmaa.maa.org
20. Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Example

aquariumofpacific.org
21. Study Of The Effects Of Non-Renewable Energy Sources

ilkogretim-online.org
22. Competition and Resource Scarcity on a Nonrenewable Resource Market

eui.eu
23. Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Sources and Their Costs

uakron.edu
24. Crediting the Displacement of Non-Renewable Biomass
cdm.unfccc.int
25. Nonrenewable Resources Eco-Energy for Schools

ecoenergyforschools.com
26. Fossil Fuel and Other Non-Renewable Material Depletion

edepot.wur.nl
27. Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Example

ngemc.com
28. Printable Non-Renewable Resources Example

dallasfed.org
29. Non-renewable Resources in Asian Economies

eria.org
30. The Supply of Non-Renewable Resources Example

parisschoolofeconomics.eu
31. Fossil Fuel and Non-Renewable Resource Example

walshmedicalmedia.com
Benefits of Non-Renewable Energy Sources
Despite the environmental concerns associated with non-renewable energy sources, they have played a pivotal role in driving global industrialization and economic development. Here are some key benefits of non-renewable energy:
High Energy Density
- Efficiency: Non-renewable energy sources like oil, coal, and natural gas have a high energy density, meaning they can produce a large amount of energy from a small amount of fuel. This makes them highly efficient for generating electricity and powering transportation.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Lower Initial Costs: The infrastructure for extracting and using non-renewable energy sources is well-established, often making them cheaper upfront compared to some renewable sources that may require significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure.
- Economic Stability: The established global market for fossil fuels can offer more predictable pricing compared to some renewable resources that might be affected by weather variability and technological development stages.
Reliability and Availability
- Consistent Power Supply: Non-renewable energy sources provide a steady, reliable source of power that isn’t dependent on weather conditions, making them crucial for base-load energy production.
- Widespread Availability: Fossil fuels are found in many parts of the world, providing significant strategic and economic advantages to countries that possess these resources.
Supporting Industries and Economic Growth
- Industrial Growth: Non-renewable energy sources have historically supported the growth of industries by providing a reliable energy supply for manufacturing, transportation, and other sectors.
- Job Creation: The extraction, processing, and distribution of non-renewable energy resources employ millions of people worldwide, contributing to economic stability and growth.
Technological Advancement
- Innovation: The non-renewable energy sector has driven technological advancements in exploration, extraction, and energy conversion processes, contributing to more efficient and safer practices.
While non-renewable energy sources have their benefits, the shift towards renewable energy reflects a global recognition of the need to balance these advantages with environmental sustainability and long-term energy security. The transition to a more sustainable energy mix aims to retain the economic and reliability benefits of energy systems while significantly reducing environmental impacts.
How to Reduce One’s Usage of Non-Renewable Resources
All electrical gadgets and appliances use electricity to work and function, which allows us to maintain a high level of quality of life. Due to the finite amount of non-renewable resources, it is important to lessen one’s use of electricity or goods that require the usage of these types of resources.
Step 1: Limit One’s Usage of Cars
Cars use fuels and gasoline, which are finite and non-renewable resources. If the location is close or there are safe alternatives to reach a specific location, then one should limit the usage of cars and either walk or use public transportation to reach the said place.
Step 2: Plug Out any Unused Electrical Equipment or Gadgets
Any electrical equipment or gadget that the person is not currently using should be plugged out to prevent any unintended usage of electricity. Not only that but there is a chance that unattended electrical gadgets can cause unintentional emergencies or situations.
Step 3: Recycle Goods or Products
Specific goods and products will require the refinement of specific non-renewable resources. A person should try to recycle specific goods and products to increase the lifespan of that object and reduce the amount of waste one creates.
Step 4: Limiting the Usage of Water
When showering or using the faucet, these appliances require the use of electricity to move the water from the water supply to one’s pressure tank. Not only that, but the water we use to wash ourselves will also require electricity to filter and treat the quality of the water. This means you should try and limit the amount of water you use to wash yourself and other objects.
FAQs
Why should we care about non-renewable resources?
We often use non-renewable resources to fuel specific industries and objects, which will not only improve our quality of life but it will also allow us to have access to specific conveniences. These resources have a limited lifespan, which is why we need to ensure we are using them as little as possible.
Are rocks non-renewable resources?
Rocks and minerals are specific types of resources that a person can obtain from specific parts of the earth. These rocks and minerals have a finite supply and are non-renewable resources.
How are human made resources different from natural resources?
Human-Made Resources: These are resources that people create from natural resources to make life easier and solve problems. Examples include buildings, roads, and technology. They are made by humans and wouldn’t exist without human intervention.
Non-renewable resources are specific types of resources one can use to create specific services and products,= which are limited in supply. One needs to watch the amount of non-renewable resources they use, as the supply will not last forever. Therefore it is important to consider limiting the usage of specific activities to lessen one’s individual use of non-renewable resources.


