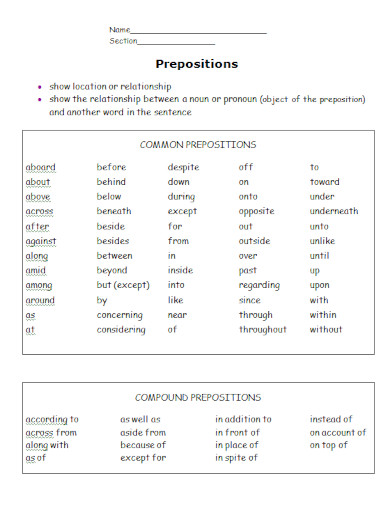
110+ Preposition Examples
We use different types of words in our everyday communication and conversations, each with its intricate uses and interpretations. One of the most common and important types of words we use every day is called prepositions.
What is a Preposition? – Definition
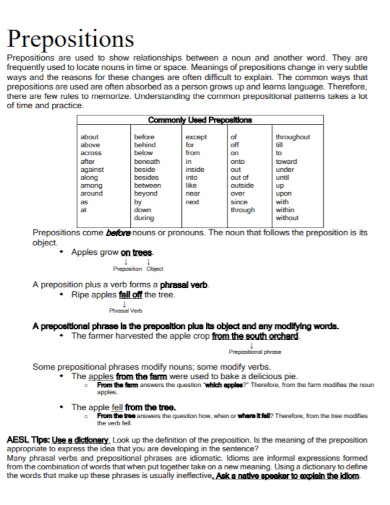
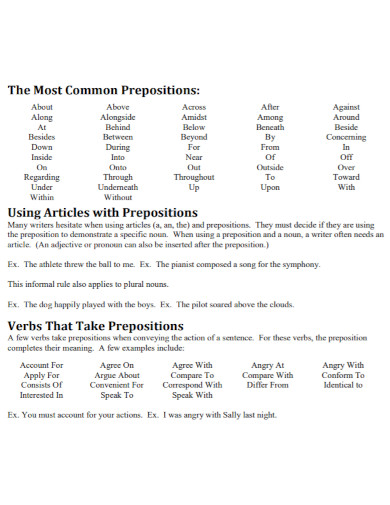
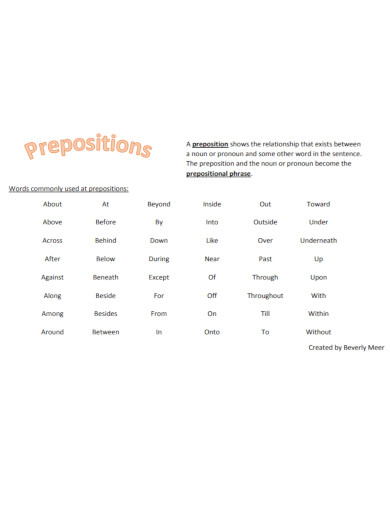
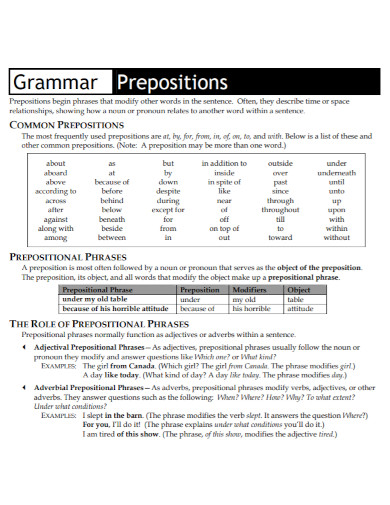
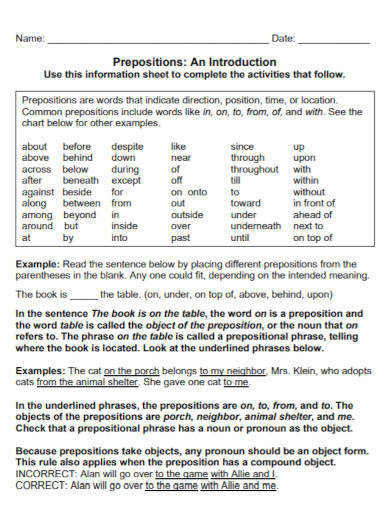
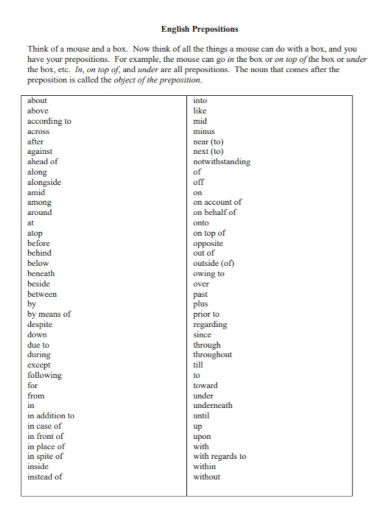
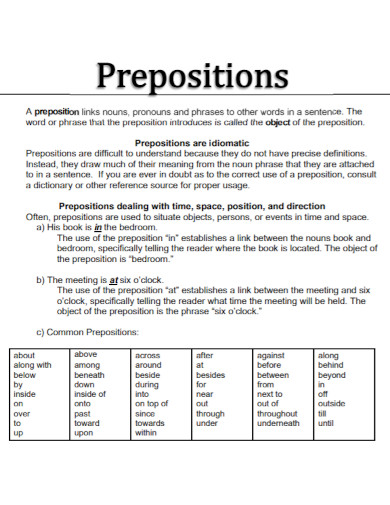
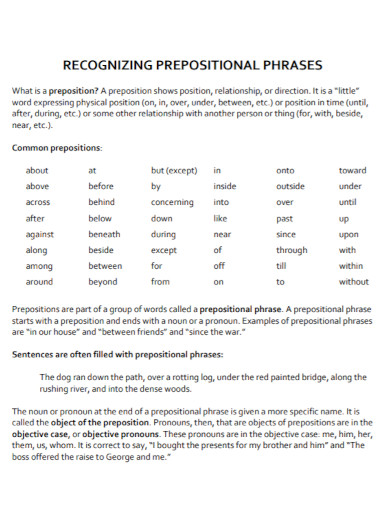
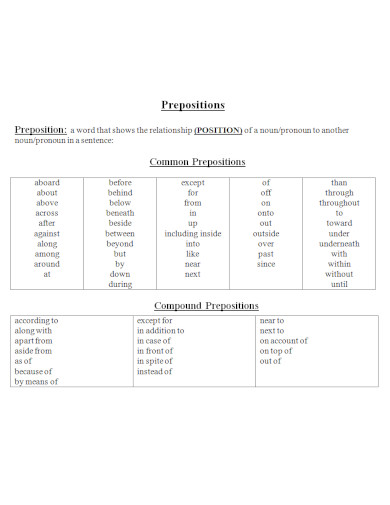
A preposition is a word that links nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. It typically indicates the temporal, spatial, or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence as in “The book is on the table” or “She lives near the school.” Prepositions are essential for providing additional details and context in sentences, such as location, direction, time, and manner. They help to create clear and concise sentences by showing how different parts of a sentence are related to each other
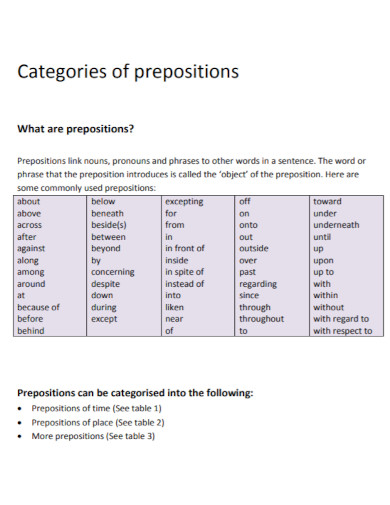
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions are versatile words that link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other parts of a sentence, indicating relationships like time, place, direction, and more. Here are the main types of prepositions:
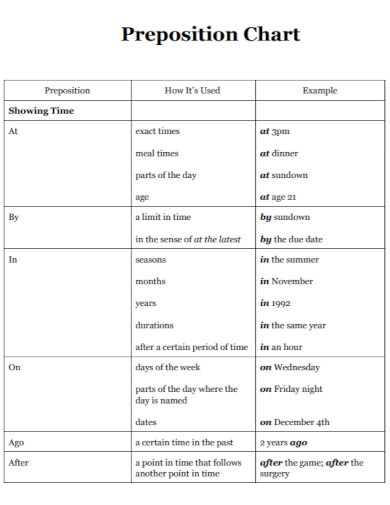
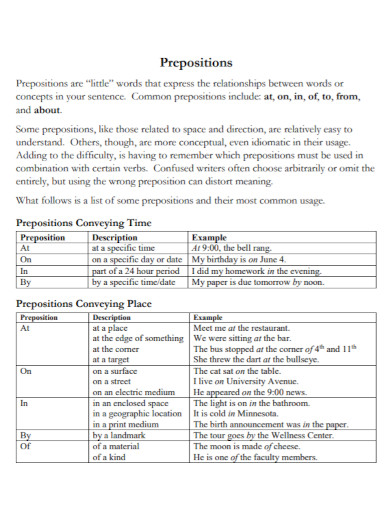
1. Prepositions of Time
These prepositions indicate when something happens. Common examples include at (precise times), on (days and dates), and in (months, years, centuries, and long periods).
- Example: We will meet at 5 PM, on Friday, in October.
2. Prepositions of Place
These prepositions show the location or position of something. Key words are at (point locations), on (surfaces), and in (enclosed spaces).
- Example: The book is on the table in the library at the university.
3. Prepositions of Direction/Movement
These indicate the direction in which something or someone moves. Examples include to (towards a place), from (origin of movement), and through (passing from one side to the other).
- Example: She walked from the store to her house through the park.
4. Prepositions of Agent
These prepositions connect a noun to the doer of an action, usually following passive voice constructions. The most common is by.
- Example: The novel was written by the famous author.
5. Prepositions of Instrument
These indicate the tool or means by which something is done, often including with and without.
- Example: He cut the paper with scissors.
6. Prepositions of Manner
These prepositions describe how something is done and include words like with, in, and on.
- Example: She speaks with enthusiasm.
7. Prepositions of Possession
These show ownership or possession and include of.
- Example: The cover of the book is blue.
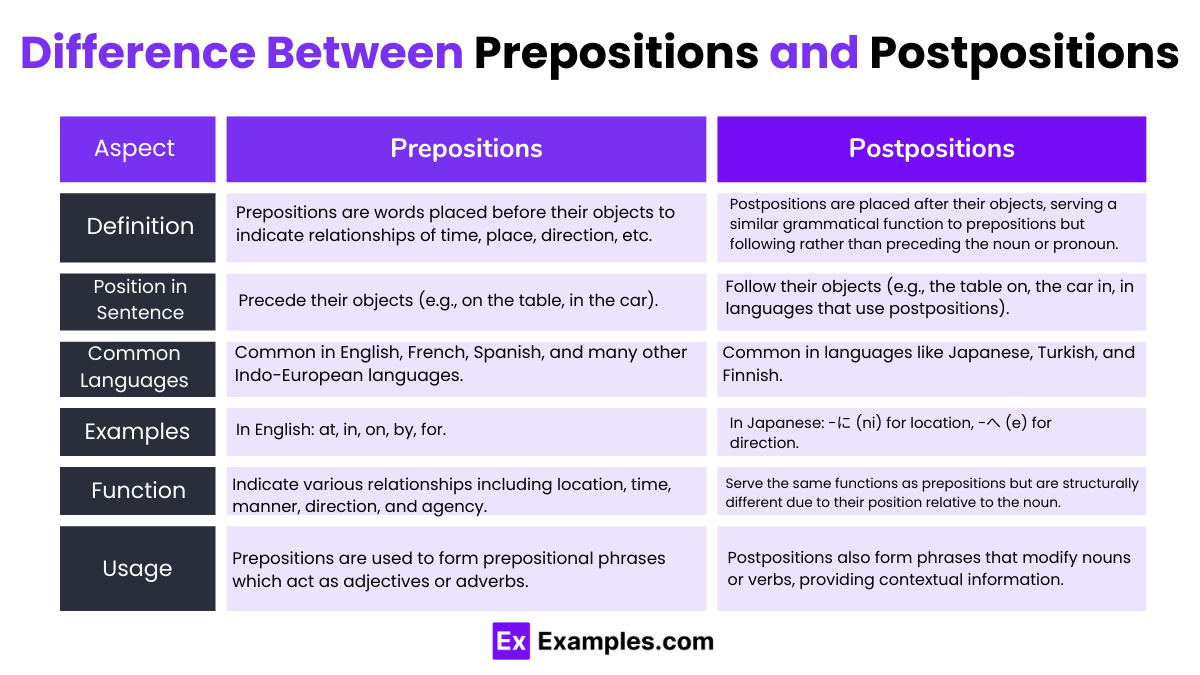
Difference Between Prepositions and Postpositions
| Aspect | Prepositions | Postpositions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prepositions are words placed before their objects to indicate relationships of time, place, direction, etc. | Postpositions are placed after their objects, serving a similar grammatical function to prepositions but following rather than preceding the noun or pronoun. |
| Position in Sentence | Precede their objects (e.g., on the table, in the car). | Follow their objects (e.g., the table on, the car in, in languages that use postpositions). |
| Common Languages | Common in English, French, Spanish, and many other Indo-European languages. | Common in languages like Japanese, Turkish, and Finnish. |
| Examples | In English: at, in, on, by, for. | In Japanese: -に (ni) for location, -へ (e) for direction. |
| Function | Indicate various relationships including location, time, manner, direction, and agency. | Serve the same functions as prepositions but are structurally different due to their position relative to the noun. |
| Usage | Prepositions are used to form prepositional phrases which act as adjectives or adverbs. | Postpositions also form phrases that modify nouns or verbs, providing contextual information. |
Common Mistakes with Prepositions
Prepositions are small words with significant impact on the clarity and correctness of your sentences. Here are some common mistakes people make when using prepositions:
1. Incorrect Preposition Choice
- Mistake: Interested on learning.
- Correct: Interested in learning.
Choosing the wrong preposition can change the meaning of a sentence or make it grammatically incorrect. Each verb, noun, or adjective is often followed by a specific preposition.
2. Using Unnecessary Prepositions
- Mistake: Where are you at?
- Correct: Where are you?
Sometimes, especially in spoken English, extra prepositions are added where they aren’t needed. This can make sentences sound informal or incorrect in written form.
3. Omitting Needed Prepositions
- Mistake: She is married with a doctor.
- Correct: She is married to a doctor.
Leaving out a necessary preposition can lead to confusion or a sentence that sounds incomplete or awkward.
4. Confusing Prepositions with Similar Meanings
- Mistake: She arrived to the airport late.
- Correct: She arrived at the airport late.
Words like “in” and “on,” or “at” and “to,” have similar meanings but are used in different contexts. Mixing them up is a common error.
5. Using the Wrong Preposition in Phrasal Verbs
- Mistake: Look after the meaning.
- Correct: Look up the meaning.
Phrasal verbs (a combination of a verb and a preposition or adverb) are tricky because their meanings can’t always be guessed from the meanings of the individual words. Using the wrong preposition changes the verb’s meaning entirely.
6. Prepositions in Idiomatic Expressions
- Mistake: At one’s wits’ end.
- Correct: At one’s wit’s end.
Prepositions often appear in idiomatic expressions, where their use does not align with their standard meanings. Learning these expressions as whole phrases is necessary to avoid mistakes.
7. Confusing Prepositions of Time and Place
- Mistake: I have been waiting since three hours.
- Correct: I have been waiting for three hours.
Prepositions of time (like “at,” “on,” “in”) and place (like “at,” “in,” “on”) follow specific rules. Mixing them up is a common source of error.
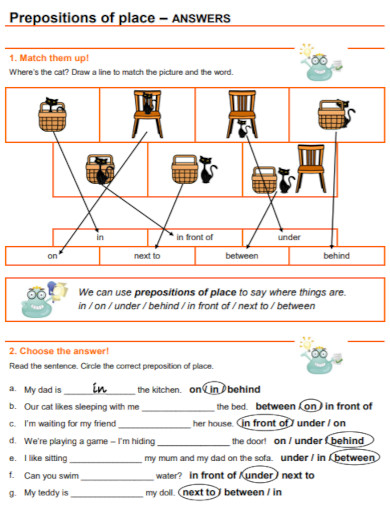
Prepositions – Place
| Preposition | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| at | Indicates a specific point or location. | She is at the entrance. |
| on | Used for surfaces. | The book is on the table. |
| in | Indicates an enclosed space. | They are waiting in the room. |
| above | Higher than something else, but not directly over it. | The picture hangs above the fireplace. |
| below | Lower than something else. | The village is below the mountain. |
| beside | Next to or at the side of. | The bank is beside the supermarket. |
| between | In the space that separates two points or objects. | The park is between the two buildings. |
| under | Directly below something else. | The cat is sleeping under the table. |
| behind | At the back of. | The parking lot is behind the building. |
| in front of | The area before or ahead of something. | The car is parked in front of the house. |
| near | Close to. | The restaurant is near the museum. |
| across from | On the opposite side of. | She lives across from the school. |
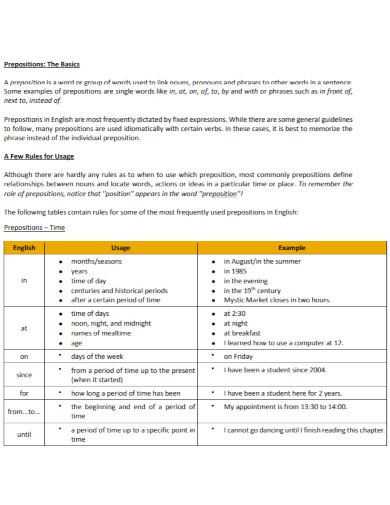
Prepositions – Time
| Preposition | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| at | For precise times | We will meet at 5 PM. |
| on | For days and dates | The meeting is scheduled on Monday. |
| in | For months, years, seasons, and parts of the day | She was born in July, in 1990, in the morning. |
| for | Duration of time | He studied for two hours. |
| since | A point in time in the past until now | I have been waiting here since 3 o’clock. |
| by | A deadline or the latest time by which something should be completed | The project needs to be finished by Friday. |
| before | Earlier than a specific time | Please call me before you leave. |
| after | Later than a specific time | We decided to go for a walk after dinner. |
| during | Throughout the entire duration or in the course of | They will be on vacation during the summer holidays. |
| until/till | Up to a certain point in time | We waited until midnight. |
Preposion of Direction
| Preposition | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| to | Direction towards a specific point | She is going to the office. |
| from | Origin of a movement | He traveled from New York to Los Angeles. |
| into | Movement to the inside of a place | The cat jumped into the box. |
| out of | Movement from the inside to the outside | She walked out of the room. |
| toward(s) | Direction in the general vicinity of something | He walked towards the park. |
| onto | Movement to the top of a surface | The bird landed onto the branch. |
| off | Movement away from a surface | The cat jumped off the counter. |
| through | Movement from one side to the other side | They drove through the tunnel. |
| across | Movement from one side to the opposite side | She swam across the lake. |
| around | Movement in a circular direction | The dog ran around the tree. |
| over | Movement directly above something | The plane flew over the mountains. |
| under | Movement beneath something | The cat crawled under the bed. |
| along | Movement following the length of something | They strolled along the beach. |
| past | Movement beyond something | He walked past the library. |
| up | Movement in an upward direction | She climbed up the ladder. |
| down | Movement in a downward direction | He walked down the stairs. |
| between | Movement from one point to another, passing two or more others | She moved between the parked cars |
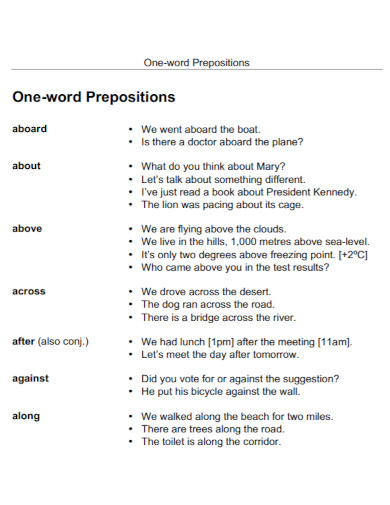
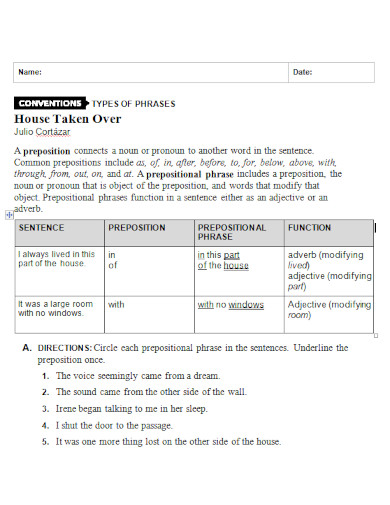
100+ Preposition Examples
1. Preposition Template
2. University Preposition
3. Preposition Chart
4. Grammar Preposition
5. Standard Preposition
6. College Preposition
7. Professional Preposition
8. Preposition Basics
9. Commonly Used Prepositions
10. Subjects, Verbs, And Prepositions
11. Preposition Notes
12. General Preposition
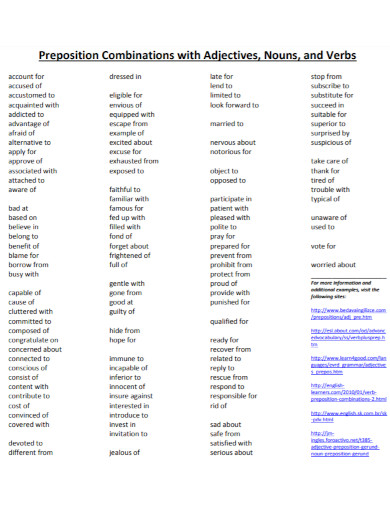
13. Common Preposition Combinations
14. Preposition Phrases
15. Articles and Prepositions
16. Prepositions in PDF
17. Preposition List
18. Preposition Sentences
19. Prepositional Phrases in PDF
20. Preposition Format
21. English Prepositions
22. Students Preposition
23. Modeling Preposition
24. Preposition Project
25. Formal Preposition
26. Common Prepositions
27. Prepositions in Applications
28. Preposition Notes in DOC
29. Preposition Worksheet
30. Prepositions With That-Clause
31. Preposition Exercises in PDF
32. Time Prepositions Two
33. The Preposition
34. Parts of Speech Preposition
35. Preposition Uses
36. Preposition Words
37. Grammar Prepositions in English
38. Prepositions with Examples
39. Preposition Information Sheet
40. Case Study Prepositions
41. Prepositions Game
42. Wayward Prepositions
43. Individual Prepositions
44. Simple Prepositions
45. Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases
46. Prepositional Phrase Worksheet
47. English Learning Prepositions
48. Preposition Selection
49. General Prepositional Phrases
50. Noun and Preposition
51. Distributional Models of Preposition
52. School Prepositions
53. Community College Prepositions
54. English Prepositions in PDF
55. Idiomatic Preposition
56. Preposition and Adjective Clauses
57. One Word Prepositions
58. Time Prepositions
59. Preposition of Place or Position
60. Little Preposition Words
61. Functional Prepositions in Acquisition
62. Readability Preposition
63. Prepositions Word List
64. Categories of Prepositions
65. Compound Preposition
66. Standard Preposition in PDF
67. Grammar Prepositions Worksheet
68. Preposition Learners
69. Technical English Prepositions
70. Prepositions Story
71. Location Based Prepositions
72. Basic Prepositional Logic
73. Convection Prepositions
74. Preposition and Nouns
75. Draft Preposition
76. Preposition Lessons
77. Professional Prepositions in DOC
78. Preposition Arbiter Use
79. Preposition Study
80. Contracted Preposition
81. Learning Activity Preposition
82. Preposition Word Bank
83. Objects of Prepositions
84. Students Preposition in PDF
85. Home Activity Preposition
86. Preposition Detective
87. Common Preposition in PDF
88. Idiomatic Use of Preposition
89. Prefixes as Prepositions
90. Preposition and Their Phrases
91. Difficult Preposition
92. Common and Compound Prepositions
93. Preposition Phrase in DOC
94. Preposition Template in DOC
95. Preposition Lesson Plan
96. Modifiers Preposition
97. Prepositional Phrase Map Worksheet
98. Preposition Football Game
99. Preposition Acquisition
100. Structure of Preposition
101. Vocabulary Preposition
How to Use a Preposition in One’s Sentence
Well-used prepositions can increase the overall quality of the sentence you will use them on. Be sure to use the proper preposition as each of these modifiers have different meanings and uses.
Step 1: Select a Sentence Structure
Begin by selecting a sentence structure you will use the preposition on. These sentence structures range from simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Step 2: Outline the Sentence
Outline the overall structure of the sentence by listing down the individual parts of the whole sentence. This outline will help provide a salient direction you can easily follow.
Step 3: Choose a Preposition
You must choose a preposition that will establish the connection or status of the two nouns or pronouns the preposition will refer to. If you need a reference you may use any list of prepositions you can find on the internet.
Step 4: Create the Sentence
You must now create the sentence using the outline and the preposition you have chosen for your sentence. If you want to create more sentences, you may follow steps one to four until you are satisfied.
FAQs
What Are the 8 Most Common Prepositions?
The 8 most common prepositions are at, by, for, from, in, of, on, and with. These prepositions are fundamental in expressing relationships of place, time, cause, and possession in sentences, making them essential for daily communication.
How Do You Find a Preposition in a Sentence?
To find a preposition in a sentence, look for a word that connects a noun or pronoun to another word, indicating relationships such as time, place, direction, or manner. Prepositions usually precede a noun or pronoun, forming a prepositional phrase.
How Do You Know if TO is a Preposition?
To is a preposition if it precedes a noun or pronoun to show direction, destination, position, or purpose, forming a prepositional phrase (e.g., “go to the store”). If to is followed by a verb, it serves as part of an infinitive (e.g., “to run”), not as a preposition.
What Is Simple Preposition?
A simple preposition is a single word that shows the relationship between two elements in a sentence, typically indicating time, place, direction, or manner. Examples include at, by, for, in, of, on, and with. These prepositions are straightforward and lack the complexity of compound or phrasal prepositions.
What Is the Golden Rule of Prepositions?
The golden rule of prepositions is that they should always precede a noun or pronoun to indicate a relationship, never ending a sentence with a preposition in formal writing. However, in everyday speech and informal writing, ending sentences with prepositions is commonly accepted.
What Is Appropriate Preposition?
An appropriate preposition is the correct preposition needed to convey the intended meaning in a phrase, based on standard usage and idiomatic expressions. Choosing the right preposition is crucial for clarity and accuracy, as the wrong preposition can change the meaning of a sentence or make it grammatically incorrect
What are common everyday examples of prepositions we use in our day-to-day communications?
We use many prepositions in our day-to-day communications, primarily when we are referring to the locations of various common nouns, plural nouns, proper nouns, and other entities and objects. People commonly use these examples of prepositions, which are above, across, among, behind, below, against, down, from, in, on, off, up, under, within, and with.
Is the word “by” an example of a preposition?
The word “by” can fill in two roles depending on the context, theme, and tone of the situation. One of the most popular and common forms of the word “by” is its usage as a preposition, which denotes a specific location that is beside or at the side of a specific object, landmark, or place. People can also use the word “by” as an adverb when it has a different context. Therefore the word “by” is an example of a preposition.
Is the word “during” an example of a preposition?
Yes, the word “during” is an example of a preposition. Unlike most prepositions, people use the word “during” before a pronoun or a noun to relate to space and time rather than a specific location.
Prepositions are specific words that people use in their writing and speaking to establish a connection between various elements in a single output, When the person properly uses a preposition, the target audience will have little to no room for misunderstanding the connection between two words, elements, or pronouns.