20+ Position Paper Examples to Download
A position paper is a detailed piece of writing where you express your opinion on a specific topic. It is commonly used in academic settings and debate formats to outline your stance and the reasons behind it. This document not only presents your viewpoint but also supports it with facts and evidence to persuade others. Writing a position paper involves deep research to back your claims and understanding the opposing views to strengthen your arguments. Whether for school, work, or a conference, mastering the art of writing a position paper can significantly enhance your ability to communicate effectively and persuasively.
What is Position Paper?

Position Paper Examples Bundle
Position Paper Format
Title
Start with a clear and concise title that reflects the topic of your position paper.
Introduction
Begin with a brief introduction that outlines the issue at hand. Clearly state your position on the topic.
Thesis Statement
Include a thesis statement at the end of your introduction that summarizes your main point or stance.
Background
Provide context and background information to help readers understand the issue. Explain the significance of the topic and the main questions being addressed.
Argument Sections
Create several sections that each focus on a specific argument supporting your position. In each section, present evidence, facts, and data that bolster your viewpoint.
Counterarguments
Address potential counterarguments by acknowledging opposing views and refuting them with well-reasoned responses and evidence.
Conclusion
Summarize your main points and reinforce your thesis statement. Emphasize the importance of your position and suggest possible next steps or actions that readers can take.
References
List all sources you used to gather information and evidence for your position paper. Ensure they are cited properly according to the required style guide.
Position Paper Example
Position Paper Examples
Position Paper for Debate

Position Paper for Divorce

Position Paper for Death Penalty

More Examples on Position Paper
- Position Paper for Crisis Committee
- Position Paper for Grade 11
- Position Paper for Abortion
- Short Position Paper
- Policy Position Paper
- Position Paper MUN
Sample Position Paper

Position Paper Format

Student Position Paper Example

Position Paper Outline Example

Position Paper Template

College Position Paper Example

Mental Health Position Paper Example

Writing a Position Paper Example

Position Paper Guide Example

Simple Position Paper Example

Basic Position Paper Example

Health Position Paper Example

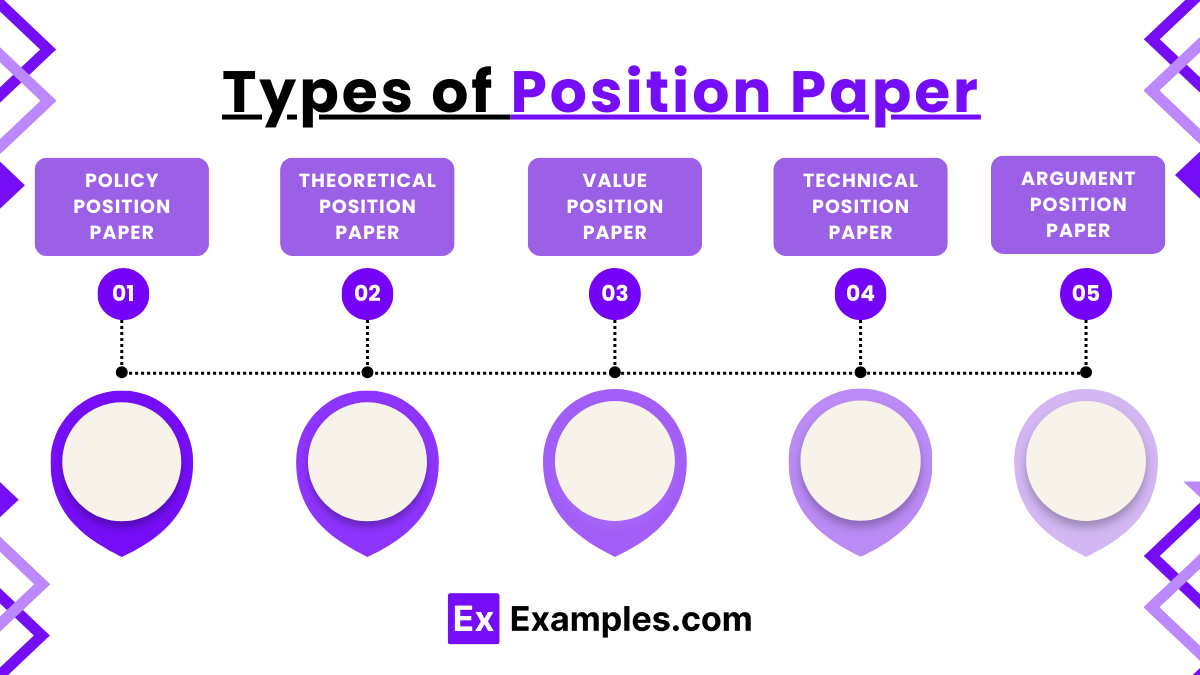
Types of Position Paper
Policy Position Paper
This type of position paper focuses on a specific issue or policy and presents a reasoned argument for adopting or changing that policy. It is often used in political, social, or governmental contexts.
Theoretical Position Paper
A theoretical position paper presents a theoretical framework or argument about a particular topic, often from a philosophical or academic standpoint. It aims to explain or analyze an issue based on theories or models.
Value Position Paper
This type addresses issues of ethics, morals, or values, providing a stance on the moral or ethical implications of an issue. It seeks to persuade the audience about the importance of adhering to certain values.
Scientific or Technical Position Paper
A scientific or technical position paper deals with complex topics and presents a viewpoint based on scientific research, data, and technical expertise. It is often used in fields like healthcare, engineering, and environmental science.
Argument Position Paper
An argumentative position paper presents a clear argument on a particular issue, supported by evidence, logic, and reasoning. The goal is to persuade the reader to accept the author’s viewpoint on the topic.
How to Write a Position Paper

- Choose Your Topic and Position:
- Start by selecting a clear and defined topic. Decide on the specific position you will advocate for in your paper. This involves understanding the various perspectives related to the topic and deciding where you stand.
- Conduct Thorough Research:
- Gather information from credible sources to support your position. This includes academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions. The more evidence you have to support your stance, the stronger your paper will be.
- Outline Your Main Points:
- Organize your arguments logically. Create an outline that includes an introduction, where you state your thesis; the body, where you present your arguments and supporting evidence; and a conclusion, where you summarize and reinforce your position.
- Write the Draft:
- Start with a strong introduction to grab the reader’s attention and clearly present your thesis statement. In the body, develop each argument coherently, always linking back to your main thesis. Use the conclusion to restate your position strongly, summarizing your arguments and suggesting possible implications or actions.
- Review and Revise:
- After writing your first draft, take time to revise and refine your paper. Check for logical flow and consistency in your arguments. Ensure your evidence is cited correctly and your writing is clear and concise. It can also be helpful to have someone else review your paper to catch any errors or unclear points you may have missed.
Tips for Writing a Position Paper
- Define Your Position Clearly: Start by clearly stating your stance on the topic. This helps set the direction for your arguments and ensures that your readers understand your perspective from the beginning.
- Research Thoroughly: Support your arguments with solid evidence. Use credible sources like scholarly articles, books, and trusted websites to gather facts, statistics, and expert opinions.
- Organize Your Arguments Logically: Structure your paper in a clear, logical manner. Start with the strongest arguments and use each paragraph to address a single point. This helps maintain a coherent flow and makes your paper more convincing.
- Address Counterarguments: Strengthen your position by acknowledging and refuting opposing views. This shows that you have considered multiple perspectives and are prepared to defend your stance against criticism.
- Revise and Proofread: After writing your draft, review your work for any errors or weak points. Check for grammatical mistakes, unclear statements, and ensure that all your citations are correct. Revising helps polish your paper and enhances its overall quality.
FAQs
Why write a position paper?
It helps you clarify your stance, argue your point, and persuade others of your viewpoint.
What should be included in a position paper?
Include a clear position statement, supporting arguments, counterarguments, and a concise conclusion.
How long should a position paper be?
Typically, it ranges from 1-2 pages, focusing on quality and conciseness over length.
Can I use first-person in a position paper?
It’s generally best to use third-person to maintain formality and objectivity, unless first-person is specifically requested.
How do I start a position paper?
Begin with a compelling introduction that outlines your main thesis and grabs the reader’s attention.


