24+ Peer Review Examples to Download
Peer review is an integral part of the academic publishing process, ensuring that research meets rigorous standards of quality, ethics, and relevance. From research papers to academic essays, manuscripts, and educational research ethics to theses, peer review plays a critical role in shaping the discourse and progress of various fields of study. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of peer review and provide a step-by-step guide on how to get a peer review for your work.
1. Peer Review and Subject Matter Expertise

aspa-usa.org
2. Benefits and Drawbacks of Peer Review

jmu.edu
3. Survive Peer Review

bmj.com
4. Peer Review Guidelines

iup.edu
5. Art and Politics Peer Review

eric.ed.gov
6. New Peer Review Ratings
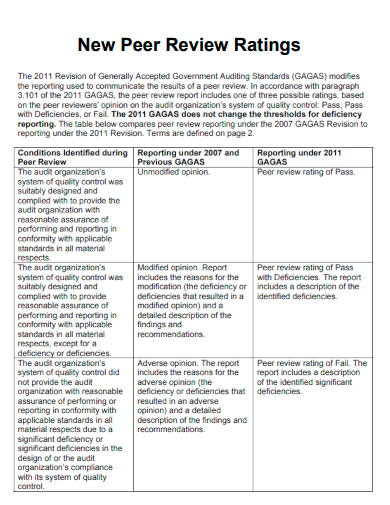
gao.gov
7. Strategies for Effective Peer Review

stcloudstate.edu
8. Peer Reviewing Journal Articles

cambridge.org
9. Ethics of Peer Review

ori.hhs.gov
10. Peer Review in Remote Environments

uvm.edu
11. Solid Peer Review

agu.org
12. Manuscripts for Peer-Review

emich.edu
13. Peer Review Manual

medicalboard.iowa.gov
14. Scholarly Communication and Peer Review

wellcome.org
15. Value of Serving as a Peer Reviewer

nsuworks.nova.edu
16.
17. Peer Review Work

wisc.edu
18. Conflict of Interest in Peer Review

cdmrp.health.mil
19. Peer Review and Peer Involvement

epa.gov
20. Peer Review Methodology

europa.eu
21. Facilitating Effective Peer Review

lindsey.edu
22. Peer Review in Academic Publishing

ro.uow.edu.au
23. Mitigating Manipulation in Peer Review

neurips.cc
24. Scientific Peer Review

usaidlearninglab.org
25. Information Quality Peer Review

bia.gov
What is a Peer Review?
A peer review is a process in which an academic work, such as an article, manuscript, or thesis, is evaluated by other experts in the same field. The purpose of a peer review is to ensure that the work meets high standards of academic rigor and quality. Peer reviews can also help identify potential biases, errors, or areas for improvement.
How to Get a Peer Review?
Getting a peer review is an essential step in the academic publishing process. To get a peer review, you need to identify a suitable venue, familiarize yourself with submission guidelines, submit your work, and respond to feedback. By following these steps, you can ensure that your work meets high standards of quality and ethics, and make valuable contributions to your field of study.
Step 1: Choose the right journal or publication
Start by identifying the relevant journals or publications in your field that accept peer-reviewed articles. Look for journals that have a good reputation and a high impact factor.
Step 2: Follow the submission guidelines
Before submitting your work, carefully read and follow the submission guidelines provided by the journal or publication. This will help ensure that your work meets the specific requirements and expectations of the journal.
Step 3: Submit your work for review
Once you have followed the submission guidelines, submit your work for review. The journal will typically send your work to multiple experts in your field for evaluation.
Step 4: Respond to feedback
If your work is accepted with revisions or rejected, carefully consider the feedback provided by the reviewers. Address any areas for improvement and resubmit your work for further review.
What is the purpose of a peer review?
The purpose of a peer review is to ensure that academic work meets high standards of quality and rigor, and to identify potential biases or areas for improvement.
What is the role of peer reviewers?
Peer reviewers evaluate academic work to determine if it meets high standards of quality and rigor, and provide feedback to the author to help improve the work.
What is implicit bias in peer review?
Implicit bias is the tendency for reviewers to have preconceived notions or prejudices that can impact their evaluation of academic work. This can include biases based on gender, race, ethnicity, or other factors.
How does a peer review differ from an article review?
A peer review is a process in which academic work is evaluated by experts in the same field, while an article review is a critique of a published article by another author.
Peer review is a vital aspect of the academic publishing process, ensuring that research meets high standards of quality, ethics, and relevance. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can successfully navigate the peer review process and receive valuable feedback on your work. Whether you’re submitting a manuscript, thesis, or research paper, peer review is a critical step in ensuring the success of your project quality plan.
24+ Peer Review Examples to Download

Peer review is an integral part of the academic publishing process, ensuring that research meets rigorous standards of quality, ethics, and relevance. From research papers to academic essays, manuscripts, and educational research ethics to theses, peer review plays a critical role in shaping the discourse and progress of various fields of study. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of peer review and provide a step-by-step guide on how to get a peer review for your work.
1. Peer Review and Subject Matter Expertise

aspa-usa.org
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 149 KB
2. Benefits and Drawbacks of Peer Review

jmu.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 475 KB
3. Survive Peer Review

bmj.com
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 174 KB
4. Peer Review Guidelines

iup.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 171 KB
5. Art and Politics Peer Review

eric.ed.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 63 KB
6. New Peer Review Ratings

gao.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 75 KB
7. Strategies for Effective Peer Review

stcloudstate.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 111 KB
8. Peer Reviewing Journal Articles

cambridge.org
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 468 KB
9. Ethics of Peer Review

ori.hhs.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 94 KB
10. Peer Review in Remote Environments

uvm.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 209 KB
11. Solid Peer Review

agu.org
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 991 KB
12. Manuscripts for Peer-Review

emich.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 1 MB
13. Peer Review Manual

medicalboard.iowa.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 212 KB
14. Scholarly Communication and Peer Review

wellcome.org
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 468 KB
15. Value of Serving as a Peer Reviewer

nsuworks.nova.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 151 KB
16.
17. Peer Review Work

wisc.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 205 KB
18. Conflict of Interest in Peer Review

cdmrp.health.mil
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 24 KB
19. Peer Review and Peer Involvement

epa.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 184 KB
20. Peer Review Methodology

europa.eu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 247 KB
21. Facilitating Effective Peer Review

lindsey.edu
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 473 KB
22. Peer Review in Academic Publishing

ro.uow.edu.au
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 318 KB
23. Mitigating Manipulation in Peer Review

neurips.cc
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 300 KB
24. Scientific Peer Review

usaidlearninglab.org
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 179 KB
25. Information Quality Peer Review

bia.gov
Details
File Format
PDF
Size: 17 KB
What is a Peer Review?
A peer review is a process in which an academic work, such as an article, manuscript, or thesis, is evaluated by other experts in the same field. The purpose of a peer review is to ensure that the work meets high standards of academic rigor and quality. Peer reviews can also help identify potential biases, errors, or areas for improvement.
How to Get a Peer Review?
Getting a peer review is an essential step in the academic publishing process. To get a peer review, you need to identify a suitable venue, familiarize yourself with submission guidelines, submit your work, and respond to feedback. By following these steps, you can ensure that your work meets high standards of quality and ethics, and make valuable contributions to your field of study.
Step 1: Choose the right journal or publication
Start by identifying the relevant journals or publications in your field that accept peer-reviewed articles. Look for journals that have a good reputation and a high impact factor.
Step 2: Follow the submission guidelines
Before submitting your work, carefully read and follow the submission guidelines provided by the journal or publication. This will help ensure that your work meets the specific requirements and expectations of the journal.
Step 3: Submit your work for review
Once you have followed the submission guidelines, submit your work for review. The journal will typically send your work to multiple experts in your field for evaluation.
Step 4: Respond to feedback
If your work is accepted with revisions or rejected, carefully consider the feedback provided by the reviewers. Address any areas for improvement and resubmit your work for further review.
What is the purpose of a peer review?
The purpose of a peer review is to ensure that academic work meets high standards of quality and rigor, and to identify potential biases or areas for improvement.
What is the role of peer reviewers?
Peer reviewers evaluate academic work to determine if it meets high standards of quality and rigor, and provide feedback to the author to help improve the work.
What is implicit bias in peer review?
Implicit bias is the tendency for reviewers to have preconceived notions or prejudices that can impact their evaluation of academic work. This can include biases based on gender, race, ethnicity, or other factors.
How does a peer review differ from an article review?
A peer review is a process in which academic work is evaluated by experts in the same field, while an article review is a critique of a published article by another author.
Peer review is a vital aspect of the academic publishing process, ensuring that research meets high standards of quality, ethics, and relevance. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can successfully navigate the peer review process and receive valuable feedback on your work. Whether you’re submitting a manuscript, thesis, or research paper, peer review is a critical step in ensuring the success of your project quality plan.

