18+ Portfolio Examples to Download
A portfolio showcases an individual’s or organization’s projects, skills, and accomplishments. It includes a collection of work samples, case studies, and achievements, demonstrating expertise and growth over time. In the context of portfolio management, it highlights strategies for balancing risk and return, selecting investments, and optimizing asset allocation. Portfolios are used to illustrate proficiency and attract potential clients, employers, or collaborators, serving as a visual and tangible representation of one’s capabilities, creativity, and professional journey.
What is a Portfolio?
A portfolio is a curated collection of an individual’s or organization’s work, showcasing skills, projects, and accomplishments. In finance, it refers to a range of investments managed to achieve specific financial goals, balancing risk and return through strategic asset allocation.
Portfolio Format
1. Introduction
- Cover Page: Include your name, title, and a captivating image or design.
- Personal Statement: Write a brief introduction about yourself, your design philosophy, and what makes you unique.
2. Table of Contents
- List the sections and projects included in your portfolio for easy navigation.
3. About Me
- Biography: Provide a more detailed background about yourself, your education, and your career journey.
- Skills: Highlight your key skills, tools, and software proficiency.
- Contact Information: Ensure your email, phone number, and links to social media or professional profiles are easy to find.
4. Selected Works
Each project should include the following elements:
- Project Title: Clear and descriptive.
- Project Description: Brief overview of the project, its objectives, and your role.
- Client Information: Include the client’s name and industry (if applicable).
- Project Goals: State the goals or challenges the project aimed to address.
- Process and Approach: Describe your creative process, including research, brainstorming, and development stages.
- Final Outcome: Showcase the final design with high-quality images or videos.
- Results and Impact: Highlight the success and impact of the project, including any metrics or client feedback.
5. Case Studies
- Provide in-depth analysis of a few key projects. Include detailed descriptions of your design thinking, problem-solving process, and the rationale behind your design decisions.
6. Additional Work
- Include a section for other relevant projects or freelance work that demonstrates your versatility and breadth of experience.
7. Testimonials
- Add quotes or feedback from clients, colleagues, or mentors that vouch for your skills and professionalism.
8. Resume
- Attach an up-to-date resume that includes your work experience, education, awards, and certifications.
9. Contact Information
- A dedicated page with your contact details and a professional photo.
10. Online Presence
- Provide links to your website, LinkedIn profile, Behance, Dribbble, or other relevant platforms.
Portfolio Design Tips
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent visual style throughout your portfolio.
- Readability: Use legible fonts and sufficient spacing for easy reading.
- High-Quality Images: Ensure all visuals are high resolution and well-presented.
- Interactive Elements: If creating a digital portfolio, consider adding interactive elements like hover effects or clickable links.
- Mobile-Friendly: Make sure your digital portfolio is responsive and looks good on various devices.
Portfolio Examples
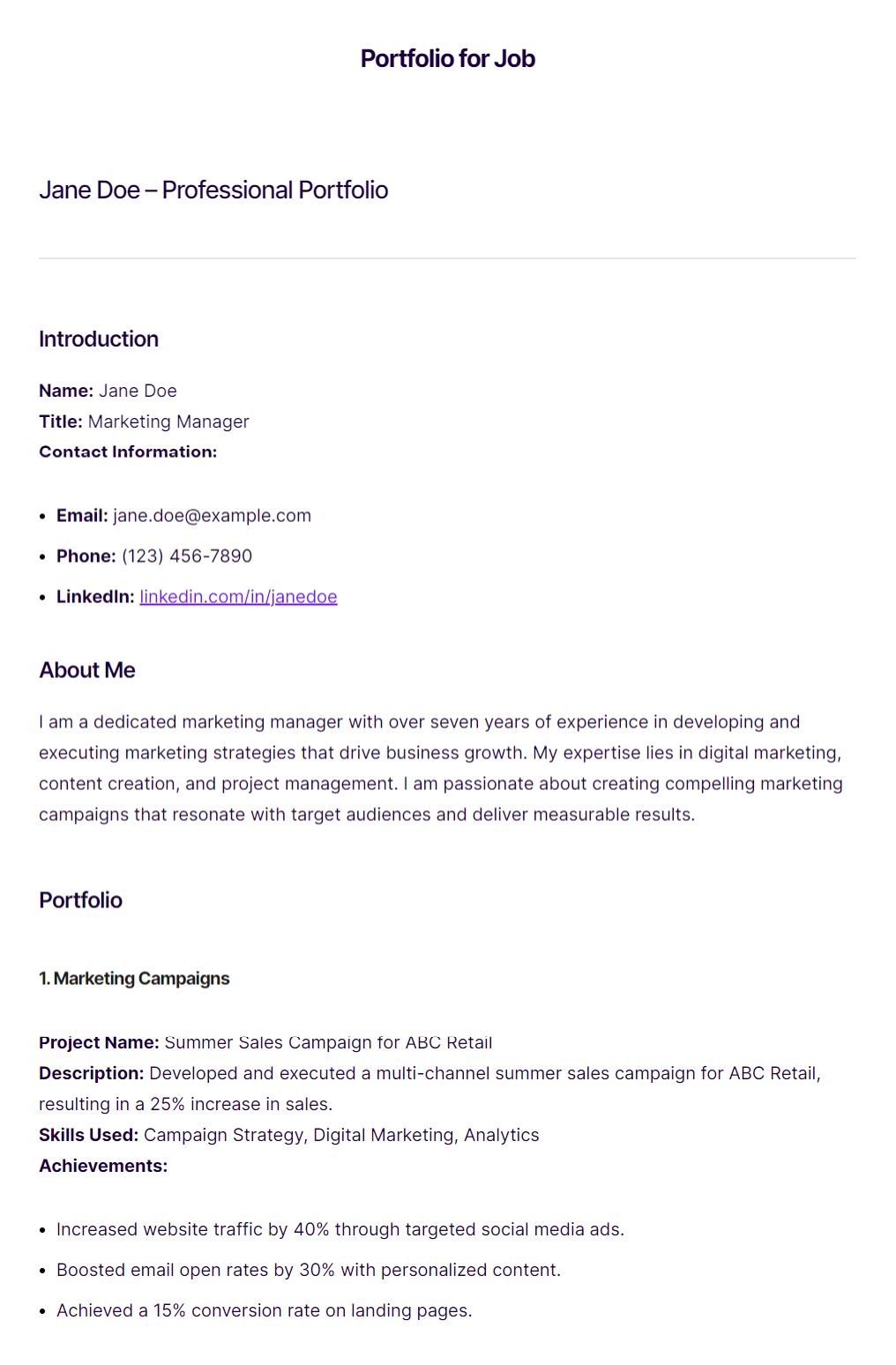
Portfolio example for jobs
Portfolio for graphic design

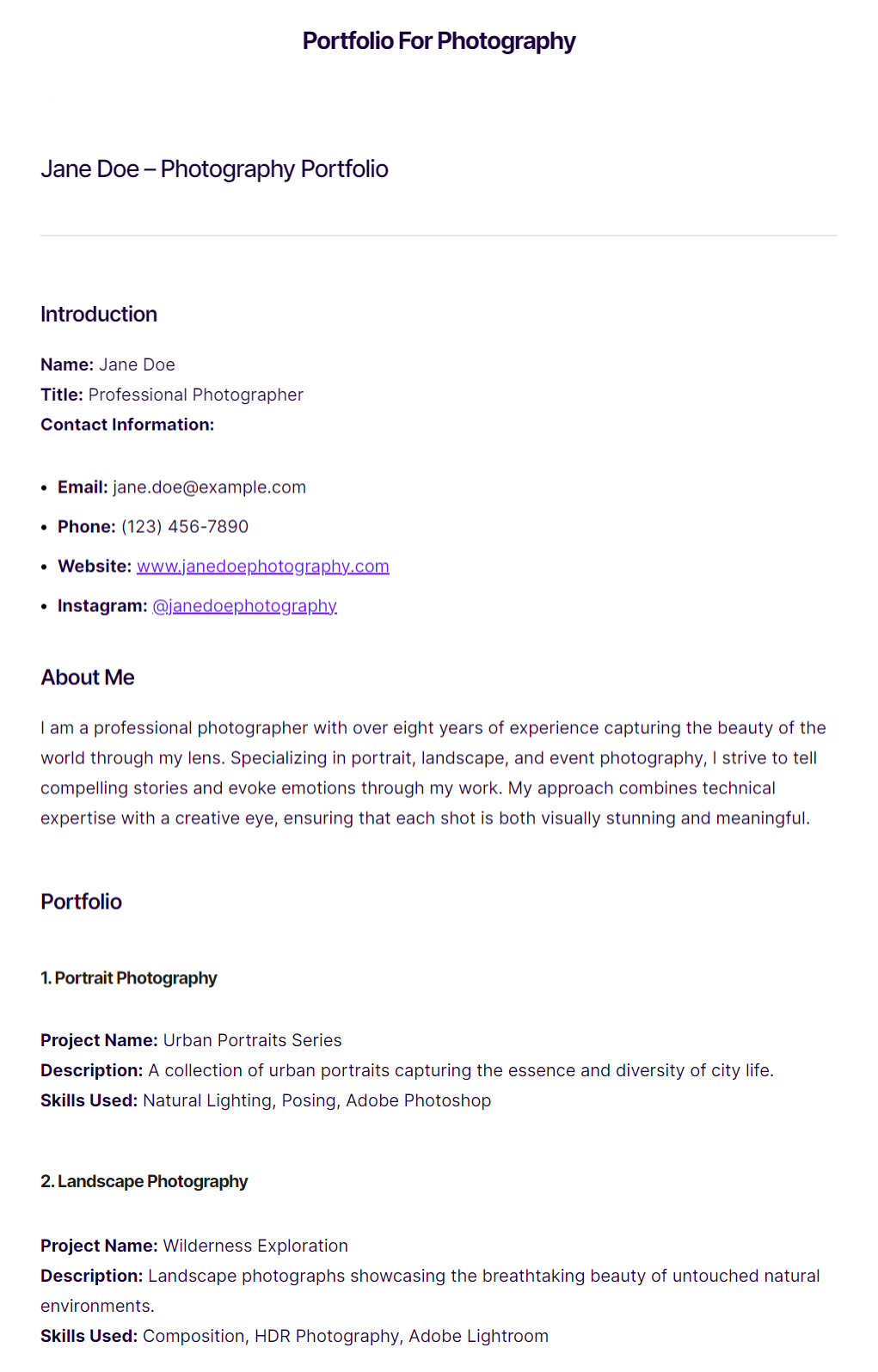
Photography portfolio example
- Portfolio For Art
- portfolio For Architecture
- Portfolio For Creative
Types of Portfolios
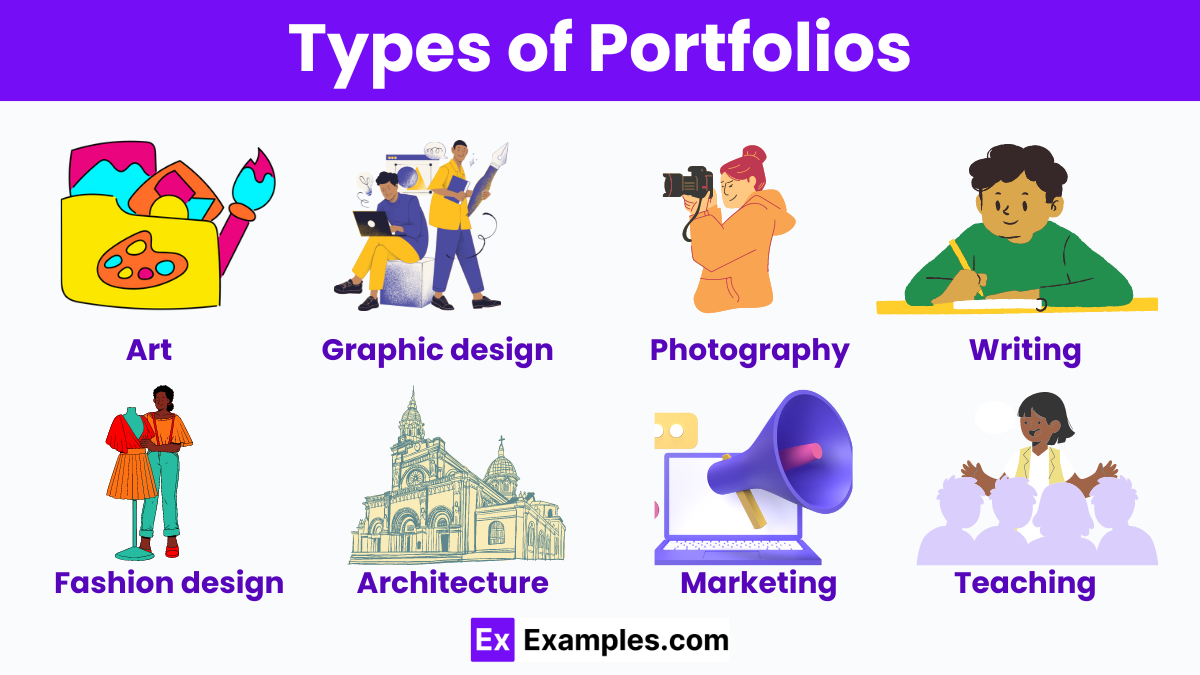
- Art portfolio – Showcases an artist’s best works, demonstrating creativity, technique, and artistic development.
- Graphic design portfolio – Displays design projects, highlighting skills in branding, typography, and visual communication.
- Photography portfolio – Presents a photographer’s top images, illustrating style, composition, and subject expertise.
- Writing portfolio – Contains a writer’s best pieces, demonstrating versatility and proficiency in different genres and styles.
- Web development portfolio – Showcases web projects, highlighting coding skills, design, and functionality.
- Fashion design portfolio – Displays clothing designs, illustrating creativity, technical skills, and fashion sense.
- Architecture portfolio – Presents architectural projects, demonstrating design ability and technical knowledge.
- Marketing portfolio – Highlights successful marketing campaigns and strategies, showcasing creativity and effectiveness.
- Investment portfolio – Investment Portfolio Contains a mix of financial assets managed to meet specific financial goals.
- Teaching portfolio – Showcases teaching philosophy, methods, and achievements, illustrating educational proficiency.
What should be included in my portfolio?
- Introduction/About Me – Provide a brief personal introduction and professional background.
- Resume/CV – Include a detailed overview of your work experience, education, and skills.
- Work Samples – Select your best examples of work relevant to the field, showcasing your skills and achievements.
- Case Studies – Include in-depth descriptions of specific projects, including objectives, processes, use cases, and outcomes.
- Skills and Expertise – List key skills and areas of expertise.
- Client Testimonials/References – Feature feedback from previous clients or employers highlighting your strengths and work ethic.
- Awards and Recognitions – Display any accolades or awards received in your field.
- Contact Information – Ensure easy-to-find details on how to get in touch with you.
How should I present my professional portfolio?
- Choose the Right Format – Decide between a physical or digital portfolio based on your field, audience preferences, and careful observation of industry standards.
- Create a Clean and Professional Design – Use a consistent layout, focus on readability, and ensure easy navigation.
- Start with a Strong Introduction – Introduce yourself, your background, expertise, and professional objectives clearly.
- Organize Your Content Logically – Arrange work samples and content in a logical order with sections and categories to create a clear and professional proforma.
- Showcase Your Best Work – Highlight your strongest, most relevant work with brief descriptions and case studies.
- Highlight Skills and Expertise – List key skills and expertise with real examples demonstrating these skills.
- Include Testimonials and References – Feature quotes from clients or colleagues that attest to your abilities.
- Display Awards and Recognitions – Show any awards or recognitions received, explaining their significance.
Portfolio For Students
- Personal Introduction – Provide a brief personal introduction, highlighting your academic background and career goals.
- Resume/CV – Include a detailed resume/CV outlining your education, internships, and relevant experience.
- Academic Projects – Showcase your best academic projects, including detailed descriptions, outcomes, and the solutions you implemented.
- Skills and Competencies – List your key skills and areas of expertise, backed by examples from coursework or projects.
- Extracurricular Activities – Highlight involvement in clubs, sports, or other activities that demonstrate leadership and teamwork.
- Awards and Honors – Display any academic awards or honors received, explaining their significance.
- References and Testimonials – Include quotes from teachers, mentors, or employers attesting to your abilities and character.
- Contact Information – Ensure your contact information is easy to find and up-to-date for potential employers or collaborators.
Portfolio Management
- Goal Setting – Define clear, measurable objectives aligned with the investor’s or organization’s strategic goals.
- Asset Allocation – Determine the optimal distribution of assets to balance risk and return based on goals and risk tolerance.
- Investment Selection – Choose specific investments or projects that align with the portfolio’s objectives and strategy.
- Diversification – Spread investments across various assets or projects to mitigate risk.
- Performance Monitoring – Regularly track and analyze the performance of the portfolio against benchmarks and goals.
- Risk Management – Identify, assess, and manage risks to minimize potential negative impacts on the portfolio.
- Rebalancing – Adjust the portfolio periodically to maintain the desired asset allocation and adapt to market changes.
- Reporting and Review – Provide regular reports and conduct reviews to ensure the portfolio remains aligned with its objectives and strategy.
How to Write a Portfolio?
- Determine the Purpose and Audience – Identify the goal of your portfolio and understand your target audience. This will guide the selection, presentation of your content, and effective marketing strategies.
- Select and Organize Content – Choose your best work samples, projects, and achievements that align with your portfolio’s purpose. Arrange them in a logical order with clear sections such as Introduction, Work Samples, Skills, and Contact Information.
- Write a Strong Introduction – Craft a brief “About Me” section that highlights your background, expertise, and professional objectives. Make sure it’s engaging and sets the tone for the rest of the portfolio.
- Describe Each Work Sample – Provide context for each item by including a description that explains the project, your role, and the outcome. Highlight specific skills used and any measurable results.
- Showcase Skills and Expertise – Create a dedicated section to list your key skills and areas of expertise. Use examples from your work samples to demonstrate these skills in action.
- Include Testimonials and Contact Information – Add quotes from clients, employers, or colleagues that attest to your abilities. Ensure your contact information is easy to find and includes multiple ways to reach you.
How Do You Create a Financial Portfolio?
- Define Your Financial Goals – Identify short-term, medium-term, and long-term financial goals with specific time horizons.
- Assess Your Risk Tolerance – Evaluate your comfort level with risk, considering factors like age, income, and obligations.
- Determine Asset Allocation – Decide on the mix of asset classes based on your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Select Investments – Choose specific investments within each asset class that align with your strategy and goals.
- Diversify Your Portfolio – Spread investments across different asset classes and sectors to reduce risk.
- Monitor and Rebalance – Regularly review your portfolio’s performance and adjust asset allocation as needed.
- Stay Informed – Stay informed with market trends and financial news to form well-researched investment decisions.
Why is a portfolio important?
It demonstrates expertise, skills, and accomplishments to potential clients or employers.
What should be included in a portfolio?
Relevant work samples, resume, skills, testimonials, and contact information.
How often should a portfolio be updated?
Regularly, to include recent work and remove outdated content.
What is portfolio diversification?
Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
How do you determine asset allocation?
Based on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon.
What are the types of portfolios?
Art, graphic design, photography, writing, investment, teaching, etc.
How do you create a digital portfolio?
Use online platforms like Behance, Dribbble, or create a personal website.
What is a professional portfolio?
A portfolio used to showcase professional skills and achievements to potential employers or clients.
How do you present a portfolio?
In a clean, organized, and professional manner, whether physical or digital.
What is portfolio management?
The strategic selection and oversight of investments to achieve financial goals.
18+ Portfolio Examples to Download

A portfolio showcases an individual’s or organization’s projects, skills, and accomplishments. It includes a collection of work samples, case studies, and achievements, demonstrating expertise and growth over time. In the context of portfolio management, it highlights strategies for balancing risk and return, selecting investments, and optimizing asset allocation. Portfolios are used to illustrate proficiency and attract potential clients, employers, or collaborators, serving as a visual and tangible representation of one’s capabilities, creativity, and professional journey.
What is a Portfolio?
A portfolio is a curated collection of an individual’s or organization’s work, showcasing skills, projects, and accomplishments. In finance, it refers to a range of investments managed to achieve specific financial goals, balancing risk and return through strategic asset allocation.
Portfolio Format
1. Introduction
Cover Page: Include your name, title, and a captivating image or design.
Personal Statement: Write a brief introduction about yourself, your design philosophy, and what makes you unique.
2. Table of Contents
List the sections and projects included in your portfolio for easy navigation.
3. About Me
Biography: Provide a more detailed background about yourself, your education, and your career journey.
Skills: Highlight your key skills, tools, and software proficiency.
Contact Information: Ensure your email, phone number, and links to social media or professional profiles are easy to find.
4. Selected Works
Each project should include the following elements:
Project Title: Clear and descriptive.
Project Description: Brief overview of the project, its objectives, and your role.
Client Information: Include the client’s name and industry (if applicable).
Project Goals: State the goals or challenges the project aimed to address.
Process and Approach: Describe your creative process, including research, brainstorming, and development stages.
Final Outcome: Showcase the final design with high-quality images or videos.
Results and Impact: Highlight the success and impact of the project, including any metrics or client feedback.
5. Case Studies
Provide in-depth analysis of a few key projects. Include detailed descriptions of your design thinking, problem-solving process, and the rationale behind your design decisions.
6. Additional Work
Include a section for other relevant projects or freelance work that demonstrates your versatility and breadth of experience.
7. Testimonials
Add quotes or feedback from clients, colleagues, or mentors that vouch for your skills and professionalism.
8. Resume
Attach an up-to-date resume that includes your work experience, education, awards, and certifications.
9. Contact Information
A dedicated page with your contact details and a professional photo.
10. Online Presence
Provide links to your website, LinkedIn profile, Behance, Dribbble, or other relevant platforms.
Portfolio Design Tips
Consistency: Maintain a consistent visual style throughout your portfolio.
Readability: Use legible fonts and sufficient spacing for easy reading.
High-Quality Images: Ensure all visuals are high resolution and well-presented.
Interactive Elements: If creating a digital portfolio, consider adding interactive elements like hover effects or clickable links.
Mobile-Friendly: Make sure your digital portfolio is responsive and looks good on various devices.
Portfolio Examples
1. Tobias van Schneider
Tobias van Schneider’s portfolio is clean and modern, with a focus on visual storytelling. His work spans branding, product design, and art direction.
2. Jessica Walsh
Jessica Walsh’s portfolio is vibrant and dynamic, reflecting her bold and colorful design style. It includes projects in graphic design, branding, and creative direction.
3. Mike Perry
Mike Perry’s portfolio is playful and artistic, featuring illustrations, animations, and typography. His work is characterized by a distinctive, whimsical style.
4. Lotta Nieminen
Lotta Nieminen portfolio showcases her versatility in graphic design, illustration, and art direction. Her site is minimalist, emphasizing her clean and elegant designs.
5. Shantell Martin
Shantell Martin’s portfolio highlights her unique black-and-white line drawings. The site is interactive, allowing users to explore her creative process.
6. Aaron Draplin
Aaron Draplin portfolio is bold and straightforward, featuring his work in logo design and branding. His no-nonsense approach is reflected in his design aesthetic.
7. Lauren Hom
Lauren Hom portfolio is colorful and fun, showcasing her skills in hand lettering and illustration. Her site includes engaging case studies and project breakdowns.
8. Gemma O’Brien
Gemma O’Brien portfolio features her striking typography and lettering work. Her site is visually engaging, with large, high-quality images of her projects.
9. David Carson
David Carson’ portfolio is unconventional and experimental, much like his design style. His work challenges traditional design norms and is visually captivating.
10. Paula Scher
Paula Scher portfolio highlights her iconic work in graphic design and branding. The site is sleek and professional, reflecting her status as a design legend.
11. Ellen Lupton
Ellen Lupton portfolio is a treasure trove of her work in graphic design and typography. Her site is educational, providing insights into her design philosophy.
12. Stefan Sagmeister
Stefan Sagmeister’s portfolio is provocative and thought-provoking. His work in graphic design and art direction is showcased through engaging visuals and narratives.
13. Debbie Millman
Debbie Millman’ portfolio covers her work in branding, podcasting, and writing. Her site is comprehensive, reflecting her multifaceted career.
14. Chris Do
Chris Do’ portfolio focuses on his work in branding and business design. The site is resourceful, offering tips and insights for aspiring designers.
15. Timothy Goodman
Timothy Goodman’ portfolio is eclectic and vibrant, featuring his work in illustration, mural art, and graphic design. His site is visually stimulating and fun to explore.
16. Kate Moross
Kate Moross portfolio is colorful and energetic, showcasing her work in graphic design, illustration, and animation. Her site is playful and engaging.
17. Sagmeister & Walsh
The joint portfolio of Stefan Sagmeister and Jessica Walsh is a visual feast. It showcases their collaborative projects, combining bold design with innovative concepts.
18. Jessica Hische
Jessica Hische’ portfolio features her beautiful hand-lettering and typography work. Her site is elegant, with a focus on her intricate and detailed designs.
19. Jon Contino
Jon Contino portfolio is rugged and vintage-inspired, reflecting his unique style in illustration and branding. His site is immersive, drawing users into his creative world.
20. Louise Fili
Louise Fili’s portfolio highlights her sophisticated work in branding and typography. The site is refined and elegant, showcasing her timeless design aesthetic
More Portfolio Examples – Edit & Download
Portfolio example for jobs

Portfolio for graphic design

Photography portfolio example

Portfolio For Creative
Types of Portfolios
Art portfolio – Showcases an artist’s best works, demonstrating creativity, technique, and artistic development.
Graphic design portfolio – Displays design projects, highlighting skills in branding, typography, and visual communication.
Photography portfolio – Presents a photographer’s top images, illustrating style, composition, and subject expertise.
Writing portfolio – Contains a writer’s best pieces, demonstrating versatility and proficiency in different genres and styles.
Web development portfolio – Showcases web projects, highlighting coding skills, design, and functionality.
Fashion design portfolio – Displays clothing designs, illustrating creativity, technical skills, and fashion sense.
Architecture portfolio – Presents architectural projects, demonstrating design ability and technical knowledge.
Marketing portfolio – Highlights successful marketing campaigns and strategies, showcasing creativity and effectiveness.
Investment portfolio – Investment Portfolio Contains a mix of financial assets managed to meet specific financial goals.
Teaching portfolio – Showcases teaching philosophy, methods, and achievements, illustrating educational proficiency.
What should be included in my portfolio?
Introduction/About Me – Provide a brief personal introduction and professional background.
Resume/CV – Include a detailed overview of your work experience, education, and skills.
Work Samples – Select your best examples of work relevant to the field, showcasing your skills and achievements.
Case Studies – Include in-depth descriptions of specific projects, including objectives, processes, use cases, and outcomes.
Skills and Expertise – List key skills and areas of expertise.
Client Testimonials/References – Feature feedback from previous clients or employers highlighting your strengths and work ethic.
Awards and Recognitions – Display any accolades or awards received in your field.
Contact Information – Ensure easy-to-find details on how to get in touch with you.
How should I present my professional portfolio?
Choose the Right Format – Decide between a physical or digital portfolio based on your field, audience preferences, and careful observation of industry standards.
Create a Clean and Professional Design – Use a consistent layout, focus on readability, and ensure easy navigation.
Start with a Strong Introduction – Introduce yourself, your background, expertise, and professional objectives clearly.
Organize Your Content Logically – Arrange work samples and content in a logical order with sections and categories to create a clear and professional proforma.
Showcase Your Best Work – Highlight your strongest, most relevant work with brief descriptions and case studies.
Highlight Skills and Expertise – List key skills and expertise with real examples demonstrating these skills.
Include Testimonials and References – Feature quotes from clients or colleagues that attest to your abilities.
Display Awards and Recognitions – Show any awards or recognitions received, explaining their significance.
Portfolio For Students
Personal Introduction – Provide a brief personal introduction, highlighting your academic background and career goals.
Resume/CV – Include a detailed resume/CV outlining your education, internships, and relevant experience.
Academic Projects – Showcase your best academic projects, including detailed descriptions, outcomes, and the solutions you implemented.
Skills and Competencies – List your key skills and areas of expertise, backed by examples from coursework or projects.
Extracurricular Activities – Highlight involvement in clubs, sports, or other activities that demonstrate leadership and teamwork.
Awards and Honors – Display any academic awards or honors received, explaining their significance.
References and Testimonials – Include quotes from teachers, mentors, or employers attesting to your abilities and character.
Contact Information – Ensure your contact information is easy to find and up-to-date for potential employers or collaborators.
Portfolio Management
Goal Setting – Define clear, measurable objectives aligned with the investor’s or organization’s strategic goals.
Asset Allocation – Determine the optimal distribution of assets to balance risk and return based on goals and risk tolerance.
Investment Selection – Choose specific investments or projects that align with the portfolio’s objectives and strategy.
Diversification – Spread investments across various assets or projects to mitigate risk.
Performance Monitoring – Regularly track and analyze the performance of the portfolio against benchmarks and goals.
Risk Management – Identify, assess, and manage risks to minimize potential negative impacts on the portfolio.
Rebalancing – Adjust the portfolio periodically to maintain the desired asset allocation and adapt to market changes.
Reporting and Review – Provide regular reports and conduct reviews to ensure the portfolio remains aligned with its objectives and strategy.
How to Write a Portfolio?
Determine the Purpose and Audience – Identify the goal of your portfolio and understand your target audience. This will guide the selection, presentation of your content, and effective marketing strategies.
Select and Organize Content – Choose your best work samples, projects, and achievements that align with your portfolio’s purpose. Arrange them in a logical order with clear sections such as Introduction, Work Samples, Skills, and Contact Information.
Write a Strong Introduction – Craft a brief “About Me” section that highlights your background, expertise, and professional objectives. Make sure it’s engaging and sets the tone for the rest of the portfolio.
Describe Each Work Sample – Provide context for each item by including a description that explains the project, your role, and the outcome. Highlight specific skills used and any measurable results.
Showcase Skills and Expertise – Create a dedicated section to list your key skills and areas of expertise. Use examples from your work samples to demonstrate these skills in action.
Include Testimonials and Contact Information – Add quotes from clients, employers, or colleagues that attest to your abilities. Ensure your contact information is easy to find and includes multiple ways to reach you.
How Do You Create a Financial Portfolio?
Define Your Financial Goals – Identify short-term, medium-term, and long-term financial goals with specific time horizons.
Assess Your Risk Tolerance – Evaluate your comfort level with risk, considering factors like age, income, and obligations.
Determine Asset Allocation – Decide on the mix of asset classes based on your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Select Investments – Choose specific investments within each asset class that align with your strategy and goals.
Diversify Your Portfolio – Spread investments across different asset classes and sectors to reduce risk.
Monitor and Rebalance – Regularly review your portfolio’s performance and adjust asset allocation as needed.
Stay Informed – Stay informed with market trends and financial news to form well-researched investment decisions.
Why is a portfolio important?
It demonstrates expertise, skills, and accomplishments to potential clients or employers.
What should be included in a portfolio?
Relevant work samples, resume, skills, testimonials, and contact information.
How often should a portfolio be updated?
Regularly, to include recent work and remove outdated content.
What is portfolio diversification?
Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
How do you determine asset allocation?
Based on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon.
What are the types of portfolios?
Art, graphic design, photography, writing, investment, teaching, etc.
How do you create a digital portfolio?
Use online platforms like Behance, Dribbble, or create a personal website.
What is a professional portfolio?
A portfolio used to showcase professional skills and achievements to potential employers or clients.
How do you present a portfolio?
In a clean, organized, and professional manner, whether physical or digital.
What is portfolio management?
The strategic selection and oversight of investments to achieve financial goals.


