59+ Proposal Examples to Download
A proposal is a vital tool for outlining your plans or suggestions, particularly in business, academia, or personal projects. It serves as a formal way to present ideas and initiate progress, whether you’re aiming to launch a new venture, apply for funding, or plan a collaboration. Crafting a clear and concise proposal helps communicate the purpose, steps, and potential benefits of your project, making it easier to gain support and approval from stakeholders or partners.
What is Proposal?
Proposal Format
Title Page
Include the proposal title, your name, date, and the recipient’s information.
Executive Summary
A brief overview of the proposal’s goals and the benefits of the proposed plan.
Problem Statement
Clearly define the problem you are addressing or the need for the project.
Proposed Solution
Describe your solution or the steps to take to address the problem.
Timeline
Outline the timeframe for implementing your solution, including key milestones.
Costs and Budget
Detail the expected costs and provide a budget breakdown.
Conclusion
Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of approving the proposal.
Proposal Example
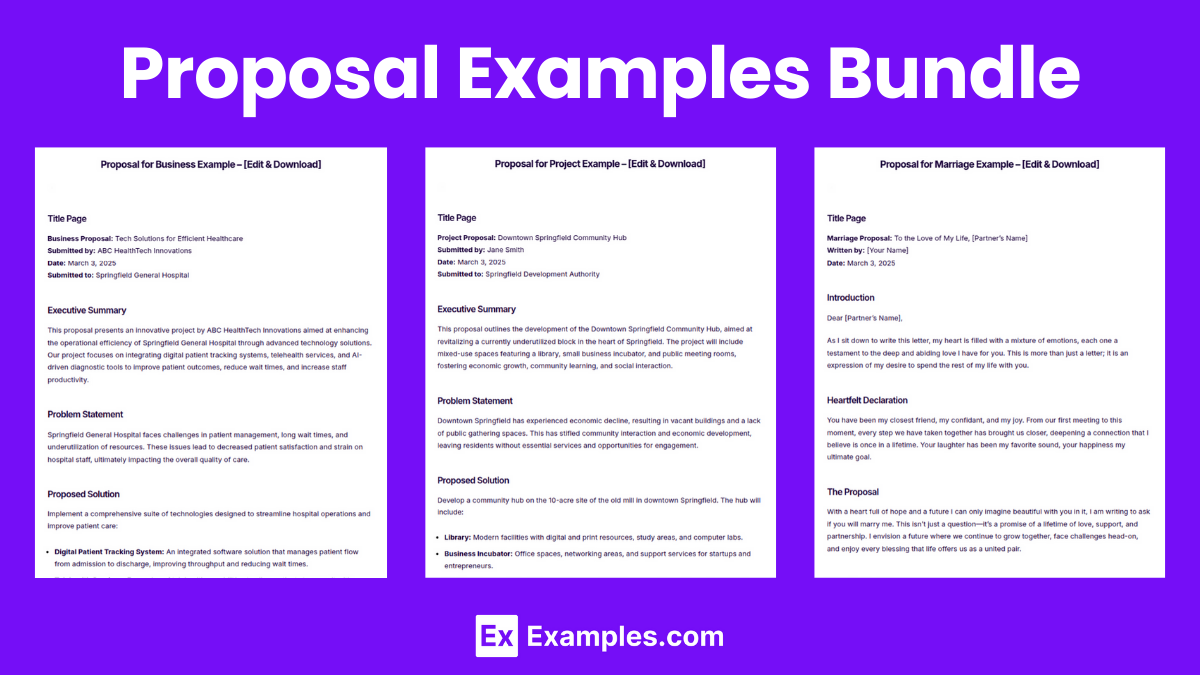
Proposal Examples
Proposal for Project

Proposal for Business

Proposal for Marriage

More Examples on Proposal
- Proposal for Funding
- Proposal for Partnership
- Proposal for Settlement Florida
- Proposal for Work
- Proposal for Services
- Proposal for Students
- Proposal for Research Paper
- Proposal for Event
- Simple Project Proposal
- Grant Proposal
- Sponsorship Proposal
- Technical Proposal
- Modest Proposal
- Indecent Proposal
Proposal Samples
Sample Proposal Example

Project Proposal Example

Research Proposal Template

Nursing Research Proposal Template

Research Proposal Format Example

IT Project Proposal Template

Funding Project Proposal Template

Sample Proposal Form Example

Thesis Proposal Template

Dissertation Proposal Template

Free Proposal Application Example
Simple Budget Proposal Template

Grant Budget Proposal Example

Annual Conference Proposal

Cultural Event Proposal Example

New Event Proposal Example

Technical and Financial Proposal Example

Technical Budget Proposal

Database System Proposal Example

Grant Proposal Form Example

Digital Marketing Proposal

Sales Marketing Proposal
Training Program Proposal

Types of Proposals
1. Business Proposal
A business proposal is a formal document that presents a business idea, project, or partnership opportunity to potential investors, clients, or stakeholders. It outlines the objectives, benefits, and financial aspects of the proposed business plan.
2. Project Proposal
A project proposal is used to seek approval and funding for a specific project. It includes project objectives, scope, methodology, timeline, and expected outcomes. This type of proposal is common in corporate, nonprofit, and government sectors.
3. Research Proposal
A research proposal is a document that outlines a planned research study, including its objectives, research questions, methodology, and expected contributions. It is often submitted for academic, scientific, or institutional funding.
4. Funding Proposal
A funding proposal is used to request financial support from investors, grant agencies, or institutions. It includes project details, budget breakdown, and expected impact to justify the need for funding.
5. Sponsorship Proposal
A sponsorship proposal is created to attract sponsors for events, programs, or initiatives. It highlights the benefits for the sponsor, such as brand visibility and audience engagement, in exchange for financial or in-kind support.
6. Partnership Proposal
A partnership proposal is used to propose a collaboration between two or more organizations. It outlines the mutual benefits, shared resources, and expected outcomes of the partnership.
7. Marketing Proposal
A marketing proposal is a strategic document that presents a marketing plan for a product, service, or brand. It includes advertising strategies, target audience analysis, and budget requirements to achieve business goals.
8. Training Proposal
A training proposal outlines a plan for employee or organizational development through workshops, courses, or skill-building programs. It includes training objectives, content, delivery methods, and expected benefits.
How to Write a Proposal

Define Your Objective
Clearly state the purpose of your proposal and what you aim to achieve. Make sure the objective is specific and aligns with the needs of the recipient.
Understand Your Audience
Tailor the proposal to the interests and expectations of the recipient. Knowing their priorities and concerns will help in making the proposal more persuasive.
Provide a Clear Structure
Organize your proposal with essential sections, including an executive summary, problem statement, proposed solution, timeline, and budget. A well-structured proposal is easier to read and understand.
Use Concise and Persuasive Language
Write in a clear, professional, and compelling manner. Avoid unnecessary jargon and focus on delivering your message effectively to keep the reader engaged.
Include Supporting Data
Use facts, statistics, or case studies to back up your claims. Providing evidence increases credibility and helps justify why your proposal should be accepted.
Review and Edit Before Submission
Carefully proofread your proposal to eliminate any errors, inconsistencies, or missing details. A well-polished proposal enhances professionalism and improves the chances of approval
Tips for Writing a Proposal
- Be Clear and Concise – Use simple, direct language to communicate your ideas effectively.
- Know Your Audience – Tailor the proposal to the recipient’s needs, expectations, and interests.
- Use a Professional Format – Organize your proposal with headings, bullet points, and a logical flow.
- Provide Evidence and Data – Support your claims with facts, statistics, and real-world examples.
- Focus on Benefits – Highlight how your proposal will solve a problem or bring value to the recipient.
- Proofread and Edit – Check for errors, inconsistencies, and clarity before submitting your proposal.
Guidelines for Writing a Proposal
- Understand the Purpose – Clearly define the goal of the proposal and what you want to achieve.
- Follow a Structured Format – Include key sections such as an introduction, problem statement, proposed solution, timeline, and budget.
- Use Simple and Professional Language – Avoid jargon and make the content easy to understand for the reader.
- Be Persuasive and Data-Driven – Support your proposal with facts, figures, and logical reasoning to strengthen credibility.
- Keep It Concise and Relevant – Stick to essential details and avoid unnecessary information that may distract from the main points.
- Review and Revise – Proofread for clarity, coherence, and errors before submitting to ensure a polished final document.
FAQs
1. Define a Proposal.
A proposal is a written plan or a suggestion put forward for consideration by others. It is mostly formal. Business proposals are sent to the prospective client to obtain specific jobs. Also used by a seller, who writes to a buyer to know if he/she wants to buy certain services/goods from the seller.
2. Why is a Proposal important?
Proposals are a way to pitch an idea and state your requirements. It is important because it provides information in writing and you can act knowing the implications of your choices and decisions. Proposals help in making a structured and logical argument to lay down every idea and point in your favor.
3. What should a Proposal cover?
Proposals must cover the following:
- Introduction: a brief overview of the issues, costs, and benefits
- Issue: The subject, the reason for the proposal, the main argument, etc.
- Solutions: Step-by-step plan, potential obstacles and how to overcome them
- Qualifications: Your personnel requirement, experience, etc.
- Conclusions: Add the budget, benefits and reinforce your final point.
4. What makes a Good Proposal?
Preparing a winning proposal means that you are writing for the client and are proving a clear solution to their issues. Not every proposal you make is accepted by the client, so make sure that you make it from the point of view that is beneficial to the client.
5. What is the best way to conclude a Proposal?
The best way to conclude a proposal can be:
- To summarize the key points of your proposal
- Focus on why action is needed
- Emphasize the benefits the action provides
- Add bullet points of essential information
- Add verbal highlights of your key benefits
- Close on a positive note and ask them to take action.


