16+ Quota Sampling Examples to Download
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling technique used in market research and social science studies. It involves dividing a population into exclusive subgroups and setting quotas for each to ensure the sample represents specific characteristics. Researchers fill these quotas by selecting participants based on convenience or judgment until each quota is met. This method aims to reflect the diversity of the population, making it useful when time and budget constraints limit the feasibility of random sampling techniques.
What Is Quota Sampling?
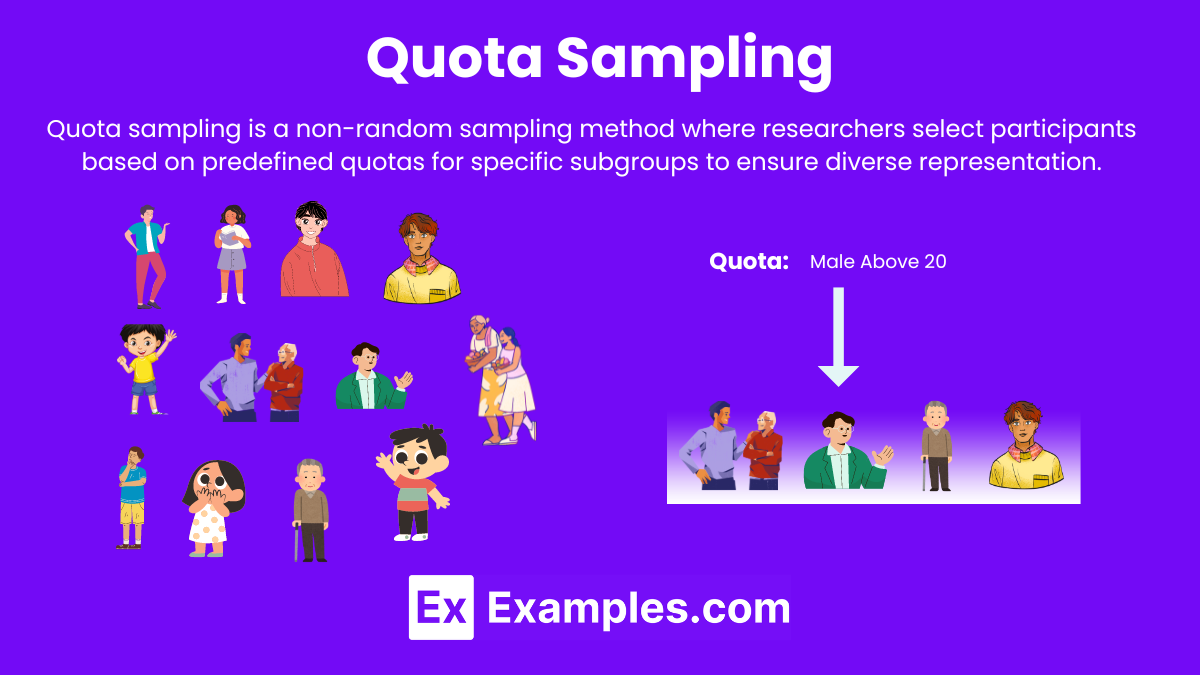
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method where researchers select participants to meet predefined quotas for specific subgroups, ensuring the sample reflects certain population characteristics.
Examples of Quota Sampling
- Market Research: Surveying 200 shoppers in a mall, ensuring 100 men and 100 women are included.
- Political Polling: Interviewing 500 voters with quotas for age groups, ensuring equal representation from different age categories.
- Healthcare Studies: Selecting 50 participants from each income bracket to study healthcare access disparities.
- Education Research: Ensuring equal numbers of students from public and private schools in a study on academic performance.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering feedback from 300 customers, divided equally among different service usage tiers.
- Employee Satisfaction: Surveying 100 employees with quotas for different departments to ensure comprehensive representation.
- Product Testing: Selecting 20 participants from each age group to test a new tech gadget.
- Social Media Analysis: Ensuring equal representation from users of various social media platforms for a study on online behavior.
- Tourism Studies: Surveying tourists from different countries to understand international travel patterns.
- Consumer Behavior: Ensuring equal participation from urban and rural areas in a study on purchasing habits.
- Public Health Research: Interviewing 200 smokers and 200 non-smokers to study the impact of smoking on health.
- Transportation Studies: Surveying commuters with quotas for different modes of transportation, like buses, trains, and cars, to analyze payment preferences and behaviors.
- Brand Loyalty: Ensuring equal numbers of customers who prefer different brands in a study on brand loyalty.
- Media Consumption: Surveying viewers with quotas for different types of media, such as TV, online streaming, and radio, to inform advertising and marketing strategies.
- Environmental Research: Selecting participants equally from urban, suburban, and rural areas to study environmental awareness.
- Financial Behavior: Ensuring equal representation from various income levels in a study on saving and investment habits to better understand cash flows.
- Dietary Habits: Surveying individuals with quotas for different dietary preferences, like vegetarian, vegan, and omnivore diets.
Types of quota sampling
- Controlled Quota Sampling: Researchers set strict quotas for specific characteristics such as age, gender, income, etc., and ensure these quotas are filled exactly.
- Uncontrolled Quota Sampling: Researchers set quotas for specific characteristics but allow for some flexibility, filling quotas based on convenience.
- Proportional Quota Sampling: Quotas are set to match the proportion of each subgroup in the population, ensuring the sample mirrors the population’s diversity.
- Non-Proportional Quota Sampling: Quotas are set without regard to the population’s actual proportions, focusing on ensuring adequate representation of certain subgroups to better align with the objectives of a nonprofit annual budget.
- Two-Stage Quota Sampling: Initially, broad quotas are set for major categories, and then sub-quotas are established within these categories for more detailed characteristics.
Characteristics of quota sampling
- Non-Probability Method: Participants are selected based on specific quotas rather than random sampling, making it a non-probability sampling technique.
- Predefined Quotas: Researchers establish quotas for specific characteristics (e.g., age, gender, income) to ensure the sample represents these attributes.
- Convenience Selection: Within each quota, participants are often chosen based on convenience or judgment rather than random selection.
- Ensures Diversity: Quota sampling aims to include diverse subgroups in the sample, reflecting the population’s heterogeneity.
- Time and Cost-Efficient: This method is generally quicker and less expensive than random sampling, making it suitable for studies with time and budget constraints, and ideal for analyzing marketing evolution.
Quota Sampling Process
Step 1: Identify Population Subgroups
Determine the key characteristics (e.g., age, gender, income) of the population that need representation in the sample.
Step 2: Set Quotas
Establish quotas for each subgroup based on the desired proportions or total number of participants for each characteristic.
Step 3: Design Survey or Study
Develop the survey or research instrument, ensuring it can capture the necessary data from participants within each quota.
Step 4: Select Participants
Choose participants based on convenience or judgment to fill the predefined quotas, ensuring that each subgroup is adequately represented.
Step 5: Collect Data
Gather data from the selected participants, ensuring that the quotas are met accurately to achieve a representative sample for the study.
When to use quota sampling
Quota sampling is best used in research situations where time and budget constraints prevent the use of random sampling methods. It is particularly useful when researchers need to ensure representation from specific subgroups within a population, such as age, gender, or income levels, to enhance the relevance and applicability of the study findings. This method is often employed in market research, social science studies, and public opinion polling where precise demographic representation is critical. Additionally, quota sampling is advantageous when the population is diverse, and the researcher wants to ensure that all significant subgroups are included to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Quota sampling is especially beneficial in a budget plan, as it helps manage cash flows efficiently by controlling costs and resources. However, it is important to note that quota sampling may introduce selection bias, so it should be used with caution when the research requires high generalizability.
Difference between convenience sampling and quota sampling
| Aspect | Convenience Sampling | Quota Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Participants are selected based on ease of access and proximity to the researcher. | Participants are selected to meet predefined quotas for specific subgroups. |
| Purpose | To quickly gather data with minimal effort and cost. | To ensure representation of specific subgroups within the sample. |
| Selection Criteria | Based on convenience, without specific subgroup targets. | Based on predefined quotas for characteristics like age, gender, income, etc. |
| Representation | May not accurately represent the entire population. | Aims to represent specific subgroups, enhancing the diversity of the sample. |
| Bias | High risk of selection bias due to non-random selection. | Reduced bias for subgroups included in quotas, but overall bias can still exist. |
| Usage | Suitable for exploratory research or preliminary data collection. | Suitable when specific demographic representation is necessary. |
| Data Accuracy | Lower accuracy due to potential lack of representativeness. | Higher accuracy for included subgroups but still subject to overall sampling bias. |
Advantages and disadvantages of quota sampling
Advantages:
- Quota sampling is quicker and less expensive than probability sampling methods, making it ideal for studies with limited resources.
- By setting quotas for specific subgroups, researchers can ensure that the sample includes important demographic segments of the population.
- This method is straightforward to implement, as it does not require a complete list of the population or random selection methods.
Disadvantages:
- The non-random selection process can introduce selection bias, as participants are chosen based on convenience within each quota.
- The results from quota sampling may not be generalizable to the entire population due to potential biases in the sampling process.
- The researcher’s judgment in selecting participants can affect the sample’s composition, leading to subjective biases.
How are quotas determined in quota sampling?
Quotas are determined based on characteristics such as age, gender, income, or other relevant attributes that researchers want to represent in the sample.
What is the main advantage of quota sampling?
The main advantage is that it ensures representation of specific subgroups, making the sample more diverse and relevant.
What is a disadvantage of quota sampling?
A key disadvantage is the potential for selection bias, as participants are not selected randomly.
How does quota sampling differ from random sampling?
Quota sampling uses specific quotas for selection, while random sampling selects participants entirely by chance, without any set quotas.
Can quota sampling be used for large populations?
Yes, quota sampling can be used for large populations, but the accuracy of representation depends on the quotas set.
What types of research commonly use quota sampling?
Quota sampling is commonly used in market research, social science studies, and public opinion polling.
Is quota sampling cost-effective?
Yes, quota sampling is generally more cost-effective than probability sampling methods.
Can quota sampling be combined with other sampling methods?
Yes, quota sampling can be combined with other methods, such as convenience sampling, to enhance data collection.
How do researchers select participants in quota sampling?
Participants are selected based on convenience or judgment to meet the predefined quotas.
What is a controlled quota sampling?
Controlled quota sampling involves setting strict quotas for specific characteristics and ensuring these quotas are filled exactly.