6+ Project Proposal Examples to Download
In the business industry, there are projects that every organization must consider, such as building commercial establishments and assessing road widening. Whether in the construction, engineering, or computer science departments, having effective project management is substantial. But where do you begin? Performing the project tasks must be pen down to show various perspectives that will layout the entire plan. Therefore, you need to submit a clear and compelling project proposal to your client to present an overview of the structure and check common mistakes. Check out project proposal examples below for your basis.
What is Project Proposal?

Project Proposal Examples Bundle

Download Project Proposal Bundle
Project Proposal Format
Opening Remarks
Greeting: Begin with a respectful and professional greeting.
Example: “Good morning, everyone.” or “Dear colleagues and stakeholders,”
Introduction
Purpose: Briefly state the purpose of your proposal.
Example: “I am here today to present a project proposal that aims to address [the issue/problem].”
Objectives
Goals: Clearly outline the main objectives of the project.
Example: “Our primary objective is to [describe the goal] and achieve [desired outcome].”
Scope
Project Scope: Define the boundaries and specific areas the project will cover.
Example: “This project will focus on [areas of work] and will include [specific tasks or deliverables].”
Timeline
Schedule: Provide a high-level overview of the project’s timeline and key milestones.
Example: “The project is expected to begin on [start date] and conclude on [end date], with major milestones such as [milestone 1] and [milestone 2].”
Budget
Cost Estimation: Present the estimated budget for the project, including major expenses.
Example: “The estimated budget for this project is [amount], which covers [specific costs like labor, materials, etc.].”
Methodology
Approach: Outline the strategy or methods that will be used to execute the project.
Example: “We will implement [methodology/approach], using [tools or processes] to ensure efficiency and success.”
Acknowledgments
Support and Resources: Acknowledge the support and resources needed for the project.
Example: “We appreciate the support from [stakeholders, departments] and will rely on their expertise and resources.”
Closing Remarks
- Final Summary: Recap the key elements of the project proposal.
Example: “In summary, this project seeks to [restate objectives], with a clear plan to [overview of the process].”- Call to Action: Invite feedback or approval for the project to move forward.
Example: “We look forward to your feedback and support in bringing this project to fruition.”- Farewell: Close with a polite and professional farewell.
Example: “Thank you for your time and consideration.”
Project Proposal Example
Good morning, everyone,
I am here today to present a project proposal that aims to address [specific issue or opportunity].
First and foremost, I would like to outline our primary objectives. This project seeks to [objective 1] and [objective 2], with a focus on [key goal or mission].
Our scope for this project is carefully designed to include [areas of focus] and deliver [specific outcomes]. We aim to ensure that all tasks align with the overall mission and lead to impactful results.
In terms of timeline, the project will span [start date to end date], with key milestones including [milestone 1] and [milestone 2]. Each phase will be carefully monitored to ensure timely completion.
For the budget, we estimate a total of [amount], which covers [major expenses]. This includes [specific costs such as labor, materials, technology, etc.], allowing us to operate within a responsible and effective budget plan.
We will use [methodology or approach] as our primary strategy for implementing the project, ensuring efficiency and achieving our desired outcomes.
In conclusion, this project has great potential to [summary of impact or benefits], and we believe it will make a significant contribution to [target area or field].
Thank you all for your time and consideration. We look forward to your feedback and hope to receive your support in moving forward.
Short Project Proposal Example
Good morning, everyone,
I am here to present a project proposal aimed at addressing [specific issue].
Our main objectives are to [objective 1] and [objective 2], with a clear focus on [goal].
The project will cover [scope] and will be completed by [end date].
The estimated budget is [amount], covering [specific expenses]. We will follow [methodology] to ensure success.
In conclusion, this project will [summary of benefits]. We appreciate your feedback and support.
Thank you for your time and consideration.
Project Proposal For Students

Project Proposal For Business

Project Proposal For School

More Project Proposal Examples and Samples
6+ Project Proposal Examples
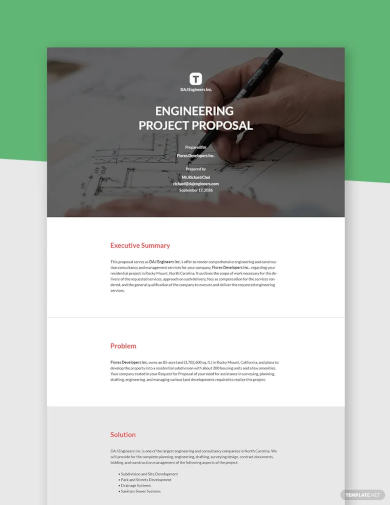
1. Engineering Project Proposal Template
2. Funding Project Proposal Template

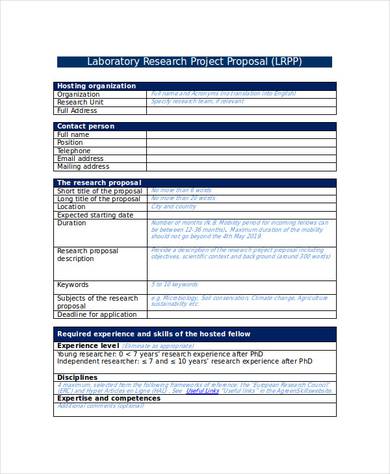
3. Laboratory Research Project Proposal
4. Video Production Project Proposal
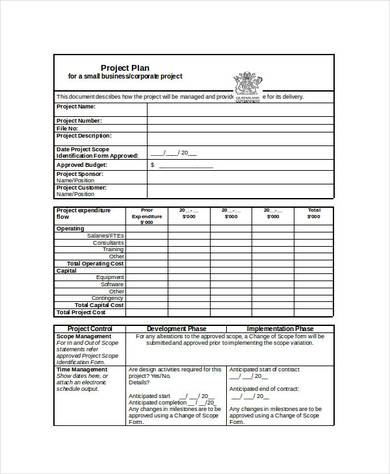
5. Small Business Project Proposal
6. Final Course Project Proposal
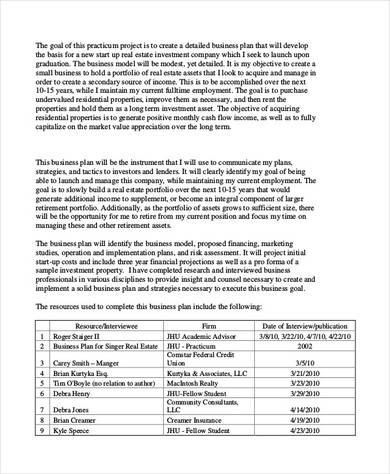
7. Real Estate Investment Project Proposal
How to Write Project Proposal?
Writing a project proposal involves clearly outlining the objectives, scope, methods, and benefits of a project, as well as justifying why it should be undertaken. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an effective project proposal:
Title Page
Project Title: Choose a concise, descriptive title for your project.
Prepared by: Include your name and organization.
Date: Specify the submission date.
Client Information: (If applicable) Include the name of the person or organization the proposal is being submitted to.Introduction
Background: Provide a brief context of the problem or opportunity the project aims to address.
Problem Statement: Identify the specific problem, challenge, or opportunity you are addressing.
Purpose of the Project: Explain why the project is necessary and how it aligns with any broader goals (organizational or community-based).Project Objectives
Define clear, measurable objectives that your project aims to achieve.
Use the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) for each objective.Scope of Work
Deliverables: List the specific outputs the project will produce.
Project Activities: Provide a detailed list of the key tasks or phases involved in the project. This will help set clear expectations for the work involved.Methodology or Approach
Approach: Describe the methods or approach that will be used to accomplish the project’s goals.
Tools and Techniques: If applicable, include any specific tools, technologies, or techniques that will be used.
Timeline: Outline the phases or steps in the project, along with start and end dates for each phase.Resources and Budget
Budget Breakdown: Include a detailed breakdown of the project’s costs, including labor, materials, equipment, and any other resources needed.
Funding: If applicable, explain where the funding will come from or if you are requesting funds from the proposal recipient.
Human Resources: Specify any team members involved and their roles.Risk Management
Identify any potential risks or challenges the project may face.
Provide strategies for mitigating these risks to ensure project success.Monitoring and Evaluation
Explain how you will track the progress of the project to ensure it stays on target.
Include measurable indicators to evaluate the project’s success.Expected Outcomes and Benefits
Describe the expected outcomes or results from the project.
Highlight how the project will benefit the client, organization, or community.Conclusion
Summarize the key points of the proposal, including why the project should be undertaken.
Reiterate the project’s goals, benefits, and impact.
Include a call to action, inviting the recipient to approve or discuss next steps.
Types of Project Proposal
There are several types of project proposals, each tailored to different needs, audiences, and purposes. Here are the main types of project proposals:
1. Solicited Project Proposal
- Description: A solicited proposal is created in response to a specific request (Request for Proposal, RFP) from a client, organization, or government entity.
- Purpose: The goal is to address the exact requirements outlined in the RFP and to compete with other proposals for selection.
- Example: A company submits a proposal for a new software system after a government agency requests bids for the project.
2. Unsolicited Project Proposal
- Description: An unsolicited proposal is not requested by the client or organization but is submitted proactively by the proposer to highlight a new idea, product, or service that could benefit the recipient.
- Purpose: To introduce new opportunities and convince the client or organization of its value.
- Example: A consultant presents an unsolicited proposal to a company, suggesting a plan to improve employee productivity through new training methods.
3. Pre-Proposal or Concept Proposal
- Description: A brief document that outlines a project idea and is often used to gauge interest before developing a full proposal.
- Purpose: To present the basic idea and determine if a full proposal should be developed.
- Example: A research team submits a concept proposal to a funding agency to get initial feedback on whether their project idea aligns with funding priorities.
4. Continuation Proposal
- Description: A continuation proposal is submitted when an ongoing project requires additional funding or time. It often reaffirms the project’s goals and provides progress reports.
- Purpose: To request further support for a project that is already underway and has proven successful.
- Example: A nonprofit organization submits a continuation proposal to extend a community health initiative after demonstrating positive results from the initial phase.
5. Renewal Proposal
- Description: A renewal proposal is submitted when a project’s original funding period has expired, and the proposer seeks to renew the project for another term.
- Purpose: To secure continued funding or resources for a project that has successfully met its objectives and aims to continue its efforts.
- Example: A research institution requests additional funding to continue studying environmental changes after completing the initial research phase.
6. Supplemental Proposal
- Description: A supplemental proposal is submitted to request additional resources or funding for a project beyond what was originally approved, typically due to unforeseen circumstances or new project developments.
- Purpose: To obtain extra resources or funding to cover additional costs or expand the scope of the project.
- Example: A construction company submits a supplemental proposal requesting additional funds to cover unexpected costs for materials.
Importance of Project Proposal
A project proposal is a crucial document that outlines the details of a proposed project. It serves multiple purposes and holds significant importance for various stakeholders involved. Here are some key points highlighting its importance:
- Clarity of Objectives
A project proposal clearly defines the project’s goals and objectives, ensuring all stakeholders understand the intended outcomes. - Feasibility Assessment
It allows for an assessment of the project’s feasibility, including financial, technical, and operational aspects, helping to identify potential challenges early on. - Resource Allocation
The proposal outlines the resources required, including budget, personnel, and materials, facilitating effective planning and allocation. - Stakeholder Engagement
A well-crafted proposal engages stakeholders by demonstrating the project’s value and relevance, fostering support and collaboration. - Risk Management
By identifying potential risks and outlining mitigation strategies, the proposal enhances the project’s resilience and increases the likelihood of success. - Decision-Making Tool
Project proposals serve as essential tools for decision-makers, providing the necessary information to evaluate and approve projects based on their merits and alignment with organizational goals. - Establishing Accountability
The proposal establishes accountability by defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring that all team members are aware of their contributions to the project.
Tips For Project Proposal
Creating an effective project proposal is essential for securing approval and support. Here are some valuable tips to consider when writing your proposal:
- Understand Your Audience
Tailor your proposal to the needs and interests of your audience. Consider their perspective and what information they find most relevant. - Be Clear and Concise
Use straightforward language and avoid jargon. Ensure your proposal is easy to read and understand by presenting information clearly. - Define Objectives and Goals
Clearly outline the project’s objectives and goals. Make them specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). - Provide a Detailed Budget
Include a comprehensive budget that details all expected costs. Justify each expense to demonstrate the project’s financial viability. - Include a Timeline
Provide a realistic timeline for project completion, highlighting key milestones and deadlines to show the project’s schedule. - Identify Potential Risks
Acknowledge potential risks and challenges the project may face. Include strategies for risk mitigation to reassure stakeholders. - Highlight Benefits
Emphasize the benefits and impact of the project. Clearly articulate how it aligns with the organization’s goals and contributes to its mission. - Use Visual Aids
Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to present data and information visually. This can help enhance understanding and retention.
FAQS
1. How do I determine the budget for my project proposal?
To determine the budget, list all potential expenses, including personnel, materials, equipment, and overhead costs. Research costs accurately and justify each expense based on project requirements.
2. How long should a project proposal be?
The length of a project proposal can vary based on complexity and audience requirements. Generally, it should be concise and focused, typically ranging from 5 to 15 pages.
3. How can I make my project proposal stand out?
To make your proposal stand out, focus on clear objectives, present compelling benefits, use engaging visuals, and demonstrate alignment with organizational goals. Tailor the content to your audience’s interests.
4. What are common mistakes to avoid in a project proposal?
Common mistakes include lack of clarity, vague objectives, insufficient detail in budget or timeline, ignoring potential risks, and failing to engage the audience. Always revise and seek feedback before submission.
5. What happens if my project proposal is rejected?
If your proposal is rejected, seek feedback from stakeholders to understand their concerns. Use this feedback to refine your proposal and address any shortcomings before resubmitting or proposing a new project.
6. How can I effectively manage project risks in my proposal?
Effectively manage project risks by identifying potential risks upfront, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies. This proactive approach shows stakeholders that you are prepared.
7. How do I follow up after submitting a project proposal?
Follow up with stakeholders a week or two after submission to inquire about their feedback and any questions they may have. Be proactive and open to discussions to address any concerns.
8. Is it necessary to include a conclusion in my project proposal?
Yes, a conclusion is important as it summarizes the key points of your proposal and reinforces the project’s significance. It provides a final persuasive statement to encourage approval.