99+ Opportunity Cost Examples
When a company rents out a building and pays its rent, it will have to compare whether its rent is less than the implicit cost caused by the company’s situation. Implicit cost is a type of opportunity cost that refers to the opportunity cost of a company if it were to use its resources.
1. Opportunity Cost Sample
2. Opportunity Cost PDF
3. The Concept of Opportunity Cost
4. Literature on Opportunity Cost
5. Opportunity Costs of Capital Example
6. The Opportunity Cost of Setups
7. Opportunity Cost and Benefits
8. Opportunity Cost of Natural Gas Subsidies
9. Opportunity Cost of Poor Quality
10. Opportunity Cost Example
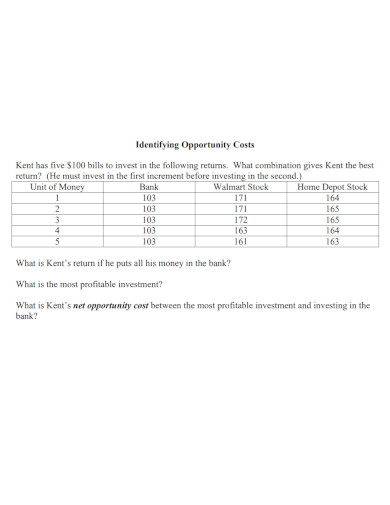
11. Identifying Opportunity Cost
12. Simple Opportunity Cost
13. Standard Opportunity Cost
14. Estimating the Opportunity Cost
15. Opportunity Cost and Possibility Curves
16. Economic Opportunity Cost
17. Microeconomic Opportunity Cost
18. Opportunity Cost of Employment
19. About Opportunity Cost
20. Calculating Opportunity Cost
21. The Opportunity Cost of Capital
22. The Opportunity Cost of Government
23. Job Opportunity Cost of War
24. Economic Rent and Opportunity Cost
25. Opportunity Cost Calculation
26. Opportunity-Cost Conflicts in Corporate Law
27. Health Opportunity Cost
28. Opportunity Cost of Educational Human Capital
29. Scarcity and Opportunity Cost
30. Opportunity Cost of Preserving Forest
31. Opportunity Cost of Labour
32. Capital Opportunity Cost
33. Money Opportunity Cost
34. The Opportunity Cost of Violence
35. The Opportunity Costs of Rent Seeking
36. Opportunity Cost Varies
37. Printable Opportunity Cost Example
38. Estimation of Opportunity Cost
39. Understanding the Opportunity Cost
40. The Limitations of Opportunity Cost
41. Comparison to Generator Opportunity Cost
42. Issuance of Opportunity Cost
43. Opportunity Cost Report
44. Opportunity Costs in Agriculture
45. Opportunity Cost
46. Opportunity Cost Consideration
47. Externalities and Opportunity Cost
48. Time-Dependent Opportunity Cost
49. The Opportunity Cost Algorithm
50. Opportunity Cost and Diversification
51. Phenomenology of Perceived Opportunity Cost
52. Food Safety Opportunity Cost
53. Opportunity Cost Introduction
54. Opportunity Cost Template
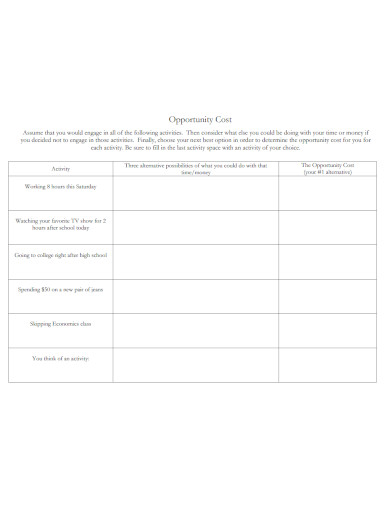
55. Opportunity Cost Worksheet
56. The Opportunity Cost of Security
57. Opportunity Cost of Employment
58. Opportunity Cost Example PDF
59. Opportunity Cost of Inaction
60. Opportunity Cost of Housing Consumption
61. Opportunity Cost for Job Assignment
62. Opportunity Cost, Competition and Firm Selection
63. Opportunity Cost in PDF
64. Opportunity Cost of Corruption
65. Opportunity Cost Approach
66. Economic Opportunity Cost Example
67. Opportunity Cost of Consumption
68. Social Opportunity Cost
69. Basic Opportunity Cost Example
70. Digital Opportunity Cost
71. Extended Opportunity Cost
72. Constant Opportunity Cost
73. Social Opportunity Cost of Capital
74. Opportunity Cost and Hidden Inventions
75. Measurement of Opportunity Cost
76. Opportunity Cost Formula
77. Calculating Opportunity Cost Example
78. Opportunity Cost Analysis
79. Types of Opportunity Cost
80. Opportunity Cost in Business
81. Opportunity Cost in Financial Management
82. Opportunity Cost in Healthcare Sector
83. Analyzing Opportunity Cost in PDF
84. The Opportunity Cost of Suffrage
85. Opportunity Cost Case Study
86. Opportunity Cost of Spending and Saving
87. Opportunity Cost of Transportation Barriers
88. Opportunity Cost of Time
89. The Opportunity Cost of Exporting
90. Opportunity Cost for Cost Estimate
91. Opportunity Cost of Land
92. Opportunity Cost Neglect
93. Professional Opportunity Cost
94. Opportunity Cost Template Example
95. Opportunity Cost Concept
96. Opportunity Cost and Participation
97. The Opportunity Cost of Monetary Conviction
98. Opportunity Cost Estimation of Ecosystem Services
99. Draft Opportunity Cost Example
100. Opportunity Cost of Collateral
What Is Opportunity Cost
The opportunity cost refers to the amount of positive and negative consequences missed when choosing one opportunity over the other. This concept is applied regardless of the impact and importance of the decision you have made.
How to Calculate Opportunity Cost
Many important decisions have high impact opportunity costs that we have to consider whether this is done consciously or unconsciously. But the more effort in practicing and mastering the calculation of opportunity costs the easier it will be for us to discern the rewards and consequences entailed by our decisions. If you are still confused about the concept of opportunity cost then feel free to check and read up on the opportunity cost examples, samples, studies, and PDFs on the list above.
1.) List Down or Think About the Different Choices Presented
Begin by listing down or thinking about the various choices you can make. Go big, don’t be afraid to think outside of the box. Note that you should also include choices that you think are unconventional as these are still part of the possible choices you can make.
2.) Note the Effort Needed by a Choice
After you have done this, you will need to note the amount of effort you will put into it, when you have selected a choice. Doing this will allow you to easily compare and contrast the opportunity cost. As some choices will provide large amounts of rewards but will also require a large amount of effort to be put into it.
3.) List Down and Evaluate the Rewards and Consequences of the Choice
After you have thought about and noted the effort needed by the choice, you must list down all the possible outcomes that will stem from the chosen choice. This will include any positive and negative consequences that will arise.
4.) Repeat Until Finished
Repeat steps two to three until you have noted down all the effort and consequences the choice will entail. This will allow you to have a top-down perspective of the opportunity cost each choice will have and may help you make an informed decision.
FAQs
Why does opportunity cost exist?
Every choice we make in our everyday lives entails a specific type of cost. These costs are called opportunity cost which refers to the cost entailed by selecting a specific opportunity and forgoing the other. This exists due to the scarcity of opportunity or the concept that an opportunity will only be available at a specific moment in time and is sacrificed when the individual chooses an opportunity.
How does opportunity cost affect our ability to make decisions?
Opportunity cost is a concept we grapple with in our everyday lives. An example of an everyday opportunity cost is the decision you will have when you are planning what you want to have for breakfast. Often, we can only choose one decision and forgo the other after giving some thought. The opportunity cost will allow us to gauge the potential foreseen rewards and consequences we will get when we pursue a specific choice. The higher the opportunity cost the more time you will have to spend thinking about which choice you will take. Note this does not account for the unforeseen rewards and consequences, as these are not taken into account in opportunity cost.
Why is it important to know about the concept of opportunity cost?
The opportunity cost will allow us to grapple with the consequences and rewards we will experience and obtain when making a specific choice. If we understand the concept of opportunity cost, we can easily reason why we often think before we act on bigger choices. Not only that but knowing the concept of opportunity cost will also allow us to deliberately think about the opportunity cost being presented in a decision.
Opportunity cost is the concept that grapples with the sacrifices we make in our everyday choices, regardless of the impact of the rewards and consequences brought about by the opportunity. Knowing how to calculate opportunity costs will allow us to deliberately and consciously think about the important decisions we make. In conclusion, opportunity cost is a concept that we unconsciously grapple with in our everyday lives, which is something we should consciously practice.