Which of the following numbers is a rational number?
√2
π
e
3/4


We use numbers a lot in our everyday lives; these numbers come in the form of the car’s current speed expressed in Miles per hour, or even the temperature of your surroundings. The numbers that we use often come in the form of rational numbers, due to their practical nature.
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction or ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. They include all the integers, fractions, and finite decimals, offering a comprehensive understanding of how numbers relate to each other in mathematics.
The best example of rational numbers is fractions, such as 1/2, 4/3, and −5/4. These represent precise values and demonstrate how dividing integers results in numbers that describe proportions, measurements, and many aspects of the real world.
Identifying rational numbers is key to understanding the vast landscape of mathematics. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction a/b of two integers, where a is the numerator, b is the denominator, and b≠0. This includes all integers, positive and negative fractions, and finite or repeating decimals. For example, 3/4, −2 (which is −2/1 ), and 0.75 are all rational because they can be written as fractions.
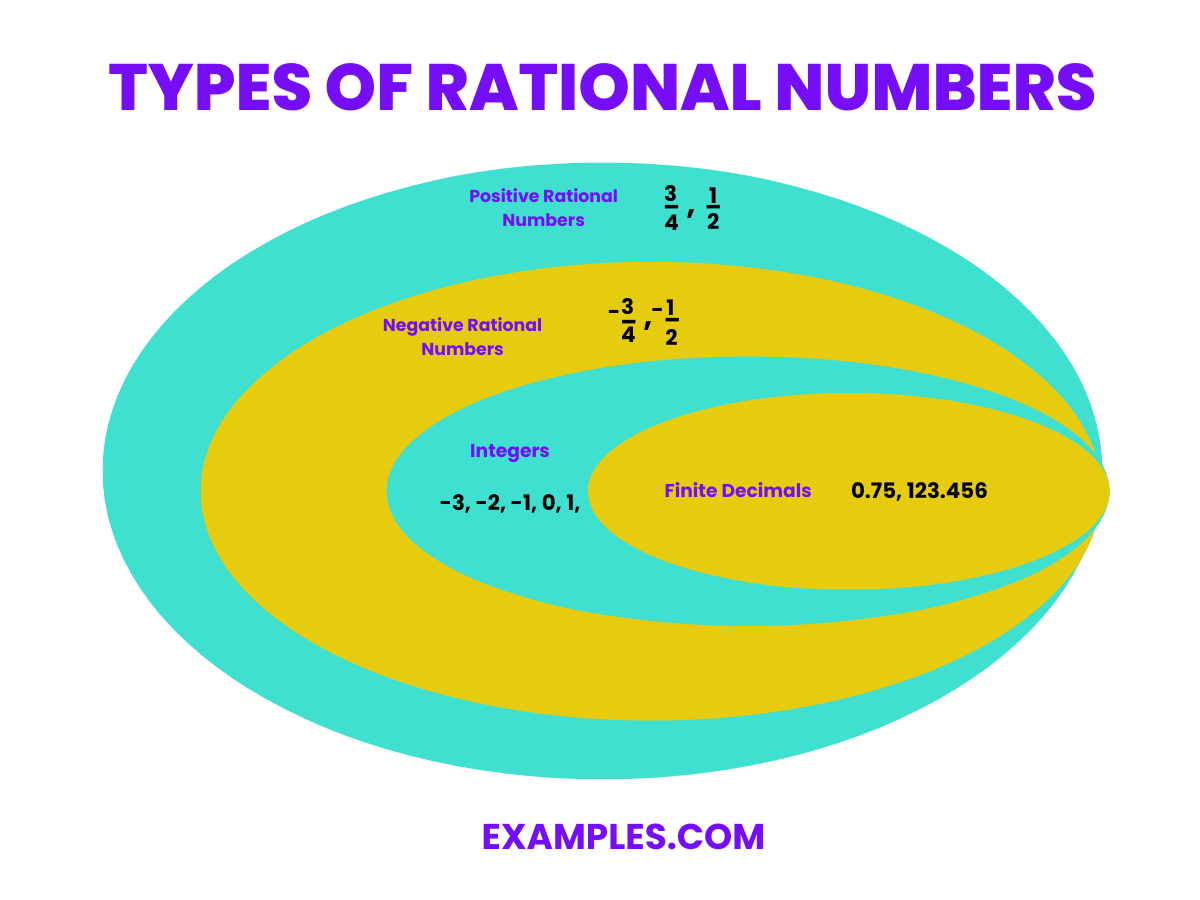
Rational numbers encompass various subsets, each with unique characteristics, yet all share the common trait of being expressible as a fraction.
The standard form of a rational number is expressed as a/b, where a and b are integers, and b is not zero. The number is in its simplest form when a and b have no common factors other than 1. For example, 8/12 simplifies to 2/3 in standard form, illustrating how rational numbers can be reduced to their most basic expression, making calculations and comparisons easier and more intuitive.
Rational numbers can be either positive or negative, indicating their position relative to zero on the number line. A positive rational number, such as 5/6, is greater than zero, located to the right of zero on the number line. A negative rational number, like −5/6, is less than zero, situated to the left of zero. This distinction is crucial for understanding the direction and magnitude of quantities in real-world and mathematical contexts.
Arithmetic operations on rational numbers—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division—follow specific rules. For addition and subtraction, the denominators must be the same; for example, 1/4+3/4=4/4=1.. Multiplication and division are straightforward, with 2/3×3/4=1/2and 4/5÷2/3=4/5×3/2=6/5. These operations allow rational numbers to be combined and manipulated in a variety of ways, supporting complex mathematical reasoning and problem-solving.
The multiplicative inverse of a rational number is another rational number that, when multiplied together, gives the product of 1. This concept is crucial for understanding divisions and solving equations in mathematics. For any non-zero rational number a/b, its multiplicative inverse is b/a. For example, the multiplicative inverse of 2/3 is 3/2, as 2/3×3/2=1. This principle supports the fundamental property of numbers in reciprocal actions.
Finding rational numbers between two rational numbers involves identifying or creating fractions that lie between them. A simple method is to average the two numbers. For instance, between 1/4 and 1/2, you can find 1/4+1/2÷2=3/8. Another method is to add the numerators and denominators of the given fractions separately and simplify if necessary. This technique ensures that there are infinitely many rational numbers between any two rational numbers, illustrating the density of rational numbers on the number line.
Rational numbers in decimal form are expressions of fractions as decimals. When a rational number is expressed as a decimal, it can either terminate (end) or repeat. For instance, 1/2=0.5 is a terminating decimal, while 1/3=0.3 is a repeating decimal, indicated by the overline. To convert a fraction to decimal, divide the numerator by the denominator using long division. This representation highlights the versatility of rational numbers, allowing for different but equivalent forms, and aids in various calculations and applications in real-life scenarios and mathematical problems.
Rational numbers are the set of all numbers that can be expressed as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers, and b is not zero. This includes integers (2/1=2), positive fractions (3/4), negative fractions (−5/6), and finite decimals which can be converted to fractions (0.75=3/4). Examples of rational numbers are 1/2, −4/3, 7 (which is 7117), and −2.5(=−52)−2.5(=2−5).
Adding and subtracting rational numbers involves finding a common denominator, then adding or subtracting the numerators. For instance, to add 1441 and 3883, convert them to have a common denominator: 1/4=2/8=8/2. Then, 2/8+3/8=5/8. Similarly, to subtract 3553 from 2332, you’d find a common denominator (in this case, 15), resulting in 61/5−91/5=−31/515/6−15/9=−15/3 or simplified to −1/5.
Multiplying rational numbers requires multiplying the numerators together and the denominators together. For example, 2/3×3/4=6/1. Dividing rational numbers involves flipping the second fraction (taking its reciprocal) and then multiplying. For instance, 3/4÷2/3=3/4×3/2=9/84/3÷3/2=4/3×2/3=8/9. These operations demonstrate how rational numbers interact under multiplication and division, always resulting in another rational number, provided that you’re not dividing by zero.
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed, denoted, and written down as whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. These numbers can be written down as square roots, as long as they result in a whole number. Square roots that result in infinite numbers are not considered rational numbers. This means not all numbers resulting from a square root are rational numbers. But the inverse is also true, indicating that not all numbers resulting from a square root are irrational numbers. If you want to check if the square root is a rational number then you must equate or solve the square root of a specific number.
Rational numbers have plenty of everyday uses, due to their practical nature. This practical nature sets rational numbers apart from irrational numbers. If you are still confused about rational numbers then you may preview and read any of the rational numbers examples, samples, templates, and PDFs.
Begin by writing down the number you want to distinguish. This will help you visualize all the numbers you will be working with. The more the numbers the easier it will be to discern them, if you write them down on a physical note or note-taking software.
If the number you are distinguishing or discerning is a fraction, you can simplify the fraction. Doing this will allow you to easily equate the fraction to a decimal or a whole number.
If the number is a square root, then you must simplify the square root to its most simple notation. Again just like the step above, it will help you equate the square root to a whole number.
After you have finished doing the necessary things you have to do, you can answer the equations needed to equate fractions and square roots to a whole number or decimal. For example, if you have written down 5/2 and ?16 you can equate these numbers to 2.5 and 4 respectively. This will help you distinguish the given numbers as rational numbers since they don’t equate to infinite numbers.
[/ns_row]
No, pi is not a rational number, this is because when pi is expressed in notation it ends up being an infinite number. All numbers resulting from an infinite number are considered irrational numbers because they cannot be expressed in fractional form.
Yes, all negative numbers are considered rational numbers. This is because all negative numbers can be expressed in fractional form, for example, -2 can be written as -2/1. This means that any negative number that does not result in an infinite number is considered a rational number.
Rational numbers are numbers that can be denoted as whole numbers, a fraction, and a decimal. These numbers have various uses in our everyday lives as most of the equations we deal with in our lives produce rational numbers. In conclusion, the concept of rational numbers can help us understand possible numbers that we can use in our everyday lives.
Text prompt
Add Tone
Types of Rational Numbers
How to Identify Rational Numbers
Which of the following numbers is a rational number?
√2
π
e
3/4
Which of the following fractions is in simplest form?
8/12
5/15
7/9
10/20
What is the sum of 1/2 and 1/3?
2/5
3/5
5/6
1/6
Which of the following is the decimal representation of 5/8?
0.4
0.625
0.5
0.75
What is the product of -3/4 and 2/5?
-3/10
6/20
-6/20
3/10
What is the quotient of 3/7 divided by 9/14?
6/7
2/3
7/18
7/9
Which of the following fractions is equivalent to 2/5?
4/10
3/7
5/2
3/5
What is the sum of -5/6 and 1/2?
-1/3
-1/6
-2/3
-1/2
Which of the following numbers is an irrational number?
3/7
0.75
√7
5
What is the sum of 1/2 and 2/3?
3/5
5/6
4/5
7/6
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

